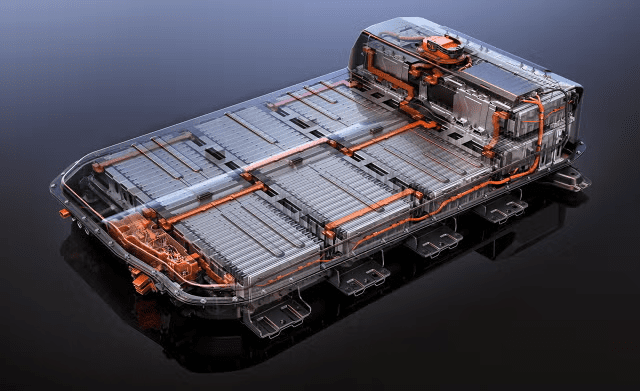
How Batteries In Electric Cars Are Installed And Protected From Faults
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss how batteries in electric cars are installed and protected from faults, and the types of challenges.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
Also, read:
- MathWorks Leads The Way In Scalable And Automated SDV Development
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- Types Of Vector Tools In Automotive Development
How Batteries In Electric Cars Are Installed And Protected
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the transportation industry with their eco-friendly and energy-efficient nature. At the core of every EV lies its battery, the most crucial and complex component of the vehicle. To ensure optimal performance, long life, and safety, the installation and protection of these batteries involve advanced engineering and meticulous design. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the processes involved in battery installation and the various strategies implemented to protect them from faults.
Understanding the Role of Batteries in Electric Cars
An EV battery serves as the vehicle’s power source, storing electrical energy and delivering it to the electric motor. Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that rely on gasoline or diesel, EVs use rechargeable batteries to power the motor, onboard electronics, and auxiliary systems. The performance, range, and efficiency of an EV depend significantly on the quality and management of its battery system.
Common battery types used in electric cars include:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and long lifespan, these are the most widely used batteries in modern EVs.
- Solid-State Batteries: An emerging technology offering improved safety and energy storage capabilities.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries: Although less common in EVs today, they are still used in some hybrid vehicles.
Given their critical role, the installation and protection of EV batteries are areas of intense focus for manufacturers.
How Electric Car Batteries Are Installed
Battery Pack Design
The first step in the installation process is the design of the battery pack. A battery pack is composed of multiple smaller units:
- Cells: These are the basic building blocks of the battery, categorized into cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells. Each type has unique advantages, such as compactness, efficiency, or flexibility in design.
- Modules: Cells are grouped into modules for easier handling and maintenance.
- Battery Pack: Modules are combined into a battery pack integrated into the EV chassis.
The battery pack also includes key components such as:
- Thermal Management Systems: Ensure temperature regulation through cooling or heating mechanisms.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Monitors and controls battery performance, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Casing: Provides physical protection from external impacts and environmental factors.
Installation Process
Pre-Assembly and Testing
Before installation, battery packs are manufactured and tested in controlled environments. Engineers perform extensive quality checks to ensure the cells, modules, and pack meet safety and performance standards. This includes:
- Voltage and current testing.
- Thermal performance evaluation.
- Mechanical stress tests.
Integration into the Chassis
Most modern EVs use a “skateboard” chassis design, where the battery pack is mounted under the floor. This layout offers several benefits:
- Space Optimization: Maximizes cabin and storage space.
- Lower Center of Gravity: Enhances vehicle stability and handling.
- Crash Protection: Positions the battery pack within the vehicle’s structural safety zones.
The battery pack is securely bolted to the chassis and connected to the vehicle’s electrical systems. High-voltage connections are carefully insulated to prevent electrical hazards.
Sealing and Waterproofing
After installation, the battery pack is sealed to protect against dust, water, and other contaminants. Most EV batteries comply with IP67 or IP68 standards, which ensure resistance to water immersion and dust ingress.
How Batteries Are Protected from Faults

Thermal Protection
One of the most significant challenges for EV batteries is managing heat. Excessive heat can lead to thermal runaway, a dangerous chain reaction that can cause fires or explosions. To prevent this, manufacturers employ advanced thermal management systems:
- Liquid Cooling Systems: Circulate coolant around the cells to maintain optimal temperature.
- Air Cooling Systems: Use fans to dissipate heat, often seen in less energy-intensive EVs.
- Phase-Change Materials: Absorb and release heat as the battery temperature fluctuates.
These systems ensure that the battery operates within its safe temperature range, even under heavy loads or extreme environmental conditions.
