Exploring Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): The Future Of Safe Driving
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will be exploring the advanced driver assistance systems in modern vehicle and it’s features.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
Also, read:
- Safety Standards For Battery Management (BMS) In Electric Vehicles
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- No Electric Vehicles For The Next 10 To 15 Years In India?
Exploring Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are a set of electronic systems in vehicles designed to assist drivers in various driving tasks. These systems enhance safety by reducing the likelihood of accidents and improving the overall driving experience. ADAS integrates sensors, cameras, radar, and software to monitor the vehicle’s environment and take preventive or corrective actions when necessary.
With increasing adoption in modern vehicles, ADAS is paving the way for semi-autonomous and autonomous driving, ensuring safer roads and a better driving experience. Below is a list of commonly implemented ADAS features, along with brief explanations.
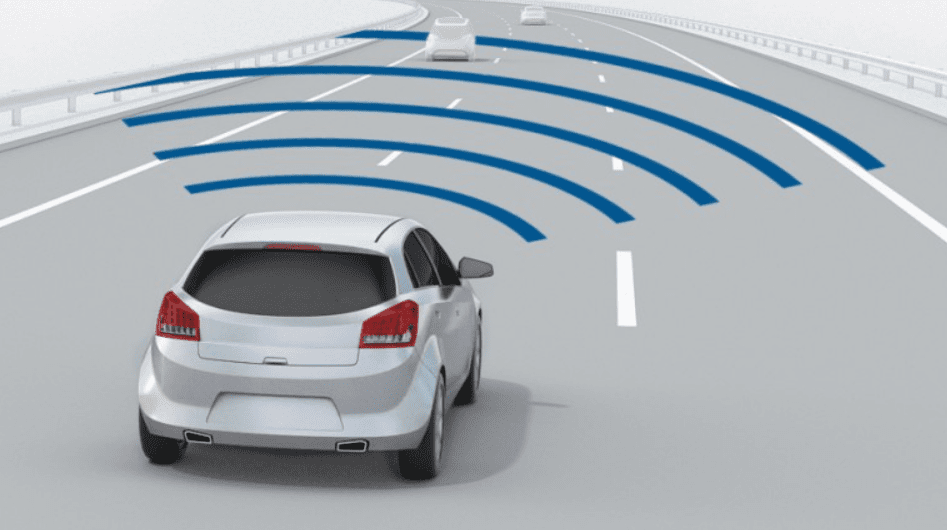
01. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
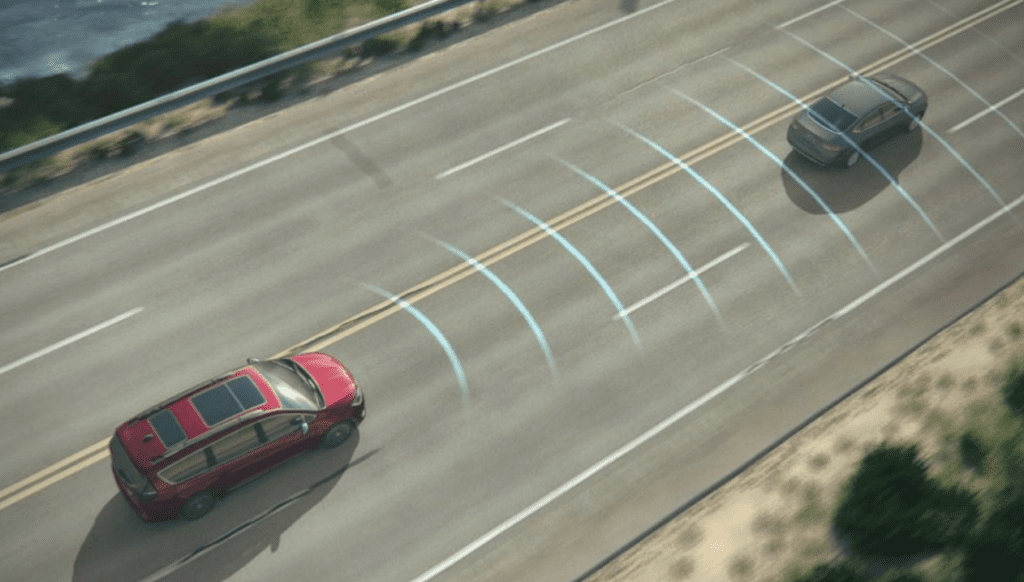
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is a sophisticated system that automatically adjusts the speed of your vehicle to maintain a safe distance from the car in front. Unlike traditional cruise control, ACC actively monitors the traffic using radar sensors and cameras to adapt to varying speeds. This feature is particularly useful for highway driving as it reduces the need for constant acceleration or braking. It significantly enhances comfort and minimizes driver fatigue during long trips. By maintaining a consistent speed, it also ensures better fuel efficiency.
