Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss the world’s top 20 technologies in railways, or railway technology, and how these technologies will benefit society.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- Top 16 Robots That Will Change The World, Humanoid Robots
- Top 100 Software Companies In The World To Work
- Top 12 Microcontroller Manufacturing Companies In The World
Top 20 Technologies In Railways
With carriages that are either totally electric or hybrid diesel-electric and only remaining as charming attractions, the rail business is already substantially electronic. Railways foreshadow innovations that will likely spread throughout national infrastructures, from sleek, secret until lit keyboards to blue lights that prevent people from committing suicide.
The industry is constantly innovating, and with smart cities, the internet of things (IOT), and increasing autonomy on the horizon, the railway industry is leading the way. The UK government has offered £3.6 million in funding to 10 initiatives that would revolutionize train passenger transport, demonstrating its understanding of the significance of cutting-edge electronics for the rail sector.
Due to the increased need for quick travel between and between cities and nations, rail transportation is undergoing substantial changes. Drones and intelligent sensors for examining railroad lines, digital communication platforms, and automatic train control are the main trends in the rail business (ATC). Rail tech firms, who are notoriously hesitant to adopt new technology, are attempting to scale a number of solutions that aim to integrate biometric data, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing.
The Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable the installation of predictive maintenance to check for any irregularities for train operators and railroad firms. Along with condition-based monitoring, more recent rail industry trends like the hybridization of rolling equipment and high-speed rail also add to the growing body of cutting-edge railway technologies.
20. Augmented & Virtual Reality In railway
In the rail sector, mixed reality is used for consumer engagement, design visualization, and employee training. In-train entertainment and route information are provided by interactive windows, and augmented reality (AR) mobile apps let users participate in the planning of rail infrastructure. Virtual reality (VR) headsets also make training more engaging and educational.
Railway firms may increase revenues by lowering the cost of employee training and enhancing passenger happiness and loyalty using AR and VR technologies.
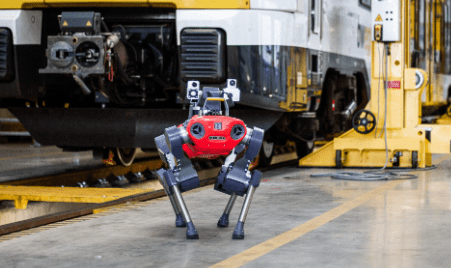
19. Robotic Railyards
Robots that can operate on their own in railyards have been the subject of research and development. These devices are made to handle risky railroad tasks, especially those that call for passengers to interact with moving trains. A test was conducted to determine how well a robot could decouple a moving railway carriage, and the results showed that the robot could do it up to two miles per hour with reliability.
18. Big Data & Analytics In Railways
Predictive analytics, asset management, passenger information systems, and data management platforms are made possible by the use of big data in the railway industry. Millions of data points are collected and processed through the use of smart railway sensors, significantly enhancing the reliability, security, and safety of rail infrastructure.
The availability of rail is increased by the ability of rail operators to plan repairs in advance of failures. IoT sensors are being developed by startups and scaleups to gather information for rail infrastructure, including railcars, tracks, and signalling units.
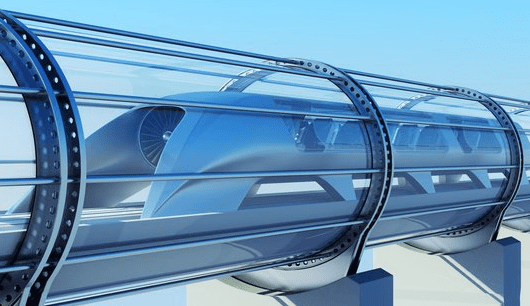
17. The Hyperloop Argument
It’s debatable if hyperloop is a new type of train transportation or something else different. The system claims to cost about the same as current public transportation while cutting the 125-minute trip from Manchester to London to just 14 minutes (approximately nine times faster due to travelling at about 700 mph).
It has the potential to completely transform modern life by democratising access to employment, education, comforts, and entertainment. It may be overly optimistic to expect prices to be comparable to slower trains, though, because rail prices in general would have to drop dramatically or people would only use the much faster option. Before the hyperloop can solve all of our problems, however, the enormous, expensive systems need to be built.
16. Rail Automation
Beyond autonomous train operations, the railway industry is increasingly automated (ATO). Startups and scaleups create drone technologies for remote inspection and robotic systems for cleaning and maintaining infrastructure.
Automation of the traction control system also reduces delays and raises the standard of safety for train infrastructure. In order to improve asset efficiency, monitoring, and maintenance, railway firms can use smart rail automation. This improves passenger experience and train reliability.
15. Wearable Tickets
Paperless tickets are a common and environmentally friendly replacement for traditional tickets, whether they are E-tickets on travellers’ smartphones or travel cards like the Oyster cards provided by Transport for London.
With contactless payment currently permitted in place of Oyster cards, commuters are moving beyond using cards or phones as tickets and are instead utilising watches and sunglasses to both purchase and validate their right to travel. Wearable technology is the future of paperless ticketing. Our skin-implanted RFID interfaces or electronic skin patches might be the future of tickets.
14. Passenger Experience
Rail businesses use automatic ticketing, video monitoring, train delivery services, and train hotels to enhance the passenger experience. Video monitoring assists in maximising passenger load and detecting theft. Additionally, smartphone and mobile apps automate price comparisons and ticketing for customers of rail firms.
