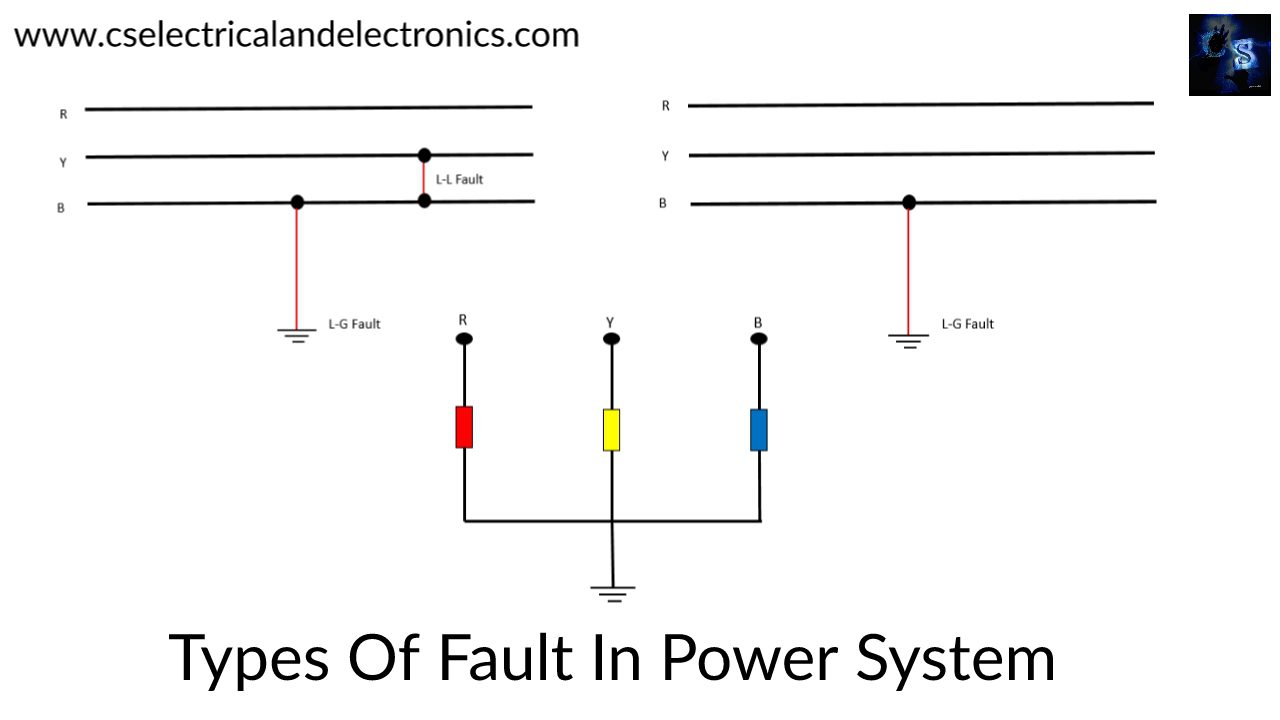
Types Of Faults In Power System, Symmetrical, Asymmetrical Faults
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss the different types of faults in power system, symmetrical faults in lines, asymmetrical faults in lines, why fault occurs in lines, etc.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask question. You can also catch me @ Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Top 10 Renewable Energy Power Plants In World You Must Know.
- Top 05 Ways To Make Money For Students, How Student Can Earn Money.
- Top 10 Websites For Engineers You Must Know, Don’t Miss It.
Types Of Faults In Power System
A fault in electrical equipment is defined as a defect in its circuit due to which the current is diverted from the flowing intended path. The power system is mainly classified into three phases such as generation, transmission, and distribution. Coming to faults in generation faults are less compared to transmission and distribution because of the usage of overhead lines, so transmission and distribution faults are taken into consideration. Faults in the overhead lines are mainly occurred due to the breaking of conductors, short-circuited by large birds, kite strings, tree branches, and failure of insulation medium between the line conductors.
The types of faults in the power system network are classified into two types, namely (a) Open conductors (series faults) and (b) Short circuit (Shunt faults). Most of the faults about two-thirds are liable to occur is short circuit type and these are further divided into two types, namely
Symmetrical faults
- Three phases short circuit fault (L-L-L)
- Three phases to ground fault (L-L-L-G)
Asymmetrical faults
- Line –to- ground fault (L – G fault )
- Line – to – Line fault (L – L fault )
- Double line to ground fault (L – L- G fault)
- Line – to – Line and third line to ground fault (L-L & L G fault )
The faults can be minimized by improving the system characters like design, quality of the equipment, and maintenance. However, the faults can not be eliminated completely.
Representation Of Symmetrical Fault
This type of faults are mainly two types,
01. Three phase fault (or) Three phases shorted:
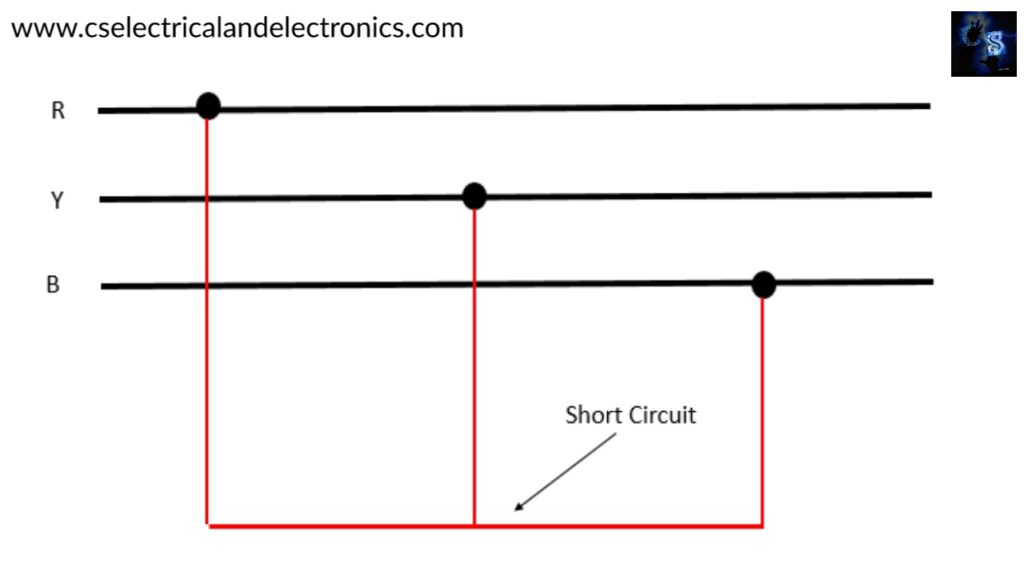
This type of fault may occur if two conductors of a 3-phase system get break and fall on the third line conductor. The line conductors R & Y may get break and fall on the third conductor.
02. Three-phase to ground fault:
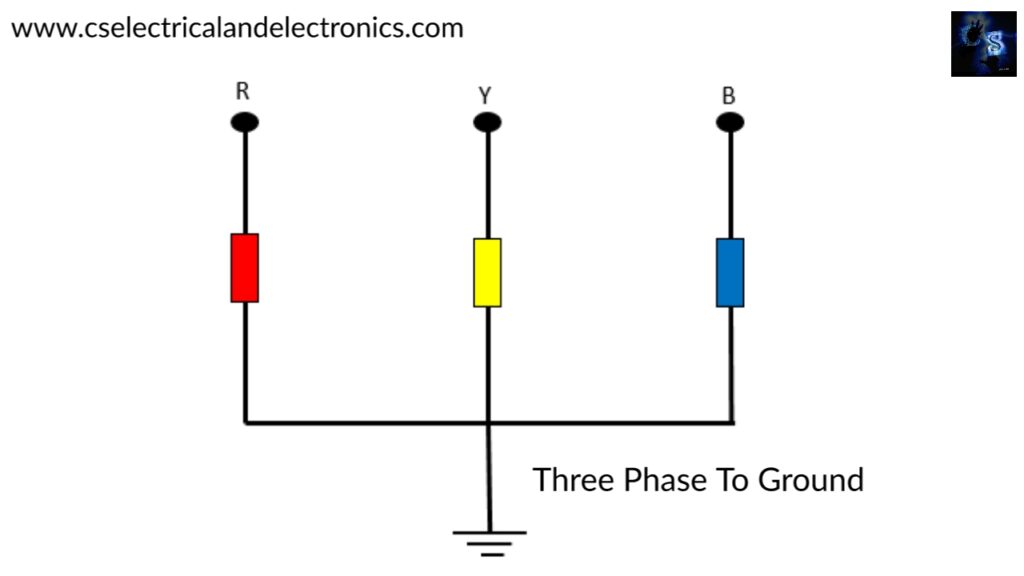
This type of fault may occur if the three conductors may break and fall on the ground. As shown in below figure the three-phase to ground fault in which all the line conductor may get a break and falls on the ground.
