Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. In this article, I will discuss the difference between fault tree analysis (FTA) and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) with some real-world examples.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
- On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) – A Complete Tutorial
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vs Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) Vs Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): Which Is Better?
- CAPL Scripting Tutorial For Automotive Engineers
Difference Between Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Both Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) are widely used techniques in risk assessment, safety engineering, and reliability analysis. They help in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential failures in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, healthcare, and manufacturing.
While both methods serve the purpose of risk assessment, they differ in their approach, scope, and application. Let’s explore these differences in detail with real-world examples to understand how they work in practice.
What is Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)?
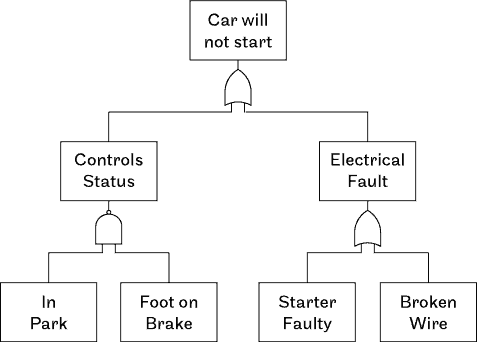
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a deductive (top-down) approach that starts with a specific failure (Top Event) and works backward to determine possible causes. It uses a fault tree diagram consisting of logic gates (AND, OR, NOT) to analyze different failure paths leading to the main event.
Key Features of FTA
✔ Starts with a single failure event and traces backward to identify its causes.
✔ Uses Boolean logic (AND/OR gates) to represent dependencies.
✔ Helps in quantifying failure probabilities.
✔ Used in safety-critical systems where preventing catastrophic failures is essential.
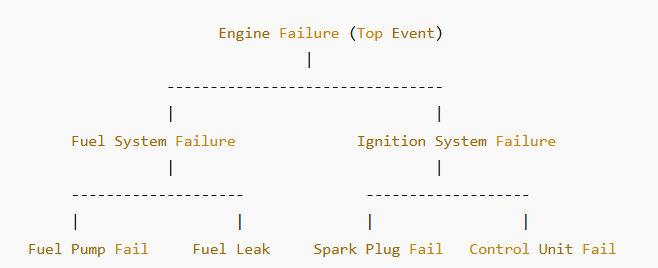
Example 1: Fault Tree Analysis of an Aircraft Engine Failure
Imagine an aircraft engine failure during flight. Engineers use FTA to determine all possible reasons for this failure.
Analysis
- The top event (engine failure) could be caused by fuel system failure or ignition system failure.
- Fuel System Failure could be due to a failed fuel pump or a fuel leak.
- Ignition System Failure could result from a faulty spark plug or a malfunctioning control unit.
- Boolean logic is applied: If any of the failures occur, the system may fail.
✅ Outcome:
- Engineers can use probability analysis to determine which failure is most likely.
- Actions can be taken to improve fuel pump reliability, use redundant ignition controls, or better insulate fuel lines.
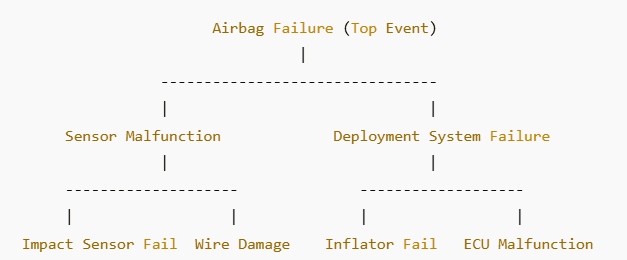
Example 2: Fault Tree Analysis of a Car Airbag Failure
In an automobile, airbags must deploy in case of a crash. If they fail to deploy, FTA can be used to find the root causes.
✅ Outcome: By analyzing the fault tree, manufacturers can take corrective actions such as:
- Enhancing impact sensor reliability
- Using stronger wiring harnesses
- Adding redundancies in airbag deployment mechanisms
What is Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)?
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is an inductive (bottom-up) approach that focuses on identifying all possible failure modes of individual components and assessing their impact on the overall system.
Key Features of FMEA
✔ Starts at the component level and works upward to analyze effects on the system.
✔ Uses Risk Priority Number (RPN) to prioritize failures based on Severity (S), Occurrence (O), and Detection (D).
✔ Helps in preventing failures by designing out high-risk failure modes.
✔ Used in design improvement, reliability engineering, and manufacturing.
