Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. In this article, we will discuss the difference between NCAP and GCAP in automotive, its purpose, and the testing procedures.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
Also, read:
- Mercedes Benz And Daimler Trucks Interview Questions
- Adaptive Lighting Systems: How They Improve Road Safety
- How China Took Over The Global Car Industry In A Few Years
Automotive Engineers Must Know NCAP Vs GCAP
The automotive industry has witnessed remarkable advancements over the years, with safety becoming one of the most critical aspects of vehicle design and manufacturing. Vehicle safety programs like NCAP (New Car Assessment Program) and GCAP (Global Car Assessment Program) have played a significant role in shaping safety standards and promoting consumer awareness. While both initiatives aim to improve vehicle safety, their approaches, scopes, and impacts differ considerably. This guide provides a comprehensive comparison of NCAP and GCAP, shedding light on their unique features, methodologies, and contributions to global road safety.
What is NCAP?
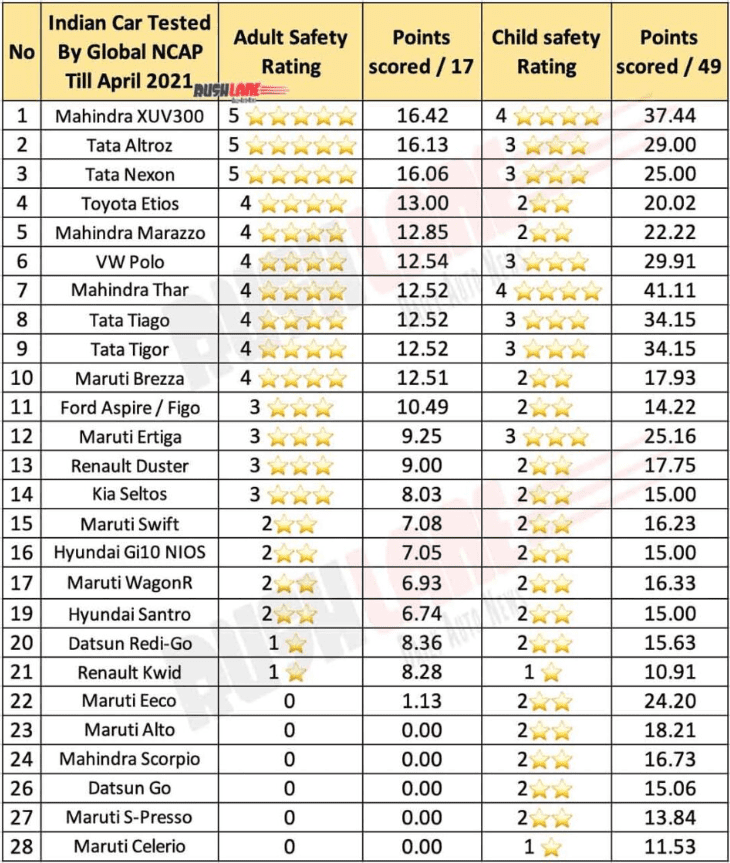
NCAP, or New Car Assessment Program, is a set of consumer-oriented vehicle safety rating programs designed to evaluate the safety performance of vehicles in various crash scenarios. Established in 1979 by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), NCAP was the first program of its kind. Over the years, several regional NCAPs have emerged, including Euro NCAP, ASEAN NCAP, Bharat NCAP, and others.

The primary objective of NCAP is to provide consumers with transparent and comparable information about vehicle safety so that they can make informed purchasing decisions. Each regional NCAP operates independently, tailoring its testing protocols to local conditions and regulatory frameworks.
Testing Procedures and Standards: NCAP tests typically involve:
- Frontal Impact Testing: Evaluates the vehicle’s ability to protect occupants during a head-on collision.
- Side Impact Testing: Measures protection against side collisions.
- Pedestrian Safety Tests: Assesses the risk of injury to pedestrians during an impact.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Evaluation: Includes technologies like automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assistance.
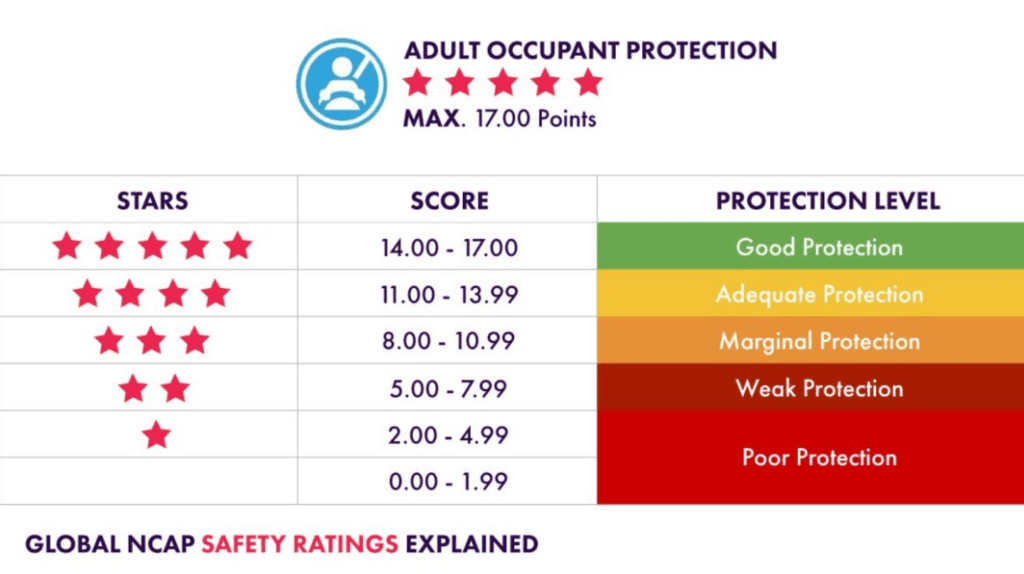
Scoring System and Star Ratings: Vehicles are assigned a star rating based on their performance in various tests, with higher ratings indicating better safety. Some NCAPs also incorporate bonus points for advanced safety technologies.