Representation Of Asymmetrical Fault
The asymmetrical faults are of four types, namely
01. Single line to ground fault (L – G Fault):
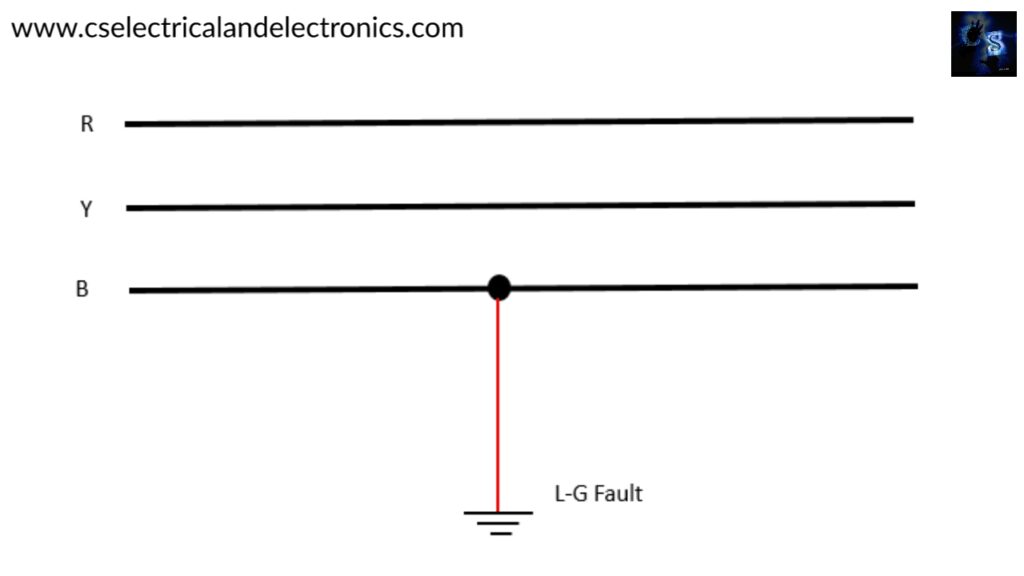
This fault may occur due to one of the conductors of the power line breaks and falls on the ground as shown in the figure.
02. Line to Line Fault (L – L Fault):
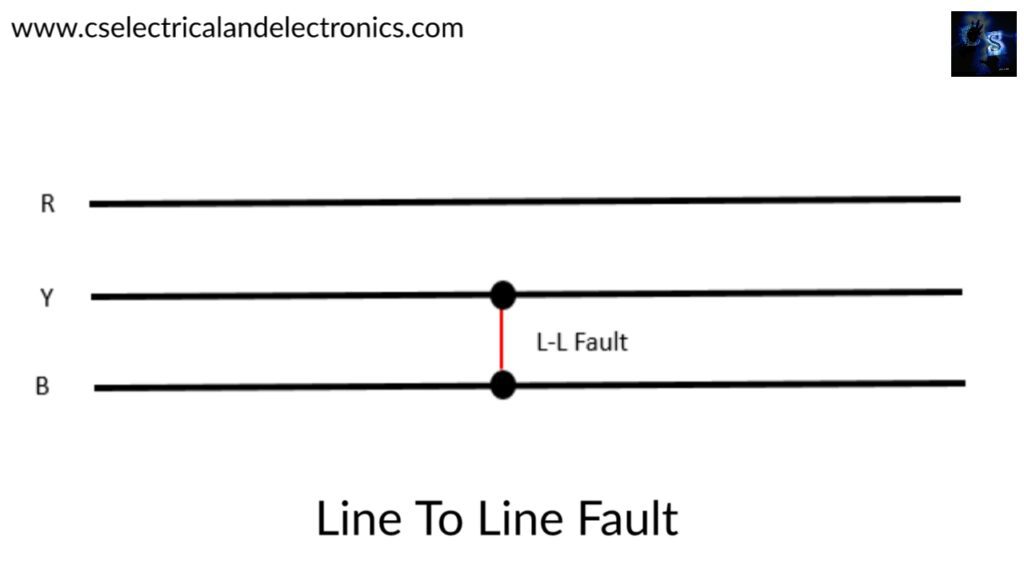
This type of fault may occur due to one of the conductors of the three-phase line breaks and falls on the other conductor. The below figure shows the Line to Line fault in which the Line-R conductor breaks and touches the Line-y Conductor.