- Adjusts speed automatically based on traffic flow.
- Uses radar and cameras to monitor vehicles ahead.
- Reduces the risk of rear-end collisions.
- Enhances driver comfort, especially on long journeys.
- Improves fuel efficiency by optimizing speed.
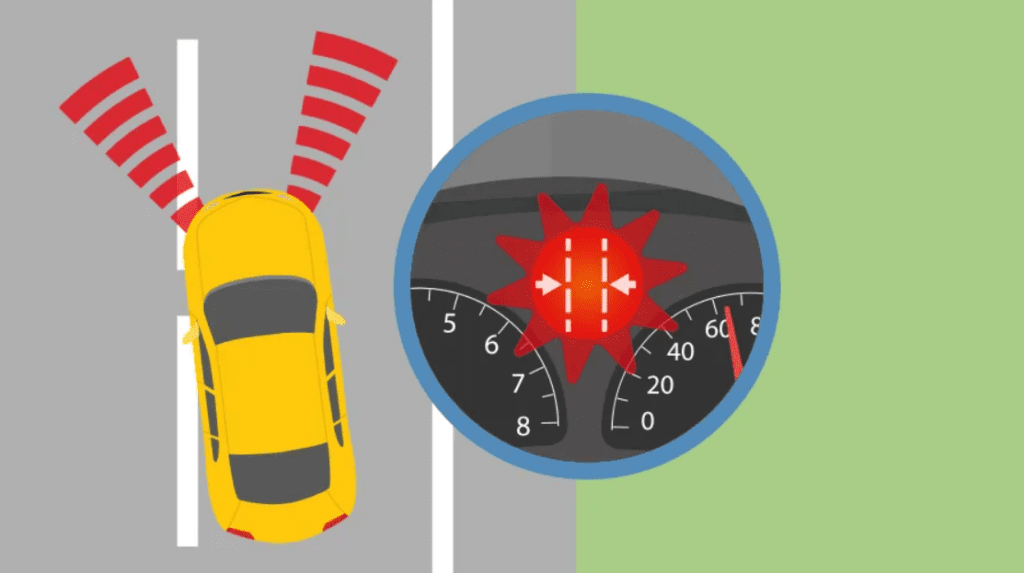
02. Lane Departure Warning (LDW)
Lane Departure Warning (LDW) is designed to alert drivers if they unintentionally drift out of their lane without signaling. This system utilizes cameras to track lane markings on the road and provides alerts through vibrations, sound, or visual warnings. It is especially effective in preventing accidents caused by distractions or drowsiness. By ensuring that the driver stays within the intended lane, LDW enhances safety on highways and during long-distance travel.
- Monitors lane markings for unintended drifting.
- Alerts drivers using sound, vibration, or visuals.
- Reduces risks caused by distractions or fatigue.
- Ideal for highways and long-distance drives.
- Encourages better lane discipline and awareness.
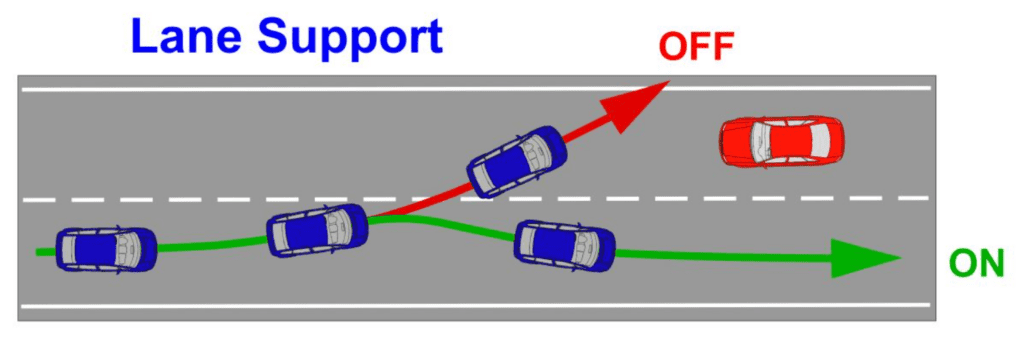
03. Lane Keep Assist (LKA)
Lane Keep Assist (LKA) goes a step further than LDW by not only alerting the driver but also actively correcting the vehicle’s position within the lane. This feature is particularly beneficial during long drives, as it provides gentle steering inputs to prevent unintentional drifting. LKA works in tandem with cameras that detect lane boundaries and ensure that the vehicle stays safely centered.
