Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss the types of memories used in embedded systems, definition, applications of all memories used, the difference between the primary and secondary memories, etc.
If you need an article on some other topics then comment us below in the comment box. You can also catch me @ Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Different Types Of Logic Gates, IC Numbers, Table, Diagram, Working.
- Difference Between Diode and SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier).
- What Is A MATLAB, Applications, Alternatives, Advantages, Disadvantages.
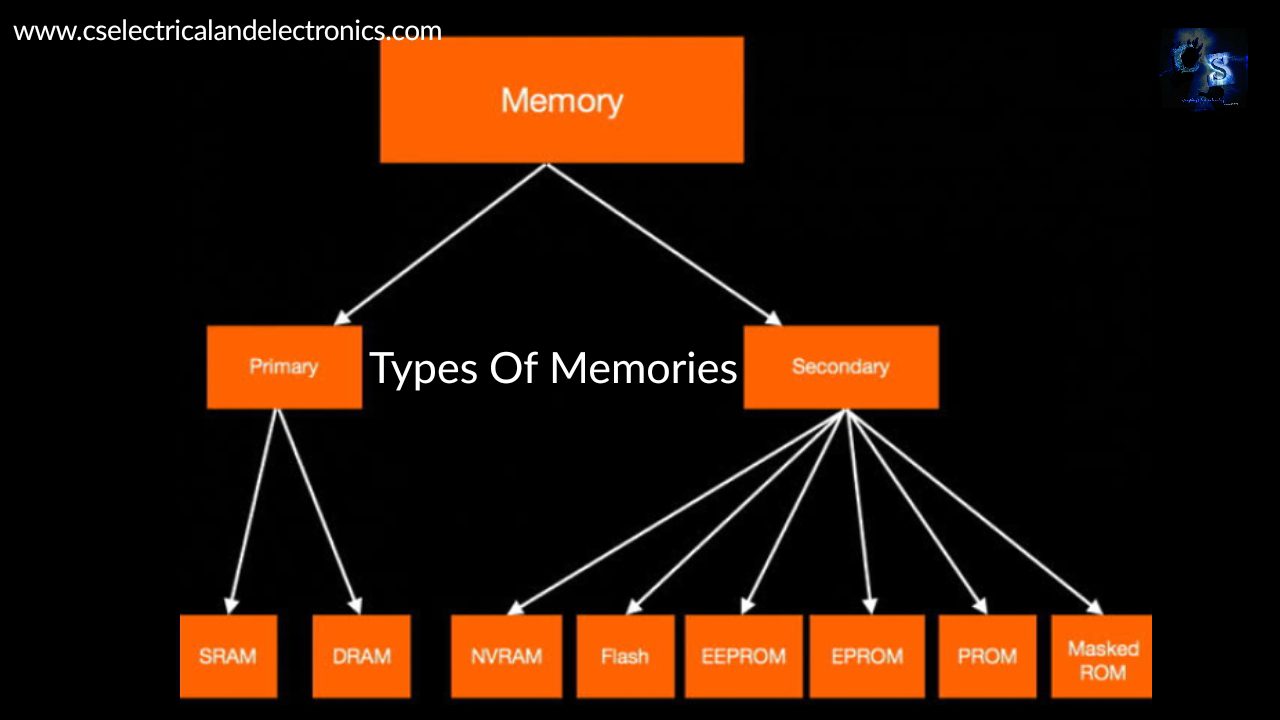
Types Of Memories
Nowadays, memories are used in almost each and every device to store the data and information. But based on requirements there are different types of memories used in devices. In today’s world, the demand for memories is high because of data, daily a lot of data is getting generated due to the digital world, so to store these data and information, memories are required.

The types of memories are primary and secondary memory. The primary memory will store the data and information until the power supply is present means the memory holds the information only the memory is connected with the power supply. If the power supply goes then the data and information which is stored in the memory will be erased or lost. The primary memories are SRAM and DRAM, later I will discuss what is SRAM and DRAM.
