How China Took Over The Global Car Industry In A Few Years
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss how China took over the global car industry in a few years and what will be the future of the Automotive Industry in the upcoming days.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
Also, read:
- Difference Between HiL, SiL, MiL In Automotive
- Exploring Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): The Future Of Safe Driving
- Safety Standards For Battery Management (BMS) In Electric Vehicle
How China Took Over The Global Car Industry
In the past few decades, China has emerged as a formidable force in numerous industries, but perhaps none as surprising as the automotive sector. From a country once associated with low-cost manufacturing and copycat designs, China has transformed into a global leader in the car industry, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) segment. This article delves into the factors behind China’s meteoric rise, the strategies it employed, and the implications for the global automotive landscape.
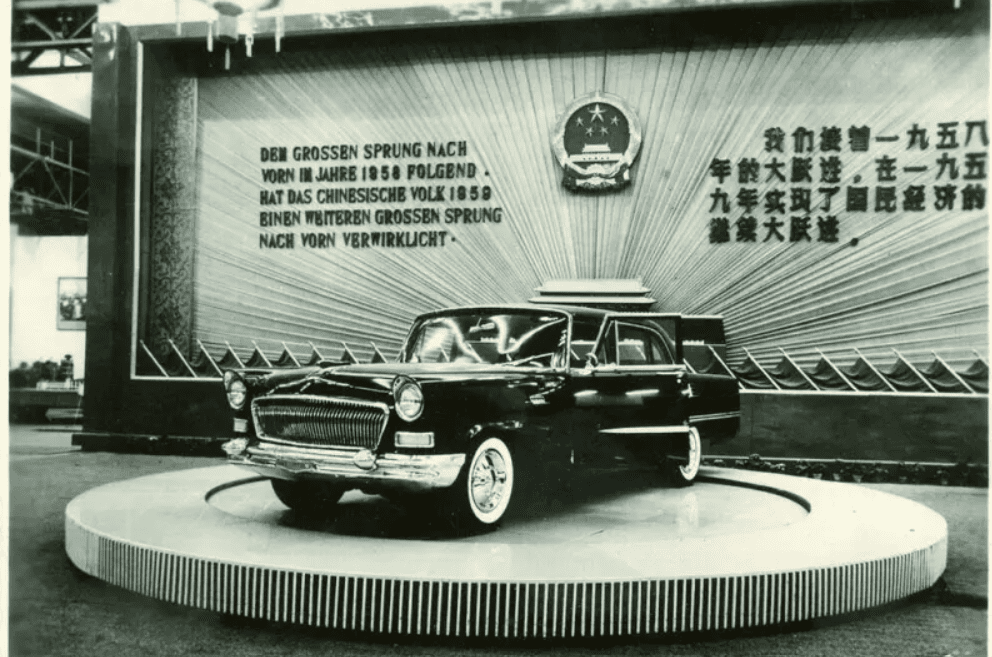
The Early Days of China’s Automotive Industry
China’s automotive journey began in the mid-20th century, with state-owned enterprises producing basic vehicles primarily for domestic use. The industry remained relatively stagnant for decades, overshadowed by global giants from the United States, Europe, and Japan. However, the turn of the 21st century marked the beginning of a new chapter. China began opening its market to foreign automakers, forming joint ventures with companies like Volkswagen, General Motors, and Toyota. These partnerships brought advanced technology and expertise to China, laying the groundwork for the nation’s automotive aspirations.
The EV Revolution: A Turning Point
One of the most significant factors in China’s rise to automotive prominence is its early and aggressive adoption of electric vehicles. Recognizing the potential of EVs to reduce pollution and decrease reliance on imported oil, the Chinese government made a strategic decision to prioritize this segment. The following initiatives played a crucial role:
Government Subsidies and Incentives: The Chinese government poured billions of dollars into subsidies for EV manufacturers and buyers. This financial support made EVs more affordable for consumers and provided a safety net for manufacturers to innovate and scale production.
Stringent Emission Standards: To combat urban air pollution, China implemented strict emission regulations, forcing automakers to either comply or shift to cleaner technologies. Many foreign manufacturers found it challenging to meet these standards, giving local EV producers a competitive edge.
Infrastructure Development: China invested heavily in building a robust EV infrastructure, including charging stations and battery-swapping facilities. By the end of 2023, China accounted for nearly half of the world’s EV charging points.
Technological Advancements: Chinese companies like CATL and BYD became leaders in battery technology, significantly reducing the cost of EV batteries while improving their efficiency and lifespan.
