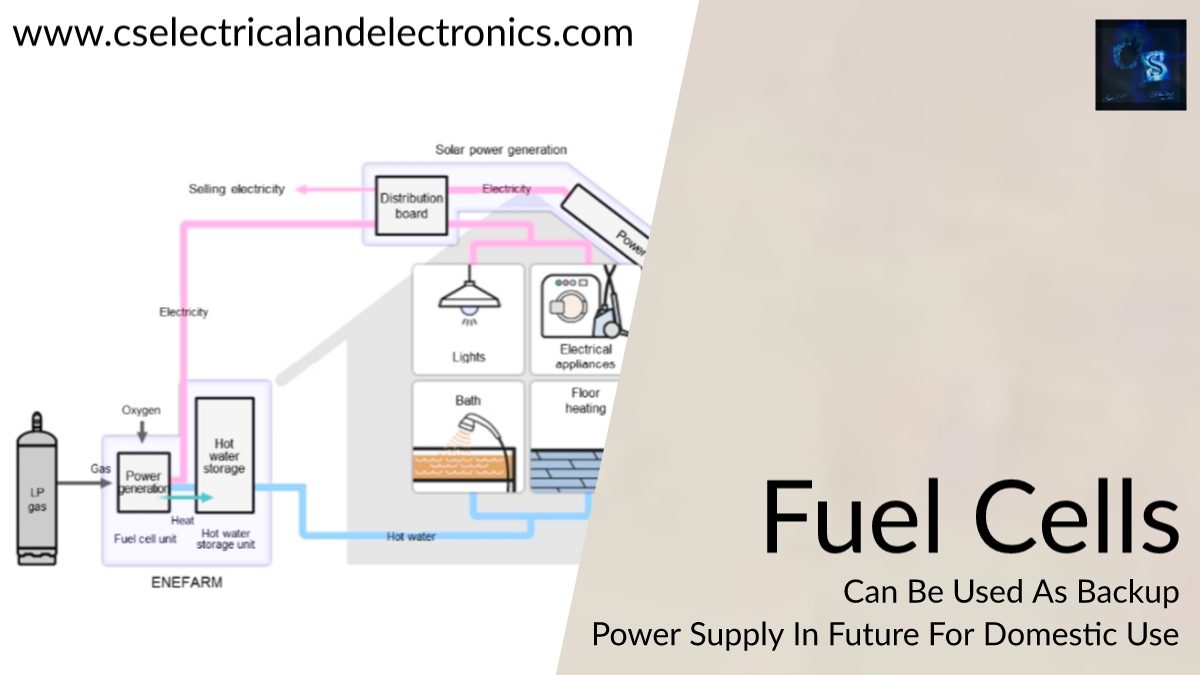
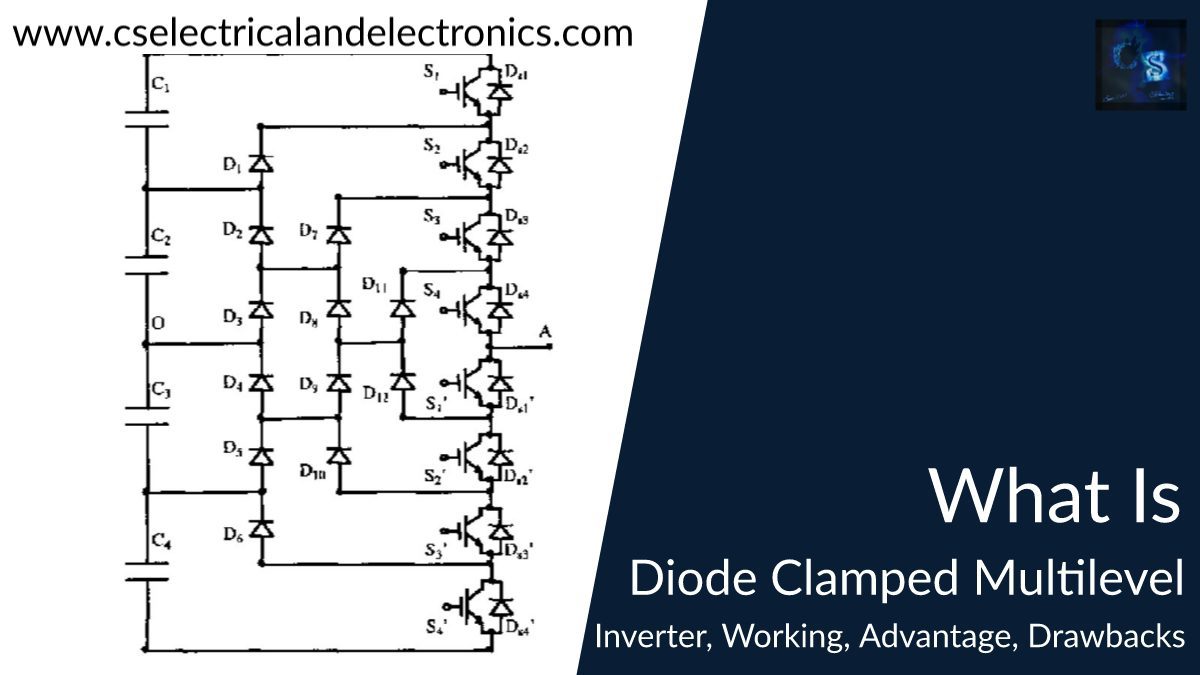
In a bold and decisive move, China has officially released its latest electric vehicle (EV) battery safety regulation—GB38031-2025—marking a new era in the safety landscape of the EV industry. This updated regulation, published at the end of March 2025, supersedes the previous GB38031-2020 version and introduces comprehensive, forward-thinking safety protocols that go far beyond incremental improvements.