Electrical Protection
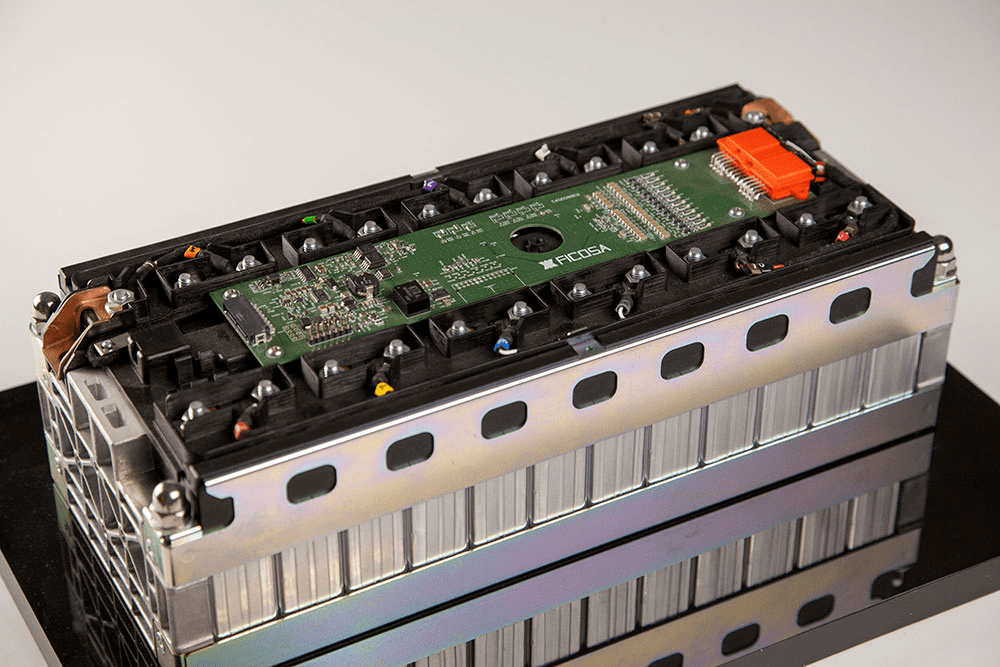
Electrical faults such as overcharging, short circuits, or imbalanced cells can significantly impact battery performance and safety. To address these issues, EV batteries are equipped with:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Continuously monitor the state of charge (SoC), state of health (SoH), and temperature of each cell. The BMS also balances the charge across cells to prevent overcharging or deep discharging.
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Protect against overcurrent and short circuits by interrupting the electrical flow when faults are detected.
- Isolation Monitors: Detect faults in the insulation between high-voltage and low-voltage systems, preventing potential electric shocks.
Mechanical Protection
To safeguard against physical damage, EV batteries are designed with robust mechanical protection features:
- Crash-Resistant Casings: Reinforced structures that absorb impact forces during accidents.
- Vibration Dampers: Reduce the effects of road vibrations on the battery pack.
- Waterproof and Dustproof Sealing: Protect the battery from environmental factors, ensuring long-term durability.
Fire and Explosion Prevention
Fire and explosion risks are minimized through multiple safety measures:
- Fire-Resistant Materials: Non-flammable coatings and barriers between cells prevent thermal propagation.
- Gas Venting Systems: Allow gases generated during thermal events to escape safely, reducing explosion risks.
Software-Based Protections
Software plays a critical role in battery safety. Real-time monitoring systems analyze data from sensors within the battery pack, allowing for early detection of potential issues. Predictive maintenance algorithms help identify and resolve faults before they escalate. Additionally, EVs have built-in safety protocols that shut down the battery system in the event of a critical fault.
Challenges and Future Innovations
While current technologies have significantly improved battery safety and efficiency, challenges remain:
- Weight and Space Optimization: Balancing battery capacity with size and weight.
- Cost: Advanced safety features increase manufacturing costs.
- Environmental Durability: Ensuring performance in extreme temperatures and conditions.
Looking ahead, several innovations promise to enhance battery technology further:
- Solid-State Batteries: These use solid electrolytes, offering improved safety and higher energy density.
- AI-Driven BMS: Machine learning algorithms for smarter fault prediction and management.
- Self-Healing Materials: Batteries that repair internal damage, extending lifespan.
- Wireless Charging: Batteries designed for efficient and safe wireless power transfer.
Conclusion
The installation and protection of batteries in electric cars involve a combination of advanced engineering, innovative design, and stringent safety measures. From their integration into the vehicle chassis to the sophisticated systems safeguarding against faults, every step is meticulously planned to ensure reliability, performance, and safety.
As the EV industry continues to grow, ongoing advancements in battery technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation. With innovations such as solid-state batteries and AI-powered monitoring systems on the horizon, electric vehicles are poised to become safer, more efficient, and more sustainable than ever before.
This was about “How Batteries In Electric Cars Are Installed And Protected From Faults“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- Electronic Control Unit, ECU Flashing Process
- Guide On Writing Testcases For HiL Testing
- Everything You Need To Know About Sensor Fusion For Autonomous Driving
- System Pause, Driver Resume: The Art of Reclaiming Control
- Types Of Errors Found In MiL, SiL, And HiL Testing
- Automotive Ethernet: The Future Of In-Vehicle Communication
- Goodbye Drunk Driving: The Road towards Safety
- Top 100 Advanced Level ADAS Interview Questions With Answers