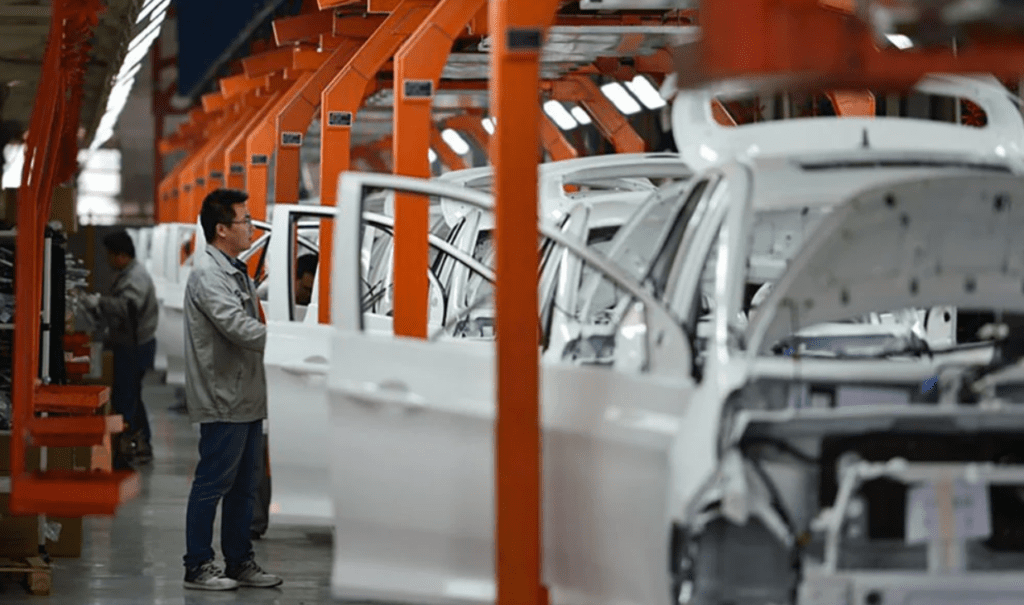
Dominating the EV Market
China’s focus on electric vehicles has paid off spectacularly. Today, it is the world’s largest EV market, with over 50% of global EV sales occurring in the country. Leading Chinese brands such as BYD, Nio, and Xpeng have gained international recognition for their high-quality, affordable, and technologically advanced vehicles.
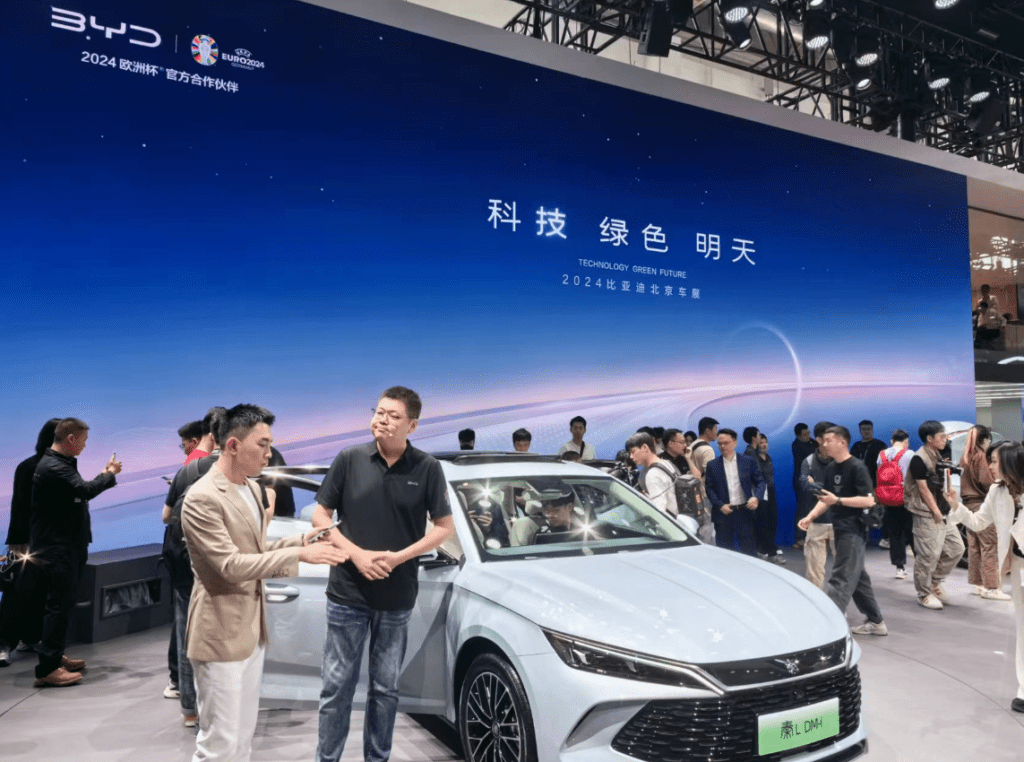
BYD: The Game Changer
BYD (“Build Your Dreams”) has emerged as a pioneer in the EV space. Backed by investments from Warren Buffett, the company transitioned from manufacturing batteries to producing some of the most popular electric cars in the world. Its innovative Blade Battery technology, which offers superior safety and performance, has set a new standard in the industry.
