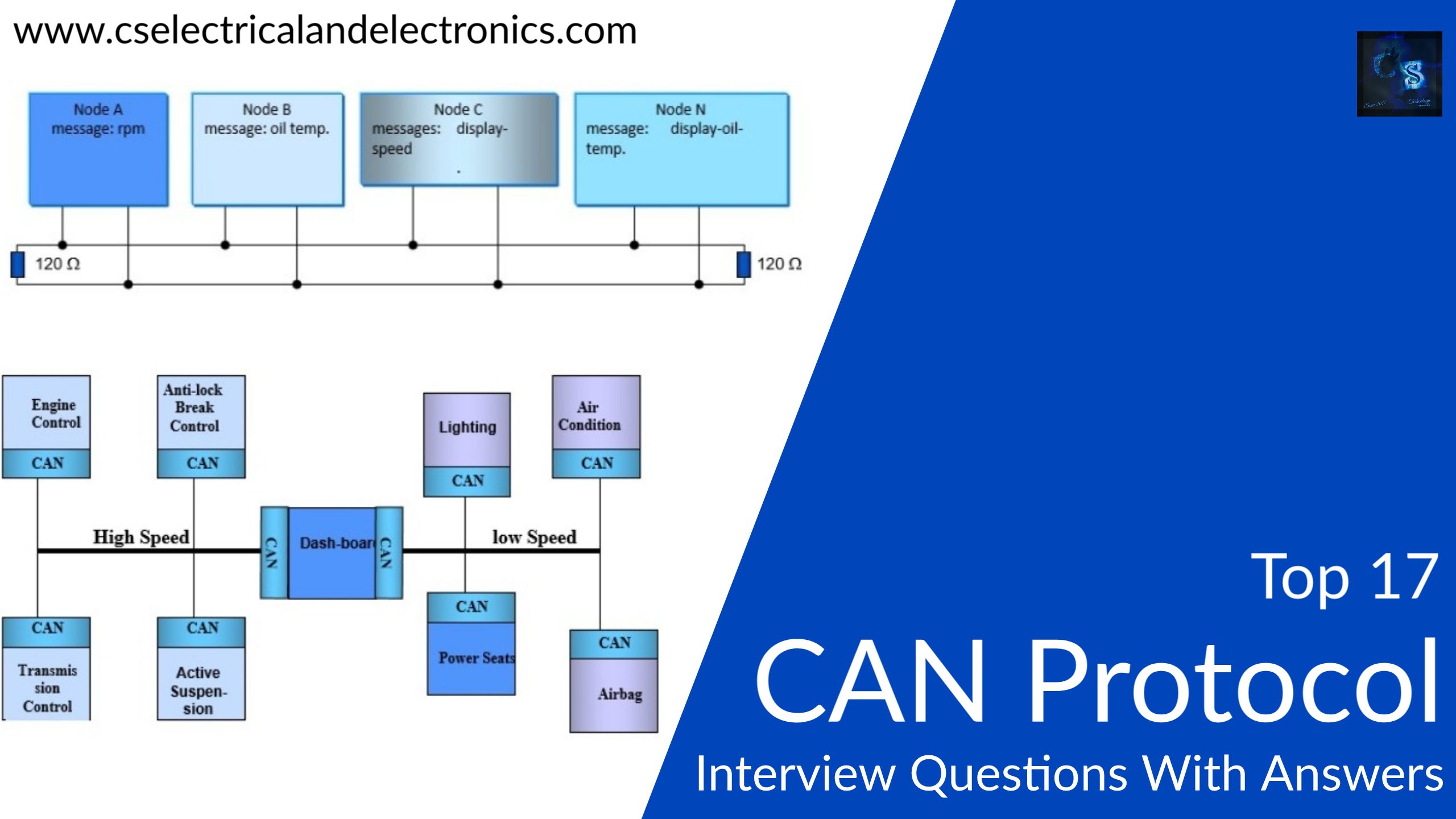
Top 17 CAN Protocol Questions Asked In An Interview With Answers
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss the top 17 CAN protocol questions asked in an interview with answers or interview questions on CAN protocol with answers.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Difference Between SRAM And DRAM, Characteristics, Advantages
- What Is ADC, How Analog To Digital Converters Works, Types Of ADC
- What Is Malware, Types Of Malware That Will Kill Your System, Prevention
Top 17 CAN Protocol Questions
01. What are the two types of the frame format of CAN?
Ans.