What is GCAP?
GCAP, or Global Car Assessment Program, is an international initiative aimed at promoting vehicle safety standards in low- and middle-income countries. Launched in 2011, GCAP collaborates with local governments, organizations, and stakeholders to improve safety awareness and testing capabilities in regions with limited regulatory frameworks.
Focus on Low- and Middle-Income Countries: GCAP’s mission is to reduce road fatalities by encouraging the adoption of minimum safety standards in vehicles sold in developing markets. It targets regions where safety regulations are often outdated or inadequately enforced.
Testing Approach and Collaboration: GCAP conducts crash tests similar to those of NCAP but emphasizes the importance of affordability and accessibility. It works closely with manufacturers to enhance vehicle safety without significantly increasing costs, ensuring that safer vehicles are accessible to all income groups.
Contribution to Global Vehicle Safety: Through advocacy, crash testing, and partnerships, GCAP has successfully elevated safety standards in several emerging markets. Its efforts have also led to the introduction of key safety features, such as airbags and anti-lock braking systems, in entry-level vehicles.
Key Differences Between NCAP and GCAP
| Aspect | NCAP | GCAP |
| Scope | Regional focus (e.g., Euro NCAP, ASEAN NCAP) | Global focus, especially on low-income regions |
| Testing Protocols | Comprehensive and advanced | Simplified to suit emerging markets |
| Target Audience | Consumers in developed markets | Consumers and policymakers in developing markets |
| Primary Goal | Provide detailed safety ratings for consumers | Improve safety standards in affordable vehicles |
| Impact on Market | Influences premium and mid-segment vehicles | Focuses on entry-level vehicles |
Testing Procedures
NCAP Testing Procedures:
- Frontal Impact Test: Simulates a collision at 64 km/h against a deformable barrier.
- Side Impact Test: Measures occupant protection during a side collision at 50 km/h.
- Pedestrian Safety Test: Evaluates the design of the front hood, bumper, and windshield for pedestrian safety.
- Child Safety Test: Assesses the effectiveness of child restraint systems.
- ADAS Evaluation: Includes features like lane departure warning, blind-spot detection, and adaptive cruise control.
GCAP Testing Procedures:
While GCAP follows similar procedures, its tests are simplified to accommodate vehicles designed for developing markets. For instance, frontal crash tests may be conducted at lower speeds to reflect real-world conditions in emerging markets.
Impact on Automotive Manufacturers
NCAP’s Influence:
- Encourages manufacturers to prioritize safety during vehicle design and development.
- Drives innovation in safety technologies, especially in premium and mid-segment vehicles.
- Creates a competitive market where high safety ratings become a selling point.
GCAP’s Role:
- Pushes manufacturers to include basic safety features, even in budget-friendly models.
- Facilitates collaboration with governments to implement regulatory changes.
- Promotes cost-effective safety solutions, ensuring affordability.
Consumer Perspective
NCAP Ratings: Consumers in developed regions rely heavily on NCAP ratings to select vehicles with superior safety features. High-rated vehicles often come equipped with cutting-edge technologies, providing enhanced protection for occupants and pedestrians.
GCAP’s Efforts: GCAP focuses on educating consumers in low- and middle-income countries about the importance of vehicle safety. Its campaigns highlight the risks of purchasing vehicles that lack basic safety features, fostering demand for safer models.
Challenges and Limitations
NCAP:
- Adapting to rapidly evolving technologies, such as autonomous driving.
- Ensuring consistent standards across different regional NCAPs.
GCAP:
- Balancing safety and affordability in cost-sensitive markets.
- Overcoming resistance from manufacturers reluctant to adopt higher safety standards.
- Limited resources for extensive crash testing and advocacy in some regions.
Future Trends
Integration with Autonomous Vehicles:
Both NCAP and GCAP are adapting their protocols to assess the safety of autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles, focusing on advanced driver assistance systems.
Focus on Electric Vehicles (EVs):
As EVs gain popularity, safety programs are developing specialized tests to address unique challenges, such as battery safety and fire risks.
Global Convergence of Standards:
Efforts are underway to harmonize safety standards across NCAP and GCAP, enabling consistent evaluation and comparison worldwide.
Use of Virtual Testing:
Advancements in simulation and virtual testing technologies are streamlining crash test procedures, reducing costs and time.
Conclusion
Both NCAP and GCAP have significantly contributed to improving vehicle safety and reducing road fatalities. While NCAP focuses on empowering consumers in developed regions, GCAP addresses the unique challenges of emerging markets. Together, these programs drive the automotive industry toward a safer and more inclusive future. By understanding their methodologies and impacts, consumers and stakeholders can make informed decisions, fostering a culture of safety and innovation.
This was about “Automotive Engineers Must Know NCAP Vs GCAP“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- “Mother of All Deals”: How The EU–India Free Trade Agreement Can Reshape India’s Economic Future
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 7 Ways EV Batteries Stay Safe From Thermal Runaway