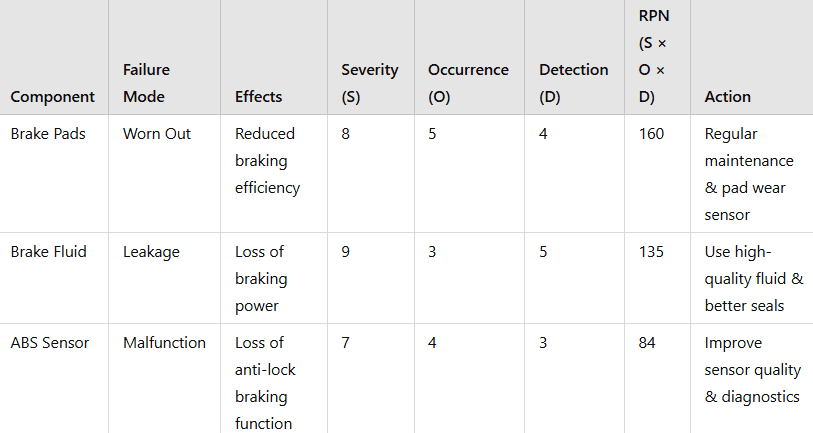
Example 1: FMEA of a Car Braking System
A car’s braking system is crucial for safety, Engineers use FMEA to analyze potential failures and their effects.
✅ Outcome:
- Brake fluid leakage has a high severity rating (9), making it a priority for immediate improvement.
- Engineers may decide to use high-quality seals, implement better quality control, and design real-time leak detection sensors.
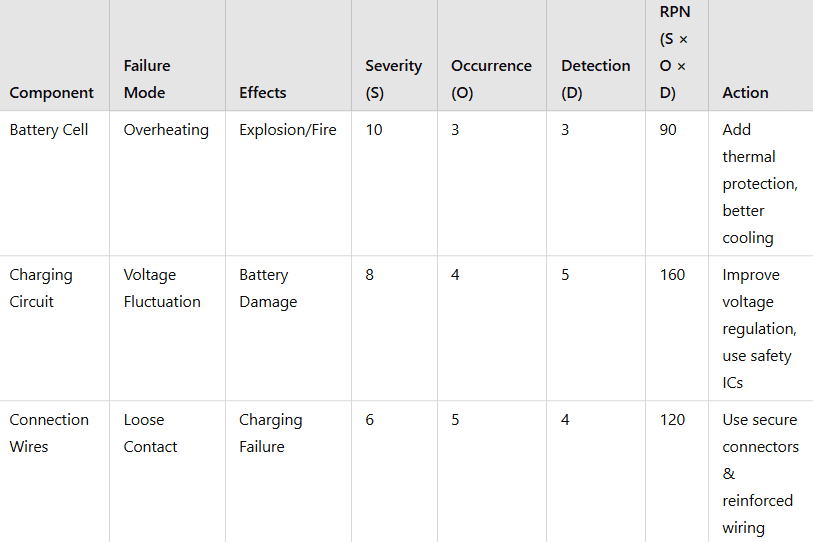
Example 2: FMEA of a Smartphone Battery
A smartphone battery must operate safely and efficiently. Engineers analyze failure modes to prevent overheating, explosions, and reduced performance.
✅ Outcome:
- Charging circuit failure has the highest RPN (160), meaning it poses the greatest risk.
- Engineers improve battery protection circuits, add fail-safes, and design better charging ICs to reduce failures.
FTA vs. FMEA: Key Differences
| Feature | Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) | Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) |
| Approach | Deductive (Top-Down) – Starts with a failure and finds causes | Inductive (Bottom-Up) – Identifies potential failure modes and their effects |
| Focus | Investigates a single major failure event | Analyzes all possible failure modes |
| Representation | Logic diagram (Fault Tree) with AND/OR gates | Table format with risk scoring |
| Risk Quantification | Uses probability analysis | Uses Risk Priority Number (RPN) |
| Use Cases | Safety-critical failures (Aircraft crashes, Car brake failure, Nuclear plant failures) | Product design & process improvement (Car manufacturing, Electronics, Medical devices) |
Conclusion
Both FTA and FMEA play crucial roles in risk management and system reliability.
- FTA is best used for analyzing catastrophic failures by identifying their root causes.
- FMEA is best used for preventing failures by identifying potential failure modes and prioritizing risks.
For a comprehensive risk analysis, many industries use both together—FMEA helps in early design improvements, while FTA ensures no critical failure is left unchecked. ?
This was about “Difference Between Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) – With Detailed Examples”. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- FlexRay Protocol – Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Top 50 AI-Based Projects for Electronics Engineers
- UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services) — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Automotive Ethernet — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Controller Area Network (CAN) — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Top 30 High-Paying Embedded Tools You Must Learn in 2026
- Automotive Resource For Free On GitHub
- When Technology Fails: How a Trapped EV Crash Changed Car Safety in China