- Base frame format: with 11 identifier bits
- Extended frame format: with 29 identifier bits
02. What is the length of the CRC and CRC delimiter?
Ans.
- CRC= 15
- CRC Delimiter =1
03. What is the Feature of CAN Protocol?
Ans.
- Simple and flexible in Configuration.
- CAN is a Message-Based Protocol.
- Message prioritization feature through identifier selection.
- CAN offer Multi-master Communication.
- Error Detection and Fault Confinement feature.
- Retransmission of the corrupted message automatically when the bus is idle.
04. Types of errors detected in CAN?
Ans.
- Bit error: Transmitted and received bit is different (except in arbitration, acknowledgment, and passive error).
- Bit stuffing error: More than five bits of equal polarity inside of a frame is detected.
- CRC error: Receive CRC code that doesn’t match with the calculated code.
- ACK error: Transmitting node receives no dominant acknowledgment bit (no receiver accepts the transmission message).
- Form error: Fixed-form bit field contains one or more illegal bits e. g. violation of end of frame EOF format, CRC- or ACK-delimiter.
05. What is a Cyclic Redundancy Check?
Ans.
Each message features a 15-bit Cyclic Redundancy Checksum (CRC), and any node that detects a different CRC in the message than what it has calculated itself will signal a CRC Error.
06. What Is The Use Of Bit Stuffing?
Ans.
Long NRZ messages cause problems in receivers. Clock drift means that if there are no edges, receivers lose track of bit. Periodic edges allow the receiver to resynchronize to the sender clock.
07. How to recover from CAN- Busoff?
Ans.
The Bus Off state should only be left by a software reset. After software reset the CAN bus controller has to wait for 128 x 11 recessive bits to transmit a frame. This is because other nodes may have pending transmission requests. It is recommended not to start a hardware reset because the wait time rule will not be followed then.
08. Why does CAN-BUS uses NRZ encoding instead of RZ?
Ans.
NRZ encoding uses to change the Controller digital signal into BUS level.
09. For synchronization of CAN. Prop_Seg >= ……………………………………….?
Ans.
Prop_Seg >= Delay A_to_B + Delay B_to_A
Ans.
The idea behind bit stuffing is to provide a guaranteed edge on the signal so the receiver can resynchronize with the transmitter before minor clock discrepancies between the two nodes.
11. What are voltage Levels in CAN Protocol?
Ans.
- CANH voltage level is 3.3 Volt
- CANL Voltage Level is 1.5 Volt
12. Why CAN Bus uses differential Cable?
Ans.
CAN Protocol used two-wire twisted-pair cables for CAN-Bus architecture to reduce cross-talk and EMI.
13. Why Can is Having 120 Ohms At Each End?
Ans.
To minimize the reflection reference, to reduce noise. To ensure that reflection does not cause communication failure, the transmission line must be terminated.
Ans.
CAN Arbitration is nothing but the node trying to take control of the CAN bus.
15. Different Bus Management Methods?
Ans.
- Bit-wise arbitration
- Master/Slave
- Daisy Chain
- TDMA
16. How Request Frame is used?
Ans.
If a node wishes to request the data from the source, it sends a Remote Frame with an identifier that matches the identifier of the required Data Frame. The appropriate data source node will then send a Data Frame as a response to this remote request.
17. CAN controller may work in three different states such as?
Ans.
- Error active state: For each detected error there is generated an active error flag (queue of six consecutive dominant bits).
- Error passive state: For each detected error there is generated a passive error flag (queue of six consecutive recessive bits).
- Bus off state: If too many errors are detected by one node, this node is automatically disconnected from the bus.
This was about ” Top 17 CAN Protocol Questions “. I hope this article ” Top 17 CAN Protocol Questions ” may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 500+ Embedded System Projects For Engineer, Diploma, MTech, PhD
- 500+ Projects For Diploma Electrical, Electronics Student, Diploma Project
- 8051 Microcontroller Timers, TCON Register, TMOD Register
- A Complete Guide To FlexRay Automotive Protocol