- Actively corrects unintentional lane drifts.
- Provides subtle steering adjustments for stability.
- Reduces side-swipe and lane departure risks.
- Works well with adaptive cruise control systems.
- Enhances safety during straight and curved road travel.
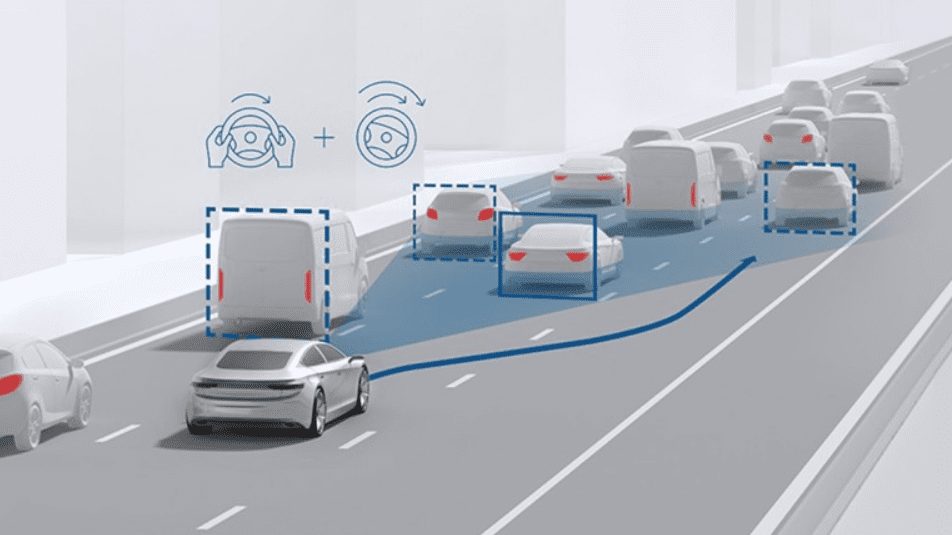
04. Traffic Jam Assist (TJA)
Traffic Jam Assist is a lifesaver in stop-and-go traffic situations. It combines Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Lane Keep Assist (LKA) to manage speed, braking, and steering automatically in congested conditions. By reducing the driver’s need to manually control the vehicle, TJA ensures a smoother and less stressful experience in urban traffic.
- Combines ACC and LKA for automatic control of traffic.
- Manages speed, braking, and steering in slow-moving scenarios.
- Reduces driver fatigue in stop-and-go situations.
- Enhances safety by maintaining proper distance and alignment.
- Promotes better fuel efficiency in urban traffic.
05. Highway Assist (HA)
Highway Assist integrates multiple ADAS features, including ACC and LKA, to provide semi-autonomous driving on highways. It ensures safe and efficient navigation by managing speed, lane centering, and collision avoidance. Ideal for long highway journeys, HA reduces driver workload and improves comfort.
- Combines ACC, LKA, and collision avoidance.
- Provides semi-autonomous highway driving capabilities.
- Reduces driver fatigue on extended trips.
- Improves safety through continuous monitoring.
- Enhances adaptability to road and traffic conditions.
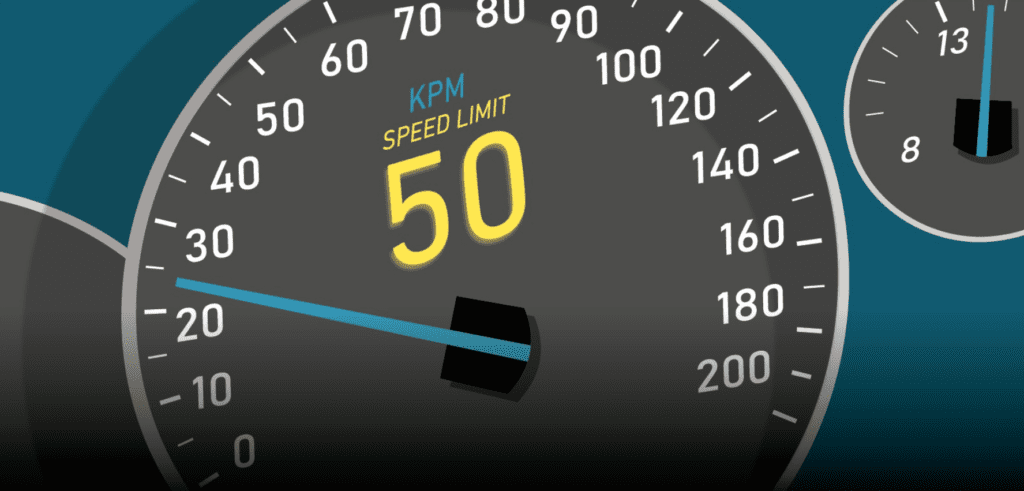
06. Speed Assist System (SAS)
The Speed Assist System (SAS) alerts the driver about speed limits and helps ensure compliance with traffic regulations. Using GPS data and camera-based traffic sign recognition, SAS detects speed limits and warns the driver if they exceed them. It enhances road safety by minimizing speeding-related risks and encourages better-driving behavior.
- Detects and displays speed limits using cameras and GPS.
- Alerts the driver if the vehicle exceeds speed limits.
- Reduces risks of speeding-related accidents.
- Promotes adherence to traffic laws.
- Enhances situational awareness in changing speed zones.
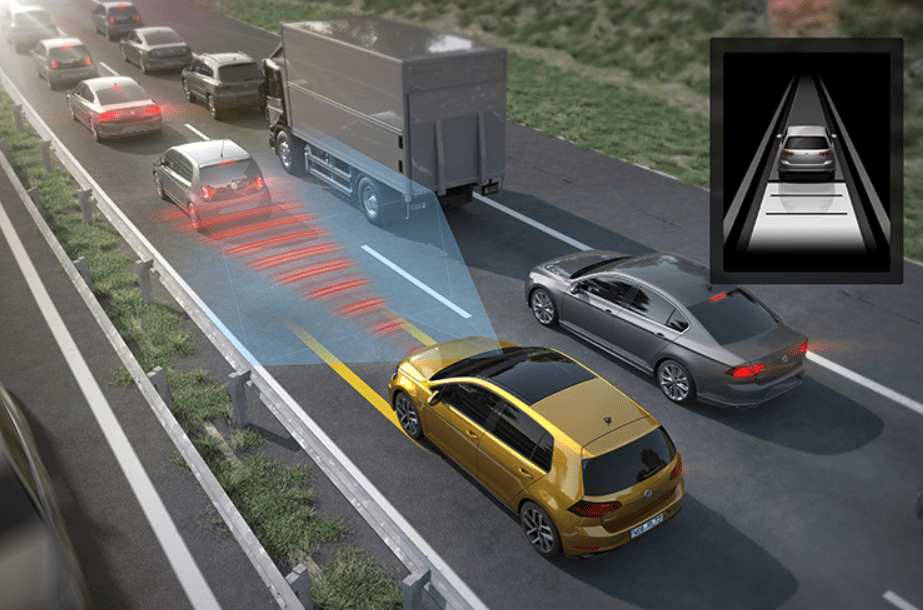
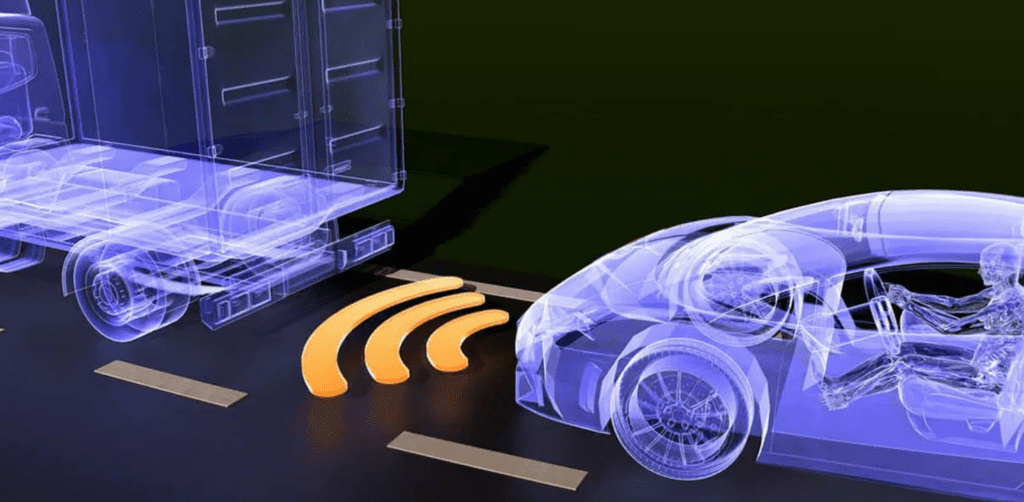
07. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) is a life-saving system that detects potential collisions and applies the brakes automatically to avoid or mitigate crashes. It uses sensors and cameras to monitor the road ahead and react faster than a human driver. AEB is highly effective in preventing rear-end collisions and reducing the severity of impacts.
- Monitors vehicles and obstacles in front of the car.
- Automatically applies brakes to prevent collisions.
- Reduces the risk of rear-end and low-speed crashes.
- Enhances safety in urban and highway driving.