The secondary memory will store the data and information even if the power supply goes. The data and information will still remain in memory after the power cut. The secondary memories are Flash, EPROM, PROM, Masked ROM, EEPROM, and NVRAM.
Primary memories are used where we want to store temporary data and information and secondary memories are used where we want to store data and information permanently.
Types Of Primary Memories
- SRAM
- DRAM
01. SRAM
SRAM stands for static random access memory, this memory consumes less power compared to the DRAM. The static random access memory is 4 times faster than the DRAM. In this memory, data is stored temporarily until the power supply is there. The cost of is memory is high compared to DRAM.
Applications Of SRAM
- Computers and laptops
- Servers
- Mobile phones
- Camera
- And other electronic devices
02. DRAM
DRAM stands for dynamic random access memory, this memory consumes more power compared to the SRAM. The dynamic random access memory is 4 times slower than the SRAM. We need to refresh the data continuously in this memory even though the supply is there. The cost of this memory is low compared to the SRAM.
Applications Of DRAM
- Servers
- Personal computers
- workstations
Types Of Secondary Memories
- Masked ROM
- PROM
- EPROM
- EEPROM
- Flash
- NVRAM
01. Masked ROM
In Masked ROM, the data is stored at the beginning only when the memory is manufactured means programmed by the integrated circuit manufacturer, and later we can’t delete the data once it is stored. This type of memory is used in long term devices.
Applications Of Masked ROM
- Network Operating Systems.
- Server Operating Systems.
- Storing fonts for laser printers.
- Storing sound data in electronic musical instruments.
02. PROM
PROM stands for programmable read-only memory this memory can be programmed only one time and we can’t reprogram this memory again and we can’t delete or erase the program.
Applications Of PROM
- In digital electronic devices to store permanent data.
- Cell phones
- Video game console
- Medical devices
03. EPROM
EPROM stands for erasable programmable read-only memory. We can erase the program in this memory and we can reprogram this memory with new data. In this memory, there is a glass window on the top, when it is exposed in the sunlight, the data stored in the memory will be erased.
Applications Of EPROM
- To store computer BIOS
- Modern electronics
- Development field
04. EEPROM
EEPROM stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory. This memory is the same as EPROM but we can erase data through electricity whereas in EPROM we can erase data through sunlight. EEPROM can be reprogrammed again with new data.
Applications Of EEPROM
- Computers
- Remote keyless system
- In microcontrollers
05. Flash Memory
The flash memory is same like EEPROM, it has all qualities of EEPROM, but the EEPROM is re-programmable one bit at a time, whereas the flash memory is reprogrammable one block at a time and the size of block will be given in the specification sheet of the memory.
Applications Of Flash
- In computers
- Microcontrollers
- Microprocessor
- For transferring data between computers
06. NVRAM
The NVRAM stands for Non-Volatile Random Access Memory, it is a special type of memory like SRAM with the power supply and the program can not be deleted means the program is stored permanently. The NVRAM is more costly compared to all types of memories mentioned above.
Applications Of NVRAM
- Computers
- Hard drives
- Cloud computing
These are the different types of memories used in an embedded system. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading. If you have any doubts related to this article, then comment below in the comment box.
Also, read:
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 100+ Indian Startups & What They Are Building
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 8051 Microcontroller Timers, TCON Register, TMOD Register
- 90% Of The World’s Most Advanced Chips Come from One Place — Why TSMC Quietly Runs the Modern World
- A Complete DSA Roadmap For Embedded Engineers
- A Complete Guide To FlexRay Automotive Protocol
- Accelerating Software-Defined Vehicles with Model-Based Design
- Active vs Passive ADAS: Which One is Driving The Future of Automotive Safety?
- Adaptive AUTOSAR Service-Oriented Architecture – Real-Life Working Examples
- Adaptive AUTOSAR Vs Classic AUTOSAR: Which One For Future Vehicles?
- ADAS Technologies Explained: Complete Guide To Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (2025)
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): How To Become An Expert In This Growing Field
- Advanced Technologies In-Vehicle Infotainment Systems
- Advancements In 3D Printing Technology And It’s Future