03. Double line to Ground Fault (L-L-G fault):
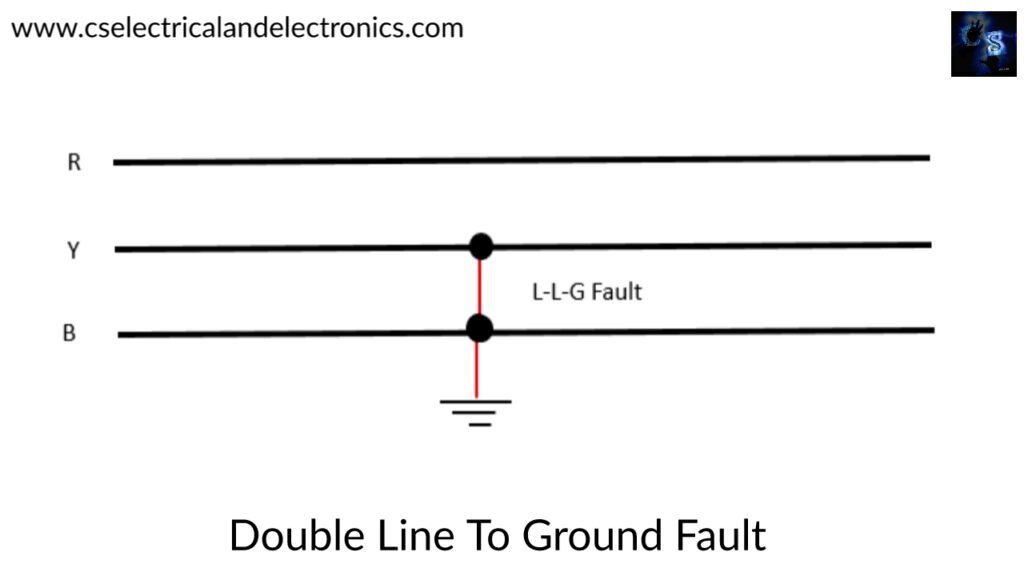
This type of fault may occur due to two conductors of a three-phase line breaks and falls on the ground. The below figure shows the double line to ground fault in which the line conductors of Y and B are break and fall on the ground.
04. Line to Line and third line to ground fault (L-L & L- G Fault):
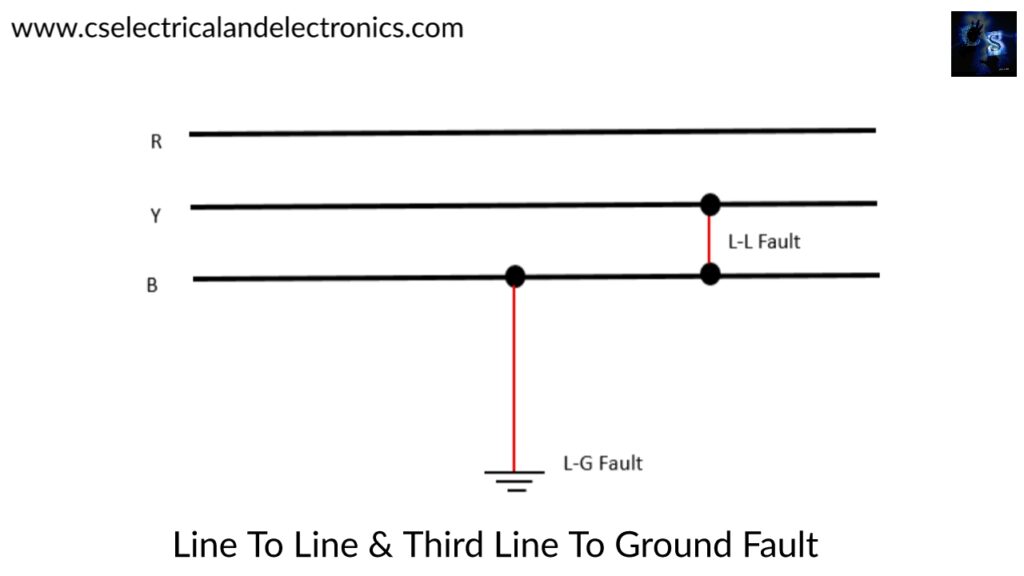
This type of fault is the combination of faults of single line to ground (L-G) and Line to Line fault (L-L). The below figure shows the L-L & L-G fault in which the R- Line conductor breaks and falls on the second conductor and also BLine conductor breaks and falls on the ground.