- Works in conjunction with other safety systems like FCW.
08. Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA)
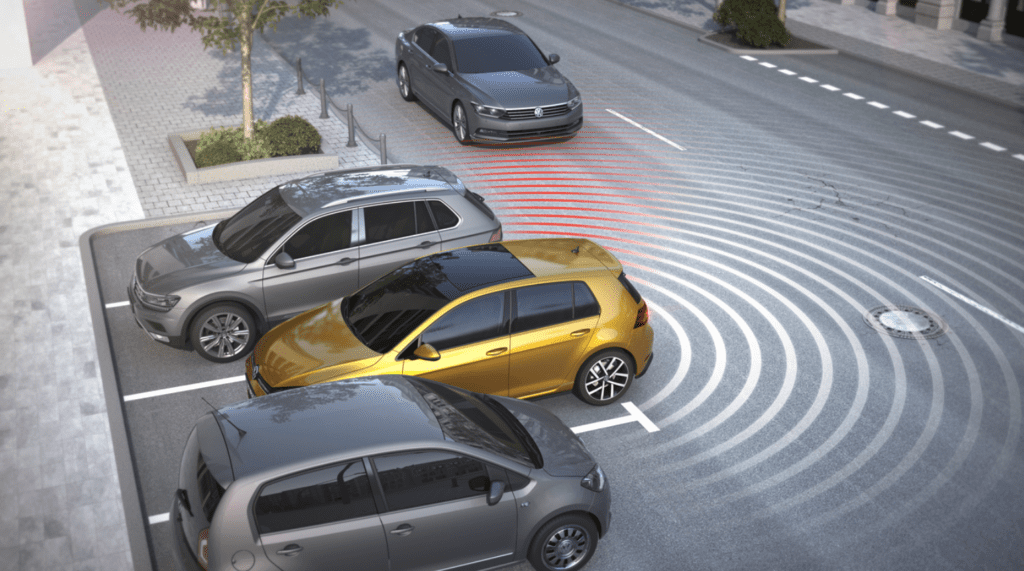
Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA) warns drivers about approaching vehicles while reversing, especially in crowded parking lots. Using radar sensors, it detects cross-traffic movement and provides audible or visual alerts to prevent accidents. RCTA makes reversing safer and more stress-free by improving situational awareness.
- Detects cross-traffic while reversing the vehicle.
- Alerts the driver with sound or visual cues.
- Reduces the risk of reversing-related collisions.
- Useful in tight parking spaces and busy streets.
- Enhances driver confidence during backing maneuvers.
09. Park Assist (PA)
Park Assist (PA) is an intelligent feature that helps drivers park effortlessly by managing steering while the driver controls acceleration and braking. It uses ultrasonic sensors to measure available parking spaces and guides the vehicle into parallel or perpendicular slots. PA simplifies parking in congested areas and minimizes the risks of scraping or bumping.
- Automatically controls steering for precise parking.
- Detects suitable parking spaces using sensors.
- Simplifies parallel and perpendicular parking.
- Reduces risks of damage while maneuvering.
- Ideal for tight or crowded parking spots.
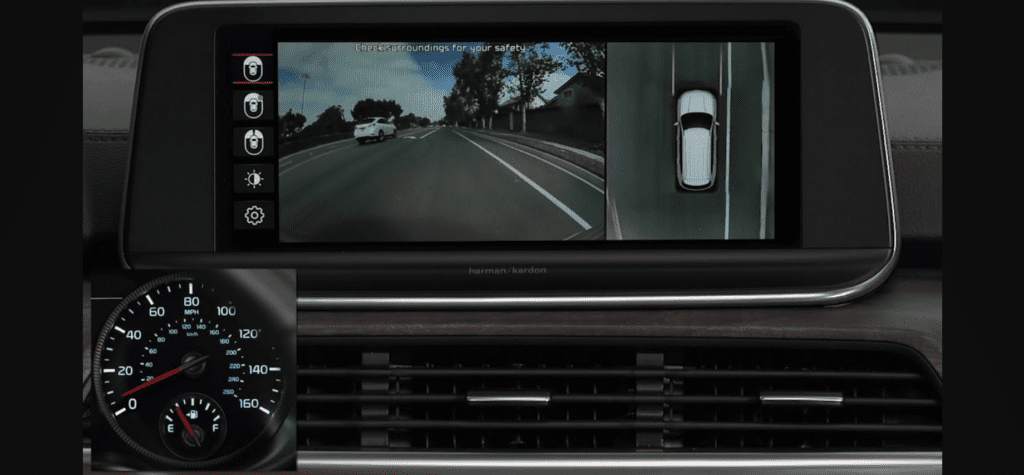
10. Surround View Monitor (SVM)
The Surround View Monitor (SVM) provides a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings, displayed on the dashboard screen. It uses cameras mounted around the car to stitch together a bird’s-eye view, making parking and tight maneuvers safer. SVM enhances spatial awareness and minimizes blind spots.
