Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss the difference between LIN, CAN, MOST, and FlexRay in applications, physical layer, data rate, message transmission, etc.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Top Quiz Questions On Networking Asked During Online Test
- What Is Inter-Process Communication In Operating System, Purpose
- Top Best MTech Branches For Electronics & Communication Engineers
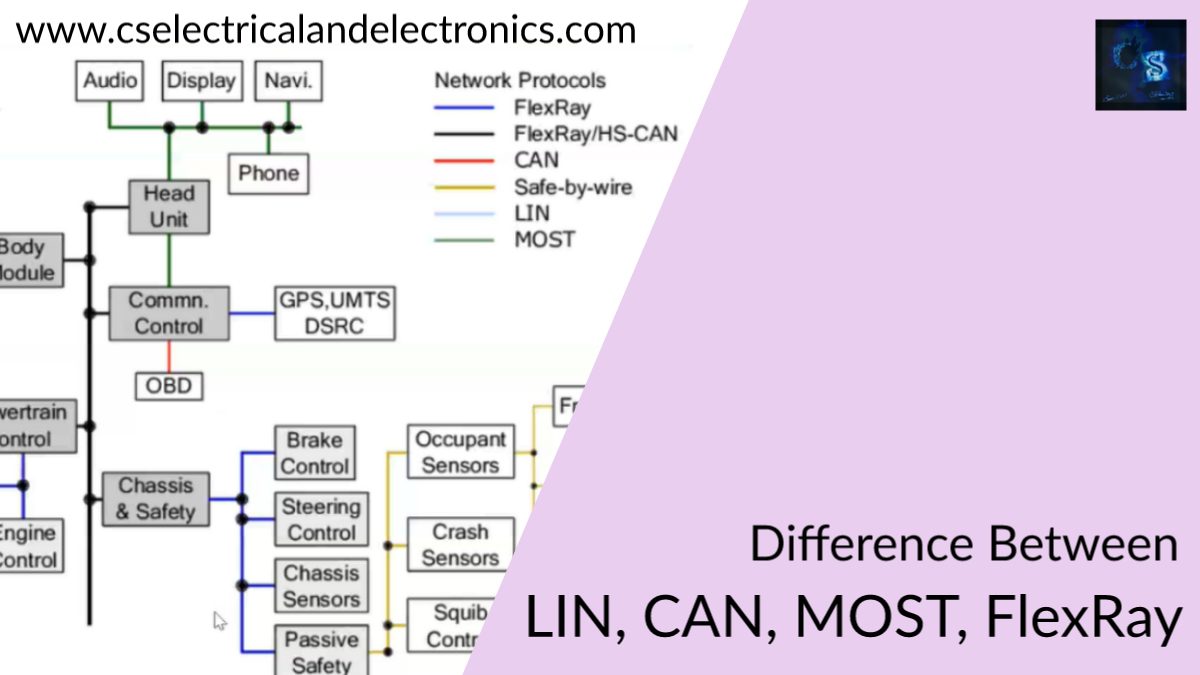
Difference Between LIN, CAN, MOST, FlexRay
- LIN stands for Local Interconnect Network
- CAN stands for Controller Area Network
- MOST stands for Media Oriented System Transport
- FlexRay
01. Application
- The LIN protocol is used in a low-level communication system. It may be used to make a connection between sensors and controllers. For example: In the body of the vehicle.
- CAN is used in soft real-time systems. For example: In engines, power trains, chassis, battery management systems, etc.
- FlexRay is used in a hard real-time system. For example: In power trains, chassis.
- MOST are used in media-related applications and control in automotive. For example: In multimedia, telematics, etc.
02. Architecture
- LIN has a single master and typically 2 to 10 slaves.
- CAN has a multi-master and typically 10 to 40 nodes.
- FlexRay has a multi-master and up to 64 nodes.
- MOST also have multi-master and up to 64 nodes.
03. Bus Access
Bus it is a communication system that is responsible for data transfer.
- LIN has polling bus access
- CAN has CSMA/CA bus access
- FlexRay has TDMA/FTDMA bus access
- MOST have TDM CSMA/CS bus access
04. Topology
Topology means it is an arrangement made to connect devices.
- LIN has a bus topology
- CAN also have bus topology
- FlexRay has BUS/Star topology
- MOST have a ring/star topology
05. Message Transmission
- In LIN, message transmission is synchronous.
- In CAN, message transmission is asynchronous.
- In FlexRay, message transmission is synchronous and asynchronous.
- In MOST also, message transmission is synchronous and asynchronous.
06. Data Rate
- In LIN, the data rate is 20 Kbps.
- In CAN, the data rate is 1 Mbps.
- In FlexRay, the data rate is 10 Mbps.
- In MOST, the data rate is 24 Mbps.
07. Data Bytes Per Second
- In LIN, the data bytes per second is 0 to 8.
- In CAN, the data bytes per second is 0 to 8.
- In FlexRay, the data bytes per second is 0 to 254.
- In MOST, the data bytes per second is 0 to 60.
08. Physical Layer
- An electrical single wire is used in the LIN protocol.
- The electrical dual wire is used in CAN protocol.
- Dual wire – optical or electrical wire is used in FlexRay.
- The optical fiber cable is used in MOST.
These are the difference between LIN, CAN, FlexRay, and MOST. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 100+ Indian Startups & What They Are Building
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting