Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss ISO 21434 cybersecurity standards for road vehicles, its structure & clauses, and ISO 21343 implementation steps.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
- Why Is C Or C++ Better Than Python For Embedded Systems?
- 7 Ways EV Batteries Stay Safe From Thermal Runaway
- Ensuring Tire Safety With Advanced Technologies
ISO 21434: Road Vehicles – Cybersecurity Engineering
ISO 21434 is an international standard that defines cybersecurity processes for the automotive industry. It ensures that electronic and software-based systems in vehicles are protected against cyber threats.
Why is ISO 21434 Important?
- Modern vehicles are highly connected, making them vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
- Ensures regulatory compliance (especially with UNECE WP.29 regulations).
- Reduces cyber risks in vehicle development, production, and operation.
- Protects passenger safety and vehicle functionality.
Key Concepts of ISO 21434
- Cybersecurity Risk Management – Identifying, assessing, and mitigating security risks in vehicles.
- Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) – A structured approach to evaluating cyber threats.
- Security-by-Design – Integrating cybersecurity into the vehicle development lifecycle.
- Incident Response – Procedures for handling security breaches in vehicles.
- End-to-End Cybersecurity – Extends from the concept phase to the decommissioning of vehicles.
ISO 21434 Structure & Clauses
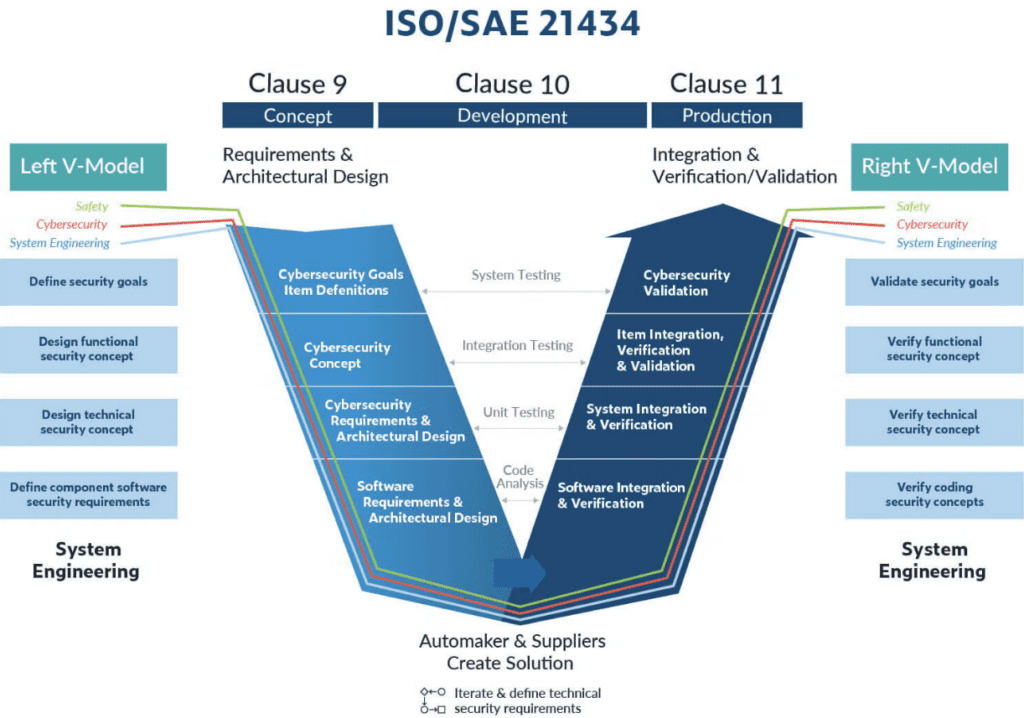
ISO 21434 consists of 13 clauses, each defining different cybersecurity aspects:
01. Scope
- Defines the applicability of ISO 21434 for road vehicles and cybersecurity engineering.
- Covers all lifecycle phases: Concept, Development, Production, Operations, and Decommissioning.
02. Normative References
- Lists related to standards like ISO 26262 (Functional Safety), ISO/SAE 21434, and UNECE WP.29 R155.
03. Terms & Definitions
- Defines key cybersecurity terms such as Asset, Threat, Vulnerability, Risk, Attack Path, Security Controls, etc.
04. General Considerations
- Introduces cybersecurity principles.
- Ensures alignment with corporate cybersecurity policies.
05. Organizational Cybersecurity Management
- Establishes cybersecurity policies, governance, and roles.
- Requires competency and awareness training for employees.
06. Project-dependent Cybersecurity Management
- Defines cybersecurity planning at the project level.
- Includes roles & responsibilities, communication plans, and cybersecurity goals.
07. Risk Assessment Methods
Defines the Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) methodology.
Key steps:
- Identify assets (ECUs, sensors, software, etc.).
- Determine threat scenarios.
- Assess attack feasibility.
- Evaluate potential impact.
- Define risk treatment measures.
08. Concept Phase
- Establishes Cybersecurity Goals based on TARA.
- Defines the cybersecurity concept and key security functions.
09. Product Development
- Integrates security requirements into software and hardware.
- Implements security mechanisms like firewalls, encryption, IDS/IPS, secure boot, etc..
- Verification & Validation of cybersecurity measures.
10. Cybersecurity Validation
- Ensures security measures are properly tested.
- Conducts penetration testing, fuzz testing, and functional security validation.
11. Production
- Defines secure manufacturing processes.
- Ensures no vulnerabilities are introduced during production.
12. Operations & Maintenance
- Covers OTA (Over-the-Air) updates, security monitoring, and patch management.
- Implements incident response strategies.
13. Decommissioning
- Defines secure disposal of vehicle components and data.
Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) in ISO 21434
TARA is a key risk assessment methodology used in ISO 21434. It consists of:
- Asset Identification – Identify critical assets (e.g., ECUs, communication modules).
- Threat Identification – Identify potential cybersecurity threats.
- Attack Feasibility Analysis – Assess how likely an attack is to succeed.
- Impact Analysis – Evaluate the consequences of a successful attack.
- Risk Treatment – Implement risk mitigation strategies.
ISO 21434 Implementation Steps

Step 1: Establish Cybersecurity Policy
- Define company-wide cybersecurity policies.
- Assign roles & responsibilities.
Step 2: Perform Threat Analysis (TARA)
- Identify threats, vulnerabilities, and risks.
- Perform risk assessment and mitigation planning.
Step 3: Implement Security-by-Design
- Integrate cybersecurity controls into ECU/software development.
- Use encryption, authentication, and secure boot mechanisms.
Step 4: Conduct Cybersecurity Testing
- Perform penetration testing, fuzz testing, and risk validation.
Step 5: Establish Incident Response
- Develop an incident response and recovery plan.
- Ensure continuous monitoring of cybersecurity events.
Step 6: Maintain & Update Security
- Apply OTA (Over-the-Air) security updates.
- Monitor cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
ISO 21434 vs. UNECE WP.29 Regulation
| Feature | ISO 21434 | UNECE WP.29 R155 |
| Scope | Guidelines for cybersecurity engineering | Regulatory requirement for cybersecurity in vehicles |
| Focus | Process-oriented | Compliance-oriented |
| Applicability | Entire vehicle lifecycle | Type approval & production |
| Mandate | Not mandatory, but recommended | Legally mandatory in UNECE regions |
Challenges in ISO 21434 Implementation
- Lack of Cybersecurity Expertise – Companies need trained cybersecurity engineers.
- Cost & Time Constraints – Cybersecurity integration adds cost & time to vehicle development.
- Evolving Threat Landscape – New threats require constant updates & monitoring.
- Compliance with Multiple Standards – Ensuring compliance with ISO 26262, ISO 21434, UNECE WP.29, NIST, etc..
Best Practices for ISO 21434 Compliance
- Adopt a Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL).
- Use a layered security approach (Defense-in-Depth).
- Perform regular cybersecurity risk assessments.
- Apply OTA security patches & updates.
- Establish a robust cybersecurity incident response plan.
- Train employees on automotive cybersecurity risks.
Conclusion
ISO 21434 provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks in modern vehicles. By implementing risk assessment, security-by-design, testing, and monitoring, automotive companies can enhance vehicle security and comply with regulations like UNECE WP.29.
This was about “ISO 21434: Road Vehicles – Cybersecurity Engineering A Complete Guide“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- FlexRay Protocol – Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Top 50 AI-Based Projects for Electronics Engineers
- UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services) — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Automotive Ethernet — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Controller Area Network (CAN) — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Top 30 High-Paying Embedded Tools You Must Learn in 2026
- Automotive Resource For Free On GitHub
- When Technology Fails: How a Trapped EV Crash Changed Car Safety in China