The majority of faults that occur in a power system are single line to ground fault(LG). Less frequent than this are line-to-line (L-L). The double line to ground faults is rarer than the line to line short circuit not involving ground.
Open Circuit Faults
These faults are rarely occurred in the power system compared to the short circuit faults. These open circuit faults take place in series with the transmission line so it is popularly known as the series faults. Series faults occur due to the failure of one are two conductors. This series of faults will affect the reliability of the power system. This open circuit is classified into three types:
- Open conductor fault
- Two conductors open fault
- Three conductors open fault
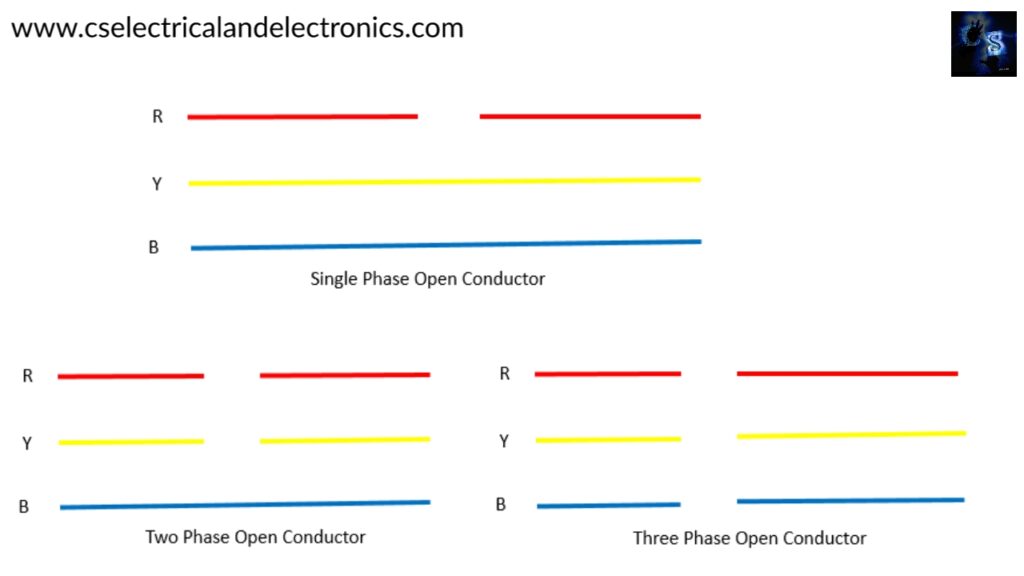
When the transmission line is running on balanced load and suddenly the open circuit fault occurred means one of the phases melts, it leads to reduction of actual load on the alternator and the speed variation occurred in the alternator. Due to speed variations voltage distributions occurs and it will overload other transmission lines. This is the same phenomenon that deals with all three types of series fault. The main cause of the series fault is a broken conductor or slow working process of circuit breaker. There will be some major effects caused by them in power system such as,
01. Abnormal voltage supply in transmission lines.
02. The overvoltage caused by faults may lead to insulation failure and other damages to the network.
03. Humans and animals can be in danger when breakdowns occur suddenly in remote areas.
Open circuit faults duration is a long period compared to the short circuit faults so minimizing them as soon as possible is very important for the protection of the power network. The causes of these faults are minimum due to the type of material used for manufacturing and the voltage disturbances and some unbalanced loads will lead to the causes of the short circuit and open circuit faults in the power system. The measurement precautions will be taken for the prevention of faults.
I hope this article “Types Of Faults In Power System” may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024