Infotainment systems entertain passengers while they are travelling, and onboarding systems further improve last-minute booking, identification control, and seat assignments. Companies use biometric ticketing technologies to further streamline the ticketing process and passenger identification.
13. Preventing Suicide
A 2009 innovation from Japan uses blue LED panels at the ends of station platforms to deter suicide. It was so successful there—the world’s suicide capital—that it has since been adopted elsewhere, including the UK. According to a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, technology has reduced suicide rates by 84% on average.
12. Rail Connectivity
With the aid of 5G technologies, contemporary rail mobile communications systems now enable low-latency communications, high performance, and the dependability of rail infrastructure. Additionally, communications-based train control (CBTC) offers effective asset monitoring and rail traffic management. Applications for train connectivity include train positioning, control, maintenance, passenger experiences, and data collection on passengers.
11. Energy Harvesting Railway Tracks
Energy-harvesting railway pads are being developed by some businesses. These pads use piezoelectric components to capture mechanical strain and transform it into electrical power. Technion University and Israel Railways have discovered preliminary results that suggest sections of track that receive 10 to 20 ten-car trains per hour can generate 120 kwh per hour, which can either be used to power nearby devices that inform trains in the area, raise and lower level crossings, or be fed back into the grid.
10. Decarbonization
Governments are attempting to further decarbonize the rail industry even though trains are the most environmentally friendly mode of transportation thanks to aggressive net-zero emissions objectives.
The most popular decarbonization strategies involve switching from diesel to electric, hydrogen fuel cell, or battery-powered trains. Rail operators employ electric locomotives that draw their power from renewable resources like solar or wind to further reduce CO2 emissions.
09. Train Recuperative Braking Devices
The main advantages of the technology, according to Bombardier and Maxwell Technologies, are a 20 to 30% reduction in grid power consumption, improved line voltage regulation across a multi-stop rail system, a significant reduction in brake maintenance expense, and backup power to allow vehicles to reach a station in the event of a grid power failure.
08. Artificial Intelligence
The main advantages of the technology, according to Bombardier and Maxwell Technologies, are a 20 to 30% reduction in grid power consumption, improved line voltage regulation across a multi-stop rail system, a significant reduction in brake maintenance expense, and backup power to allow vehicles to reach a station in the event of a grid power failure.
07. Changing Rail Carriages
In order to use the carriages for freight during off-peak hours, the Rail Safety and Standards Board (RSSB) has been developing a novel design that enables passenger seats to be stowed away. Electronic components must be able to move quickly and easily without breaking if rearrangeable carriages are to be used. This can be done with dynamically flexible circuit solutions, interconnects, and components.
06. Train Monitoring
To address the demand for greater railway security around the world, businesses like Eurotech are offering next-generation CCTV systems expressly for use on the tracks. In 2018, the Indian government said that by 2020, it would install CCTV in all 11,000 trains (50 trains already have CCTV) and 8,500 stations (currently 395 stations). The Canadian government, however, has laid out a strategy to install recording equipment on every train by 2030.
05. Augmented Reality Windows
Augmented reality windows are one of the most intriguing innovations in linked trains. When requested, they show transparent information about the travel in front of the rolling scenery, such as the current location, time, temperature, or forthcoming stops with tourist attractions.
04. Autonomous Freight locomotive
The “world’s first heavy-haul, long distance autonomous rail operation” finished its first trip in July 2018, transporting iron ore from mines to Rio Tinto’s port facilities in Western Australia. However, autonomous freight trains are paving the way in this field.
03. Autonomous Passenger Trains
Self-driving technology is further away than you may think for high-speed, long-distance rail travel because trains have a longer halt distance than any other form of vehicle. Before making a planned stop, trains must locate stations or obstructions well in advance.
To make matters worse, there is significantly less friction between the metal wheels of a train and its metal tracks than there is between a car’s tyre and the road. Therefore, a quick stop requires human supervision, and complete automation would require far more sophisticated image processing technology than what is currently available.
Before being legally permitted to operate public transportation, that technology would then need to pass more stringent reliability tests than self-driving cars, as even though both are terrible, a car crash has much less potential for devastation than a train wreck.
02. Automated Metro Systems
The technology industry is fascinated by self-driving cars, and all of the top automakers are vying with one another to put completely autonomous vehicles on the roads before a law is passed. However, we are more likely to travel in a self-driving automobile before a self-driving train since it seems easier to follow straightforward railway tracks than to negotiate the relatively complex traffic congestion, zebra crossings, and bicycles of current streets.
However, since 1967, residents have been transported by inner-city metro systems using Automatic Train Operation technology. Due to drivers’ unforeseen absences, this both results in fewer jobs and raises the possibility of upsetting closures.
01. Public Viewing
IBM, a global leader in intelligent devices and the internet of things, provides examples of devices that measure track stress and condition, air and track temperatures, and other variables that have predictive value to maintenance teams. Some of these connected railway networks, according to IBM, automatically initiate maintenance activities.
They have customers who use their Watson artificial intelligence platform to analyse video footage and identify problems on trains and tracks (perhaps serving as a driver for future trains), as well as customers who use it to gauge passenger movement in railway stations and vehicles. The goal of all this data interchange, analysis, and gathering is to deliver the ultimate rail travel experience.
This was about “Top 20 Technologies In Railways“. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 100+ Indian Startups & What They Are Building
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever