Nuclear Power Plant Working, Parts, Advantages, Disadvantages
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss nuclear power plant working, parts of the nuclear power plants, advantages of nuclear power plants, and disadvantages of nuclear power plants.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics And Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Top 10 Battery Management System Projects In Simulink
- What Is BMS, Battery Management System, Working, Components
- Top Applications Of Lithium-Ion Batteries / Cells In The Real World
Nuclear Power Plant Working, Parts, Advantages, Disadvantages
- Nuclear energy will be converted to electrical energy.
- The main source is a nuclear reactor. The fission process leads to generate electricity.
Parts Of Nuclear Reactor And Their Function
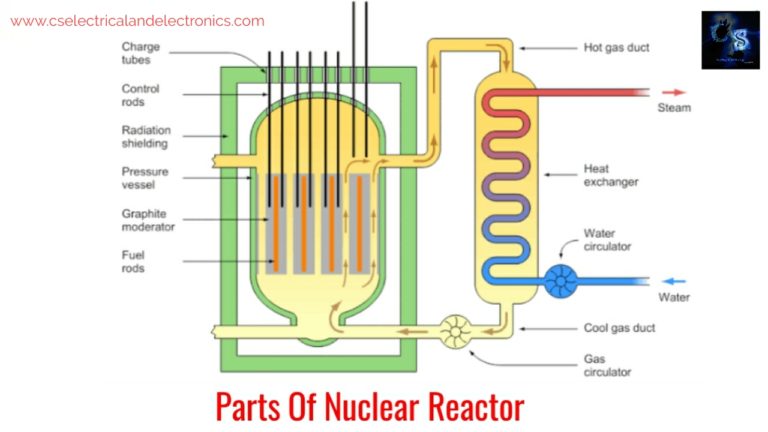
In the reactor, fuel is subjected to the nuclear fission process and the energy which will be released in the fission process will be utilized to heat the coolant, which in turn generates steam. The main function is, to control the emission and absorption of neutrons. It consists of the following components.
01. Reactor Core
In the reactor core, a neutron multiplication process will occur and then a chain reaction takes place. It consists of nuclear fuel, moderator, control rods. There will be a neutron reflector around the core which is formed of stainless rings accurately surrounding the nuclear fuel assemblies.
02. Moderator
The fission process consists of the bombarding of fuels such as uranium with energetic neutrons. This will make the target unstable and split into two parts, with the release of energy which will be further utilized to generate electricity. It’s a medium that is used to absorb a portion of the kinetic energy of neutrons.
So that they will come in the category of thermal neutrons which will help to sustain a controlled chain reaction. The moderator should have high thermal conductivity, should be available in large quantities, should provide good resistance to corrosion, should be stable under heat and radiation.
03. Coolant
The coolant is used to remove heat from the nuclear reactor core and transfer it to the heat exchanger. Coolant should not absorb neutrons, should be non-oxidizing, non-toxic, non-corrosive.
04. Reflector
To reduce the neutron loss, the inner surface of the reactor core will be surrounded by a material that helps to reflect the escaping of neutrons back towards the core of the reactor, which is known as reflecting material. It reduces the size of the reactor core for the given power output.
05. Thermal shielding
To protect the persons working near the reactor from harmful radiation. To protect, the reactor will be enclosed in steel and concrete. These will have the capacity of stopping harmful radiations to reach outside the reactor.
06. Reactor vessel Or Pressure vessel
This provides a place to insert control rods in the nuclear reactor and move them in or out of the reactor core.
Working Of Nuclear Power Plant
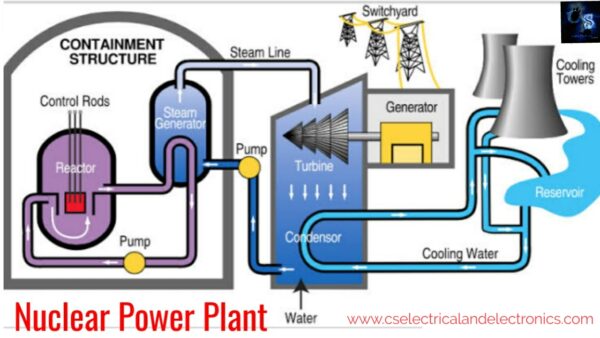
The overall arrangement or working can be divided into the following stages.
01. Nuclear reactors
This isn’t a paradox in which uranium 235 is subjected to the nuclear fission process. It will Control the chain reaction once the fission process is over. If the nuclear reactor doesn’t control the chain reaction, then the result will be an explosion due to a fast increase in the energy released. The nuclear reactor is a cylindrical stout pressure vessel and fuel roads of uranium, moderator, control rods.
The fuel rods will release huge amounts of energy when they are bombarded with slow-moving neutrons. The moderator will consist of graphite rods, which will enclose the fuel rods. This will slow down the neutrons before they bombard the fuel rods. Control rods are made with cadmium, which is a strong neutron absorber and regulates the supply of neutrons for the fission process. When we push to control roads, they absorb most of the region’s neutrons of which few are available for a chain reaction.
As they are being withdrawn, again and again, fission neutrons will cause fission Due to which the chain reaction is increased. By pulling out the control rods, the nuclear reactor power will be increased. But by pushing them, the power will be reduced. The Heat which will produce in the reactor will be removed by the coolant ( sodium metal ). The coolant will carry the heat to the heat exchanger.
02. Heat exchanger
In this, the coolant will transfer heat to the secondary loop. The water from the secondary loop will be converted into steam. The primary and secondary systems are closed-loop and these both never mix up with each other. This heat exchanger will help in keeping the secondary system free from radioactive stuff. This heat exchanger will be absent in boiling water reactors.
03. Steam turbine
The generated steam will be passed through a steam turbine that runs due to the pressure of the steam. When the steam is passed through the turbine blades, the pressure of this steam will decrease but it expands in volume. This steam turbine will be coupled with an alternator through a rotating shaft.
04. Alternators
The steam turbine will rotate the shaft of the alternator, resulting in the generation of electrical energy. This electrical energy will be delivered to a step-up transformer to transfer it over a long distance.
05. Condenser
The steam which will be coming out of the turbines after its work will be converted into the water in the condenser. The steam will be cooled by passing it through a 3rd cold water loop.
Advantages Of Nuclear Power Plant
- The space requirement will be less.
- It consumes a very small quantity of fuel.
- Increased reliability of operation.
- These are not affected by adverse weather conditions.
- The output control is extremely flexible.
- The material expenditure on metal structures is less.
- Required less quantity of water.
- These are most economical in large quantity
Disadvantages Of Nuclear Power Plant
- The initial cost will be high.
- These are not suitable for varying loads.
- If we don’t dispose of radioactive wastes carefully it may have a bad effect on the workers health.
Some Nuclear Power Plants
Kaiga ( Karnataka ):
Capacity: 880MW
Tarapur ( Maharashtra ):
Capacity: 11400MW
Kalpakam ( Tamilnadu ):
Capacity: 440 MW
Narora:
Capacity: 440MW
Kakrapur:
Capacity: 440MW
Now I think you are clear with nuclear power plant working, parts, advantages, disadvantages. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024