- Creates a 360-degree bird’s-eye view using cameras.
- Improves visibility around the vehicle.
- Reduces the risk of blind-spot-related collisions.
- Ideal for parking and tight driving situations.
- Enhances driver confidence in challenging scenarios.
11. Forward Collision Warning (FCW)
Forward Collision Warning (FCW) is a proactive safety feature that warns the driver about an imminent collision with a vehicle or obstacle ahead. It uses radar and camera systems to monitor the road and provides visual or audible alerts when a potential collision is detected. FCW gives drivers additional time to react, helping to prevent accidents or reduce their severity.
- Detects vehicles or obstacles in the path ahead.
- Warns the driver using visual and audible alerts.
- Provides critical reaction time to avoid collisions.
- Works effectively in both urban and highway environments.
- Complements other safety systems like AEB for improved protection.
12. Traction Control System (TCS)
Traction Control System (TCS) enhances vehicle stability by reducing wheel spin during acceleration, particularly on slippery or uneven surfaces. It uses sensors to monitor wheel speed and applies braking or reduces engine power to maintain grip. TCS is essential for improving safety in adverse weather conditions and challenging terrains.
- Monitors wheel speed to prevent slippage.
- Reduces engine power or applies braking to maintain traction.
- Improves stability on slippery surfaces like snow or rain.
- Enhances control during sudden acceleration.
- Promotes better handling in challenging driving conditions.
13. Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
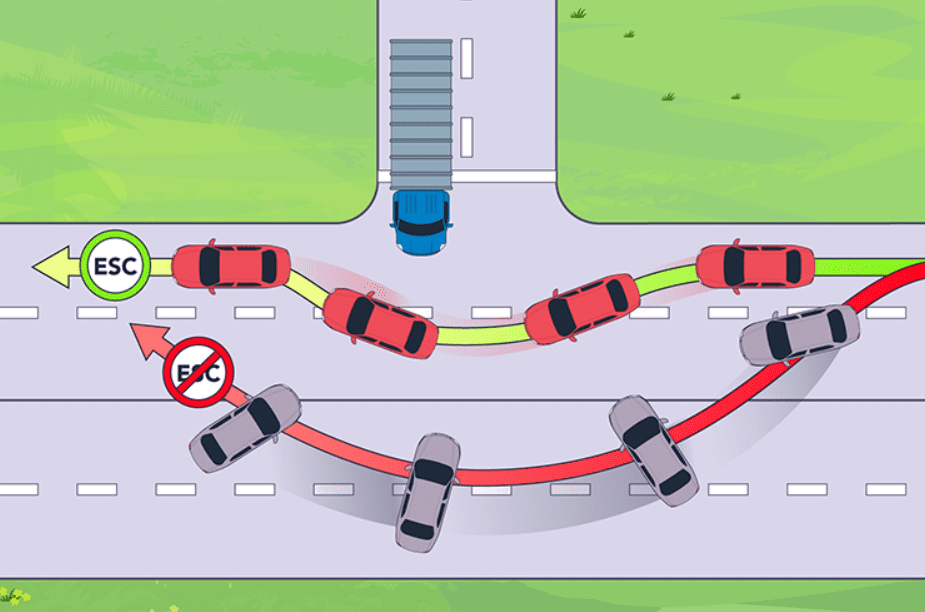
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) prevents skidding and improves vehicle stability by automatically applying brakes to individual wheels during a loss of traction. It works seamlessly with ABS and TCS to maintain control during sudden turns or emergency maneuvers. ESC is highly effective in reducing the risk of rollovers and side collisions.
- Detects and corrects loss of traction or oversteering.
- Applies brakes to individual wheels to maintain stability.
- Prevents rollovers and reduces skidding risks.
- Works with ABS and TCS for comprehensive control.
- Ideal for navigating sharp turns or slippery roads.
