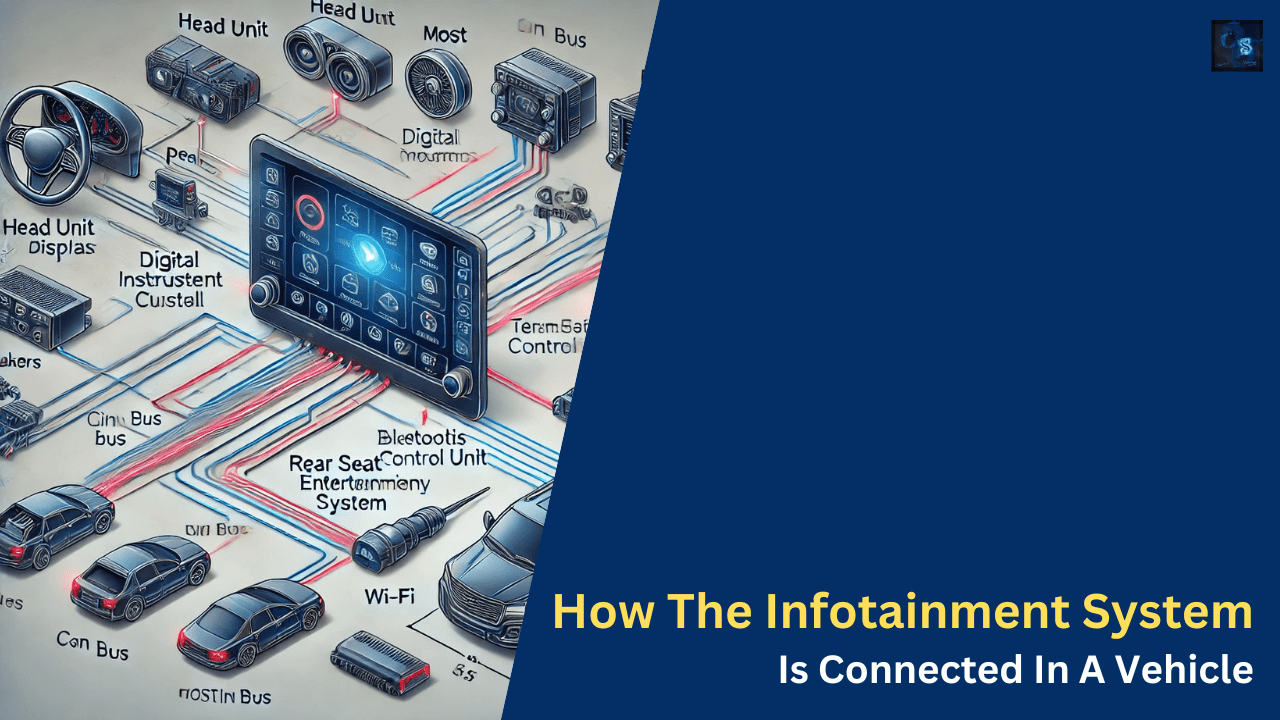
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. In this article, I will discuss how the infotainment system is connected in a vehicle, its components, and communication networks in infotainment systems.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
- Top ECU Testing Tools: A Complete Guide To Automotive Validation & Simulation
- Model Verification Methods For Simulink: Ensuring Compliance & Quality
- How Service-Oriented Communication (SoA) Enhances ECU Interoperability
How The Infotainment System Is Connected In A Vehicle
Modern vehicles are equipped with advanced infotainment systems that provide entertainment, navigation, communication, and vehicle diagnostics. These systems integrate multiple components and communicate with various electronic control units (ECUs) to enhance the driving experience. In this article, we will explore how infotainment systems are connected within a vehicle, including hardware, communication protocols, and future trends.
Components of an Infotainment System
A typical vehicle’s infotainment system consists of the following components:

- Head Unit (HU) – The central control panel that interfaces with users via a touchscreen, buttons, or voice commands.
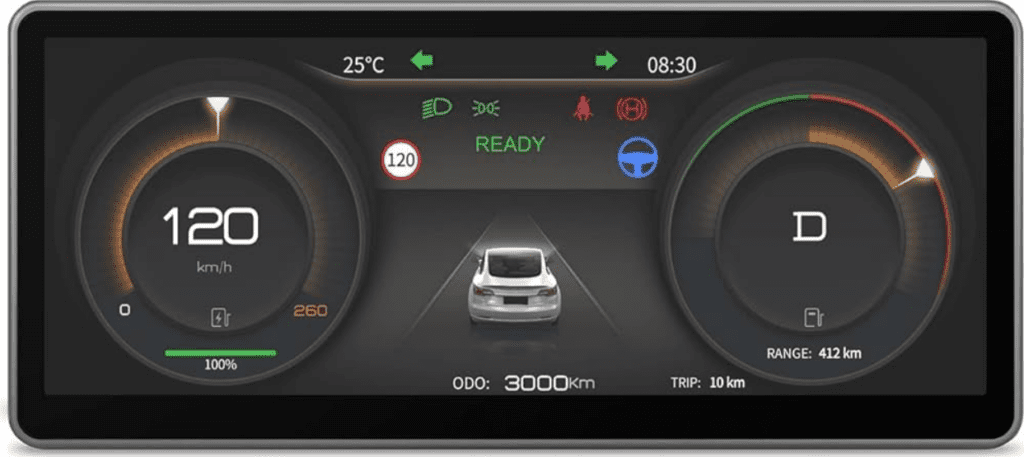
- Digital Instrument Cluster – Displays vehicle information such as speed, fuel level, and navigation data.