Nio: The Luxury EV Challenger
Positioning itself as a premium EV brand, Nio has gained a loyal following both in China and abroad. The company’s unique battery-swapping technology and customer-centric services, such as mobile charging vans, have differentiated it from competitors.
Xpeng: The Tech-Driven Innovator
Xpeng focuses heavily on integrating cutting-edge technology, including autonomous driving systems and smart features. The company’s models often compete directly with Tesla, offering similar capabilities at a more affordable price.
Leveraging Domestic Resources
China’s dominance in the EV market is not just about innovation and government support. The country also controls a significant portion of the global supply chain for EV components, particularly batteries. China is the world’s largest producer of lithium-ion batteries, a critical component for electric vehicles. It also has significant control over the mining and processing of key materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
By securing these resources, China has insulated itself from supply chain disruptions and gained a strategic advantage over competitors. This control has also allowed Chinese manufacturers to keep production costs low, making their vehicles more competitive globally.
Expanding Globally
Once firmly established in the domestic market, Chinese automakers turned their attention to international expansion. Brands like BYD and Great Wall Motors have entered markets in Europe, Southeast Asia, and South America, offering high-quality vehicles at competitive prices.
Entry into Europe
Europe, with its stringent emission standards and growing EV market, has been a prime target for Chinese automakers. Companies like MG (owned by China’s SAIC Motor) and BYD have launched models that cater to European tastes, often undercutting local brands on price without compromising on quality.
African and South American Markets
In developing markets, Chinese automakers have leveraged their cost advantage to dominate. Affordable models with modern features have made Chinese cars a popular choice in countries where price sensitivity is high.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Chinese automakers have embraced technology as a core differentiator. From autonomous driving capabilities to smart infotainment systems, Chinese vehicles often come equipped with features that rival those of premium brands. Companies like Huawei have also entered the automotive space, contributing their expertise in 5G and artificial intelligence to create smarter, more connected vehicles.
Moreover, the rise of “New Energy Vehicles” (NEVs), which include hybrids and hydrogen-powered cars, has further cemented China’s leadership. With significant investments in R&D, Chinese firms are at the forefront of developing alternative energy solutions for the automotive sector.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its impressive progress, China’s automotive industry faces several challenges:
- Quality Perception: While Chinese cars have improved significantly, some international consumers still view them as inferior to Western or Japanese brands.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Trade wars and geopolitical tensions have created barriers for Chinese automakers in certain markets, particularly the United States.
- Competition: As traditional automakers ramp up their EV offerings, Chinese brands will face stiffer competition both domestically and internationally.
- Overcapacity: China’s aggressive push for EV production has led to concerns about overcapacity, with some manufacturers struggling to sell their vehicles.
The Future of China’s Automotive Industry

The future looks bright for China’s automotive sector. The country’s “Made in China 2025” initiative aims to make it a global leader in high-tech industries, including automotive. With continuous investments in R&D, a strong focus on sustainability, and a growing presence in international markets, China is well-positioned to maintain its dominance.
Moreover, the rise of autonomous vehicles presents another opportunity for China to lead. Companies like Baidu and Pony.ai are already testing self-driving cars, and the government has created favorable regulations to accelerate their deployment.
Implications for the Global Market
China’s rise in the automotive industry has significant implications for global players:
- Increased Competition: Traditional automakers will need to innovate and adapt to compete with Chinese brands, particularly in the EV space.
- Supply Chain Dependence: Many global manufacturers rely on Chinese batteries and components, making them vulnerable to supply chain disruptions.
- Market Shifts: As Chinese automakers expand globally, they are reshaping consumer preferences and driving down prices, benefiting consumers but challenging competitors.
Conclusion
China’s rapid ascent in the global car industry is a testament to its strategic vision, technological prowess, and relentless drive for innovation. By focusing on electric vehicles, controlling critical resources, and leveraging government support, China has not only become the world’s largest automotive market but also a dominant force on the global stage. While challenges remain, the country’s influence on the future of mobility is undeniable. The question is no longer whether China can compete but how the rest of the world will adapt to its leadership in the automotive industry.
This was about “How China Took Over The Global Car Industry In A Few Years“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- RTOS In The Automotive Industry: The Brains Behind Real-Time Vehicle Control
- High Performance Computers in Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs): Architecture, Challenges, and Future Trends
- Automotive HPC Wars: The Race To Power Software-Defined Vehicles
- Why The Automotive Industry Is Down: No Automotive Jobs and When Will It Become Normal Again?
- Lane Departure Warning Systems: Your Guardian on the Road
- In-Depth Guide To UDS Service 0x19 – ReadDTCInformation
- Testing Techniques For Test Case Writing in the Automotive Domain
- Different Storage Classes In MATLAB Simulink