New Timeline and Compliance Milestones
The standard will become mandatory for all newly produced vehicles starting 1 July 2026, while existing vehicles must demonstrate full compliance by 1 July 2027. This creates a 12-month transitional period, giving automakers, battery manufacturers, and suppliers a crucial window to update their technologies and safety systems to align with the new, more stringent benchmarks.
Not Just an Update—A Complete Reset
According to Dr. Kai-Philipp Kairies, CEO of ACCURE Battery Intelligence, the changes introduced are far more than a routine regulatory update—they represent a comprehensive reset of how battery safety is approached and enforced. The scope and depth of the revisions reflect China’s commitment to becoming a global leader in EV battery safety and pushing the boundaries of what’s technologically possible and commercially scalable.
Key Enhancements Introduced in GB38031-2025
The revised standard introduces several game-changing safety measures, setting new expectations for how EV batteries are designed, tested, and integrated. Below are the most critical updates:
? Two-Hour Thermal Containment Rule
In the event of a thermal runaway, battery packs must now withstand the incident for at least 120 minutes without catching fire or exploding. This is a dramatic leap from the previous 5-minute requirement, signaling a transformative shift in containment expectations. During this time, internal pack temperatures must also remain below 60°C, drastically reducing the risk of cabin fire and ensuring more time for passengers to evacuate or for emergency services to respond.
? Mandatory Early Warning System
A 5-minute early detection window is now required for all thermal events. Within this window, the battery management system (BMS) must trigger an alert, but crucially, no visible smoke should reach the passenger compartment, protecting occupants from both fire hazards and toxic exposure.
? Realistic Failure Mode Testing
To ensure batteries respond safely to realistic abuse conditions, the standard now mandates a series of real-world failure simulations, including:
- A 30mm steel ball drop test at 150 joules of impact energy.
- Controlled internal heating scenarios that simulate internal cell short circuits.
⚡ Ultra-Fast Charging Stress Tests
Safety must now be validated after 300 cycles of ultra-fast DC charging from 20% to 80% State of Charge (SOC). This targets a growing concern about thermal stress and degradation associated with high-speed charging—especially in regions with extreme climates or high power infrastructure.
? Environmental Durability Requirements
Batteries must now undergo extended salt spray corrosion tests and delayed combustion testing, simulating long-term exposure to harsh environmental conditions. These additions aim to ensure EVs remain safe in diverse, real-world conditions—from coastal cities to snowy mountain roads.
Why This Standard Matters
This isn’t just about technical compliance or ticking boxes—it’s about China taking the lead on global battery safety, setting a benchmark that may well influence regulatory bodies around the world. It signals to automakers, researchers, and policymakers that “good enough” is no longer acceptable. Safety must evolve with the pace of innovation, and GB38031-2025 reflects that ethos with precision.
“This update is more than a compliance checklist—it’s China making a bold move to lead the global conversation on battery safety. Better is possible. And it’s coming fast.”
— Dr. Kai-Philipp Kairies
Winners and Losers in the New Regulatory Landscape
? Likely Beneficiaries
Chinese Battery Leaders: Companies like CATL and BYD are poised to benefit significantly. These giants have already implemented multi-layer thermal management systems across cell, module, and pack levels, giving them a competitive edge under the new rules.
Solid-State Battery Startups: Innovators such as QingTao and WeLion could see accelerated demand. Their inherently fire-resistant chemistries align naturally with the new containment and warning requirements.
Testing and Certification Organizations: The introduction of more rigorous safety validation will generate billions in additional business opportunities for both in-house labs and independent testing bodies worldwide.
⚠️ Potentially at Risk
Budget-Constrained Battery Makers: The new standards are not cheap to implement. Experts estimate that compliance could increase pack production costs by 10–20%, potentially pricing out lower-margin players.
Legacy NMC Chemistries: Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) battery types may struggle under the new framework due to higher flammability and lower thermal resilience, unless paired with advanced safety controls.
Conclusion: China’s Strategic Safety Play
By rolling out GB38031-2025, China isn’t just protecting drivers—it’s making a strategic move to cement its leadership in the EV battery industry, both as a manufacturer and as a regulatory powerhouse. As EV adoption surges worldwide, nations and companies will be watching closely—and many may follow China’s lead.
Whether you’re an automaker, battery engineer, startup founder, or policy advisor, the message is clear: The future of EVs is not just electric—it’s safer than ever before.
This was about “Revolutionizing EV Safety: China Rolls Out GB38031-2025 Battery Standard“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- FlexRay Protocol – Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Top 50 AI-Based Projects for Electronics Engineers
- UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services) — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Automotive Ethernet — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Controller Area Network (CAN) — Deep Visual Technical Guide
- Top 30 High-Paying Embedded Tools You Must Learn in 2026
- Automotive Resource For Free On GitHub
- When Technology Fails: How a Trapped EV Crash Changed Car Safety in China