How V2X Communication is Transforming Connected Vehicle Technology
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, I will discuss how V2X communication is transforming connected vehicle technology and key applications of V2X technology.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
- Comparing Embedded Coder, Simulink Coder, And MATLAB Coder In Automotive Applications
- Every Automotive Engineer Must Have Expertise In These Domains
- Essential Tools For Embedded System Development And Testing
V2X Communication is Transforming Connected Vehicle Technology
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication is revolutionizing the automotive industry by enabling vehicles to communicate with their surroundings. This technology enhances safety, efficiency, and traffic management, paving the way for smarter and more connected transportation systems. With advancements in 5G, artificial intelligence, and edge computing, V2X is becoming a critical component of modern vehicle technology.
Understanding V2X Communication
V2X is an umbrella term that encompasses multiple communication paradigms, including:
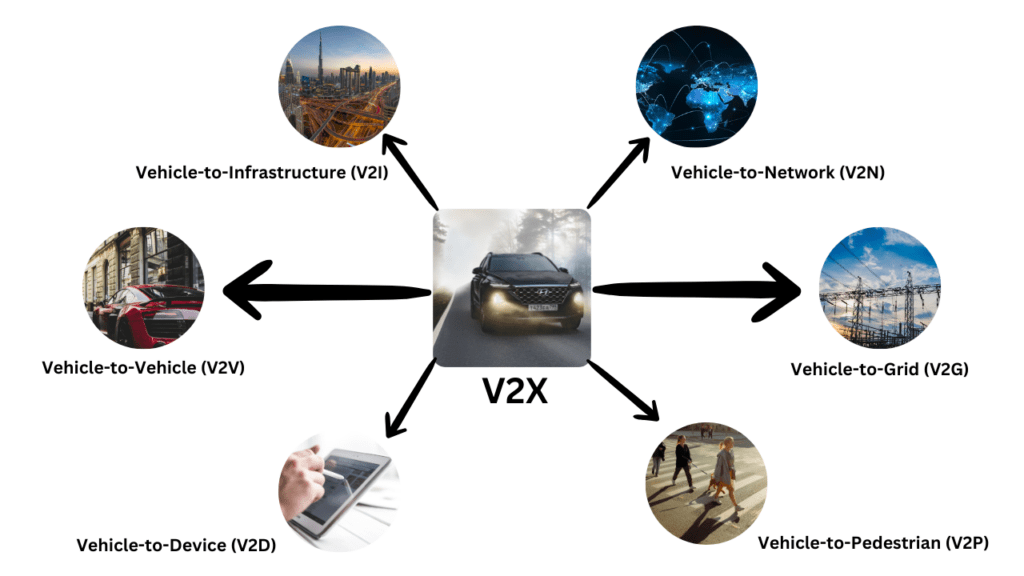
01. Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V):
This involves direct communication between vehicles, enabling them to share real-time data on speed, direction, and road conditions. By exchanging this information, vehicles can anticipate potential collisions and take preventive measures. For example, if a car ahead suddenly applies its brakes, the following vehicle receives an instant alert, reducing the risk of accidents. V2V communication is crucial for autonomous driving systems, as it allows vehicles to coordinate maneuvers such as lane changes and emergency stops without human intervention.
Furthermore, V2V communication enhances traffic efficiency by enabling cooperative driving strategies. Vehicles can synchronize their speeds to maintain smooth traffic flow, reducing congestion and fuel consumption. This technology is especially beneficial in highway scenarios where platooning—groups of vehicles traveling closely together—can improve aerodynamics and lower energy usage. By creating a seamless network of connected cars, V2V communication is paving the way for safer and more efficient transportation.
02. Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I):
V2I communication facilitates interaction between vehicles and roadside infrastructure, such as traffic lights, road signs, and toll booths. This enables traffic management systems to optimize signal timings, reduce congestion, and enhance road safety. For example, a smart traffic light can adjust its cycle based on real-time traffic data, minimizing delays and improving traffic flow.
In addition to traffic optimization, V2I communication supports predictive maintenance and road condition monitoring. Sensors embedded in road infrastructure can detect issues like potholes or icy conditions and relay this information to approaching vehicles. This proactive approach not only prevents accidents but also aids city planners in maintaining infrastructure effectively. By integrating V2I with smart city initiatives, urban mobility can be transformed into a highly efficient and safe ecosystem.
03. Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P):
This mode of communication connects vehicles with pedestrians and cyclists using mobile devices, wearable technology, and smart crosswalks. V2P technology enhances safety by alerting drivers and pedestrians to potential collisions, especially in urban areas with heavy foot traffic. For example, a pedestrian carrying a smartphone with V2P capabilities can send a signal to nearby vehicles, ensuring drivers are aware of their presence even in blind spots.
Additionally, V2P communication plays a crucial role in protecting vulnerable road users, such as children and elderly pedestrians. Smart crosswalks equipped with sensors can detect movement and trigger alerts to oncoming vehicles, reducing the risk of accidents. As urban environments become more connected, V2P technology will be instrumental in creating safer interactions between vehicles and non-motorized road users.
04. Vehicle-to-Network (V2N):
V2N connectivity allows vehicles to interact with cloud-based networks for real-time data processing, navigation, and infotainment services. This connectivity ensures that drivers receive up-to-date traffic updates, weather conditions, and hazard warnings, improving decision-making on the road. For instance, V2N-enabled vehicles can receive advance warnings about road closures or construction zones, allowing drivers to reroute efficiently.
Beyond safety and navigation, V2N enhances the in-car experience by enabling seamless infotainment and over-the-air software updates. Passengers can stream high-quality content, while automakers can push remote software patches to enhance vehicle performance. The integration of V2N with artificial intelligence and big data analytics will further refine personalized driving experiences, making connected vehicles smarter and more responsive to user needs.
05. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G):
V2G technology enables bidirectional energy transfer between electric vehicles (EVs) and the power grid. EVs can store excess electricity during off-peak hours and return it to the grid during peak demand, stabilizing energy distribution. This reduces reliance on conventional power plants and promotes the use of renewable energy sources.
In addition to supporting grid resilience, V2G technology benefits EV owners by providing financial incentives for energy sharing. Smart charging stations can optimize charging schedules based on real-time electricity prices, reducing costs for consumers. As the adoption of EVs increases, V2G communication will play a critical role in enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability.
06. Vehicle-to-Device (V2D):
V2D communication enables vehicles to interact with personal devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology. This connectivity allows drivers to control vehicle functions remotely, such as starting the engine, adjusting climate settings, or locking/unlocking doors.
Moreover, V2D enhances driver convenience by integrating personal assistants and navigation apps directly into the vehicle’s infotainment system. Voice-activated controls and AI-powered recommendations improve the overall driving experience. As automotive technology continues to advance, V2D communication will further personalize vehicle interactions and improve user engagement.
The Role of 5G in V2X Communication
The deployment of 5G networks is a game-changer for V2X communication due to its ultra-low latency and high bandwidth. Benefits of 5G in V2X include:
- Faster data transmission, reducing reaction times for collision avoidance.
- Enhanced support for autonomous vehicle functions.
- Greater network reliability, ensuring seamless communication between vehicles and infrastructure.
Key Applications of V2X Technology
01. Collision Avoidance and Traffic Safety
- Vehicles can exchange real-time information to prevent accidents.
- Emergency braking alerts can be shared between vehicles.
- Detection of pedestrians in blind spots enhances road safety.
02. Autonomous Driving Support
- V2X facilitates better decision-making for self-driving cars.
- Autonomous vehicles can predict traffic flow and adjust routes accordingly.
- Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC) enhances vehicle coordination.
03. Smart Traffic Management
- V2I enables real-time traffic monitoring and signal optimization.
- Dynamic rerouting helps in reducing congestion and improving fuel efficiency.
- Emergency vehicles receive priority signals to reach destinations faster.
04. Enhanced Infotainment and Navigation
- V2N allows real-time updates on road conditions, weather, and hazards.
- Passengers benefit from seamless streaming services and cloud-based applications.
- Over-the-air software updates ensure vehicles remain up to date.
05. Fleet Management and Logistics
- V2X improves vehicle tracking and fleet coordination.
- Fuel consumption optimization and predictive maintenance enhance efficiency.
- Smart delivery systems ensure real-time package tracking and autonomous deliveries.
Challenges in V2X Implementation
Despite its potential, V2X communication faces several challenges:
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Ensuring encrypted and tamper-proof communication is critical to preventing cyber threats.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading road infrastructure to support V2X technology requires significant investment.
- Standardization Issues: Different regions use varied V2X communication protocols (DSRC vs. C-V2X), hindering global adoption.
- High Deployment Costs: Integrating V2X technology into vehicles and infrastructure requires financial resources and regulatory approval.
Future of V2X Communication
The future of V2X is promising, with continuous advancements in AI, edge computing, and sensor technology. Key trends shaping V2X include:
- Integration with Smart Cities: V2X will play a crucial role in developing interconnected urban mobility solutions.
- Advancements in AI and Machine Learning: AI-driven predictive analytics will enhance traffic forecasting and vehicle coordination.
- Expansion of 5G and Beyond: Future wireless networks (6G) will further enhance V2X capabilities, reducing latency and improving reliability.
- Collaboration Between Automakers and Tech Companies: Partnerships between automotive manufacturers, telecom providers, and government bodies will drive widespread V2X adoption.
Conclusion
V2X communication is transforming connected vehicle technology by enhancing safety, efficiency, and automation. With the rapid evolution of 5G, AI, and smart infrastructure, V2X is set to redefine the future of transportation, making roads safer and more intelligent. As challenges are addressed and technology advances, V2X will become a cornerstone of next-generation mobility solutions, shaping the future of autonomous and connected vehicles.
This was about “How V2X Communication is Transforming Connected Vehicle Technology“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 7 Ways EV Batteries Stay Safe From Thermal Runaway
- 8 Reasons Why EVs Can’t Fully Replace ICE Vehicles in India
- A Complete Guide To FlexRay Automotive Protocol
- Adaptive AUTOSAR Vs Classic AUTOSAR: Which One For Future Vehicles?
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): How To Become An Expert In This Growing Field