- Audio System – Includes speakers, amplifiers, and digital sound processors for audio output.
- Navigation System – Uses GPS and mapping software to provide turn-by-turn directions.
- Telematics Control Unit (TCU) – Manages vehicle connectivity, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth communication.
- Rear Seat Entertainment (RSE) System – Provides screens and controls for rear passengers.
- Cameras and Sensors – Used for parking assistance, driver monitoring, and augmented reality displays.
- Microcontrollers and System-on-Chip (SoC) – Process information from various sources and run infotainment applications.
Communication Networks in Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems communicate with different vehicle components using several wired and wireless communication protocols:
01. Controller Area Network (CAN Bus)
- A widely used protocol that enables communication between ECUs in a vehicle.
- Used for functions such as volume control via steering wheel buttons and speed-sensitive volume adjustments.
02. Media Oriented Systems Transport (MOST)
- A high-speed multimedia network transmits audio, video, and data between infotainment components.
- Reduces wiring complexity while ensuring high-quality media streaming.
03. Ethernet (Automotive Ethernet)
- Supports high-speed data transfer (up to 1 Gbps) for infotainment, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
- Used for streaming HD video, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and cloud connectivity.
04. Local Interconnect Network (LIN Bus)
- A low-speed network is mainly used for simple communication between the infotainment system and auxiliary devices such as climate control and lighting.
05. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
- Enables wireless connectivity for smartphones, hands-free calling, and streaming audio.
- Allows integration with Android Auto, Apple CarPlay, and other mobile-based infotainment services.
06. FlexRay
- Used in high-performance vehicles to provide deterministic, fault-tolerant communication between critical infotainment components.
07. 5G and Cellular Networks
- Provides internet access for real-time navigation, vehicle tracking, and remote diagnostics.
- Enables cloud-based infotainment services and streaming applications.
Connectivity Between Infotainment System and Other Vehicle Components
01. Integration with Vehicle Electronics
- The infotainment system connects to the vehicle’s body control module (BCM) to manage interior lighting and climate settings.
- Connects with the powertrain control module (PCM) for performance-related data visualization.
02. Integration with ADAS
- Infotainment systems receive inputs from ADAS components such as cameras and radar sensors to display safety alerts.
- Supports features like blind-spot monitoring, collision warning, and lane departure alerts.
03. Smartphone Connectivity
- Uses USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi to sync with smartphones for hands-free operation and app integration.
- Supports voice assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa for hands-free commands.
04. Cloud and IoT Connectivity
- Over-the-air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to update software and fix security vulnerabilities remotely.
- Cloud services enable features like predictive maintenance, location-based services, and personalized user settings.
Future Trends in Vehicle Infotainment Connectivity
01. AI-Powered Infotainment Systems
- AI-driven voice assistants will enhance interaction between the driver and the infotainment system.
- Machine learning algorithms will predict user preferences and automate routine tasks.
02. Augmented Reality (AR) Displays
- AR heads-up displays (HUDs) will project navigation information and real-time road data onto the windshield.
- Enhanced user interfaces will provide interactive control over vehicle functions.
03. Edge Computing in Vehicles
- Reduces latency by processing infotainment data within the vehicle rather than relying on cloud computing.
- Improves response times for applications such as speech recognition and ADAS alerts.
04. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
- Infotainment systems will integrate with smart infrastructure to provide real-time traffic updates and hazard warnings.
- Supports vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P) communication for enhanced safety.
Conclusion
The infotainment system is a critical part of modern vehicles, integrating multiple components through wired and wireless networks. With advancements in AI, connectivity, and cloud computing, future infotainment systems will offer an even more immersive and intelligent driving experience. As automotive technology evolves, infotainment connectivity will play a vital role in enhancing safety, entertainment, and convenience for drivers and passengers.
This was about “How The Infotainment System Is Connected In A Vehicle“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- “Mother of All Deals”: How The EU–India Free Trade Agreement Can Reshape India’s Economic Future
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 7 Ways EV Batteries Stay Safe From Thermal Runaway