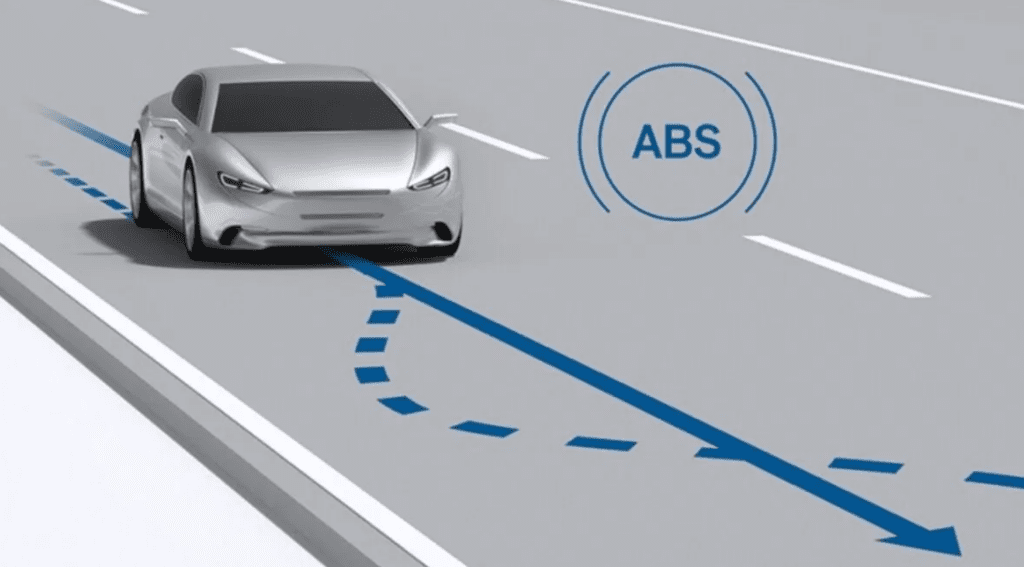
14. Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) prevents the wheels from locking during emergency braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. It uses sensors to detect wheel speed and modulates brake pressure to prevent skidding. ABS enhances vehicle safety by reducing stopping distances and ensuring directional control.
- Prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking.
- Maintains steering control even at emergency stops.
- Reduces stopping distance on slippery surfaces.
- Uses sensors to detect and adjust wheel speed.
- Improves overall braking efficiency and safety.
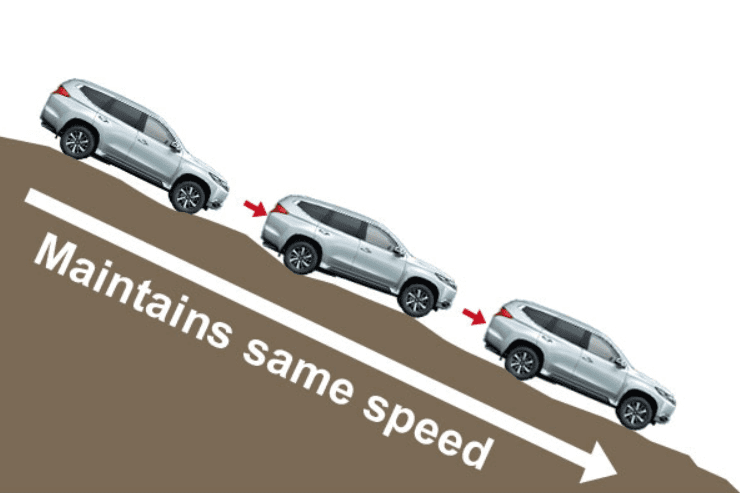
15. Hill Descent Control (HDC)
Hill Descent Control (HDC) assists drivers in maintaining a controlled speed while descending steep slopes. It uses the braking system to manage speed without requiring the driver to apply the brakes manually. HDC is particularly useful for off-road driving or steep terrain, ensuring safety and stability.
- Automatically manages speed on steep descents.
- Reduces the need for manual braking.
- Prevents skidding or loss of control on inclines.
- Ideal for off-road or mountainous terrains.
- Works seamlessly with ABS and traction control systems.
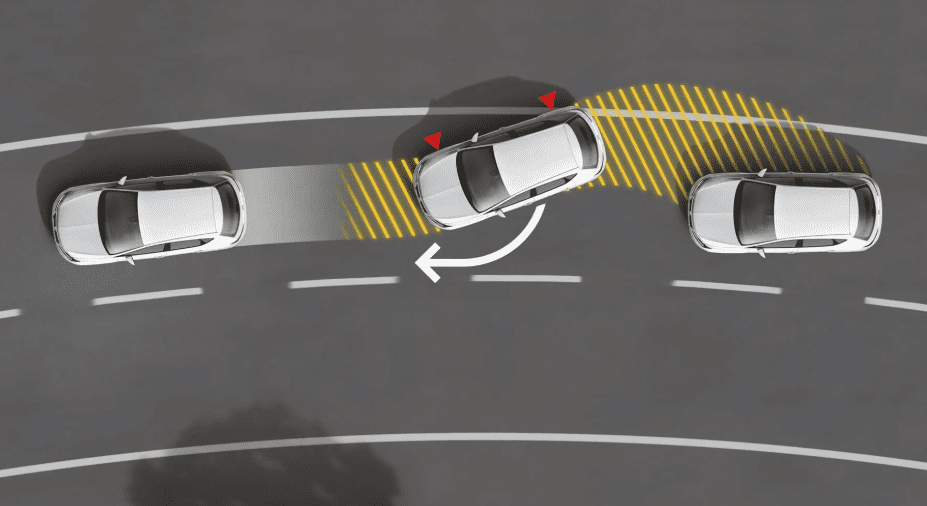
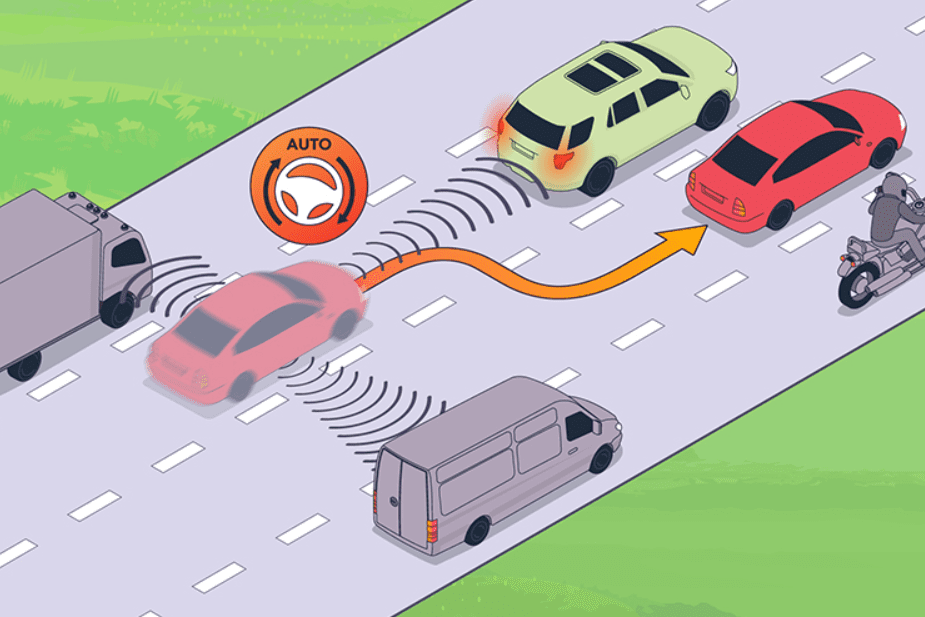
16. Autonomous Emergency Steering (AES)
Autonomous Emergency Steering (AES) is an advanced safety feature that actively assists the driver in steering the vehicle away from potential collisions. It uses sensors to detect obstacles and intervenes when braking alone may not avoid an accident. AES ensures precise, controlled maneuvers to prevent crashes, enhancing overall road safety.
- Detects obstacles requiring evasive action.
- Automatically steers to avoid collisions.
- Works when braking is insufficient to prevent accidents.
- Enhances safety during high-speed or emergency scenarios.
- Integrates with other ADAS features like FCW and AEB.
17. Adaptive Lighting System (ALS)
The Adaptive Lighting System (ALS) enhances visibility by adjusting the direction and range of headlights based on driving conditions. It detects vehicle speed, steering angle, and road curvature to direct light appropriately, ensuring optimal illumination. ALS improves safety during night driving, especially on winding roads or in poor weather.
- Adjusts headlight direction based on steering input and speed.
- Enhances visibility on curves and uneven terrain.
- Reduces glare for oncoming traffic.
- Improves safety during night driving or adverse conditions.
- Promotes a clear view of the road ahead.
18. Adaptive Lighting System (ALS)
Adaptive Lighting System (ALS) adjusts the headlight direction and intensity based on factors like steering angle, vehicle speed, and road conditions. It ensures optimal illumination during nighttime driving and bad weather, enhancing visibility on curves and uneven terrains. This system significantly improves road safety by reducing blind spots and preventing glare for oncoming traffic.
- Adjusts headlight direction based on steering input and speed.
- Enhances visibility on curves and during adverse weather.
- Reduces glare for oncoming vehicles.
- Improves driver confidence during night driving.
- Increases safety by minimizing blind spots.
This was about “Exploring Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 7 Ways EV Batteries Stay Safe From Thermal Runaway
- 8 Reasons Why EVs Can’t Fully Replace ICE Vehicles in India
- A Complete Guide To FlexRay Automotive Protocol
- Adaptive AUTOSAR Vs Classic AUTOSAR: Which One For Future Vehicles?