Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss the types of model verification, validation, and test tools in Simulink, and we will explain the purpose of each tool.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics
Also, read:
- UDS Protocol Diagnostics Interview Questions Asked By Benz, Daimler, Volve, Bosch
- Qualcomm And MapmyIndia Collaborate To Advance Automotive Innovation In India
- Modeling Based Interview Questions On Simulink
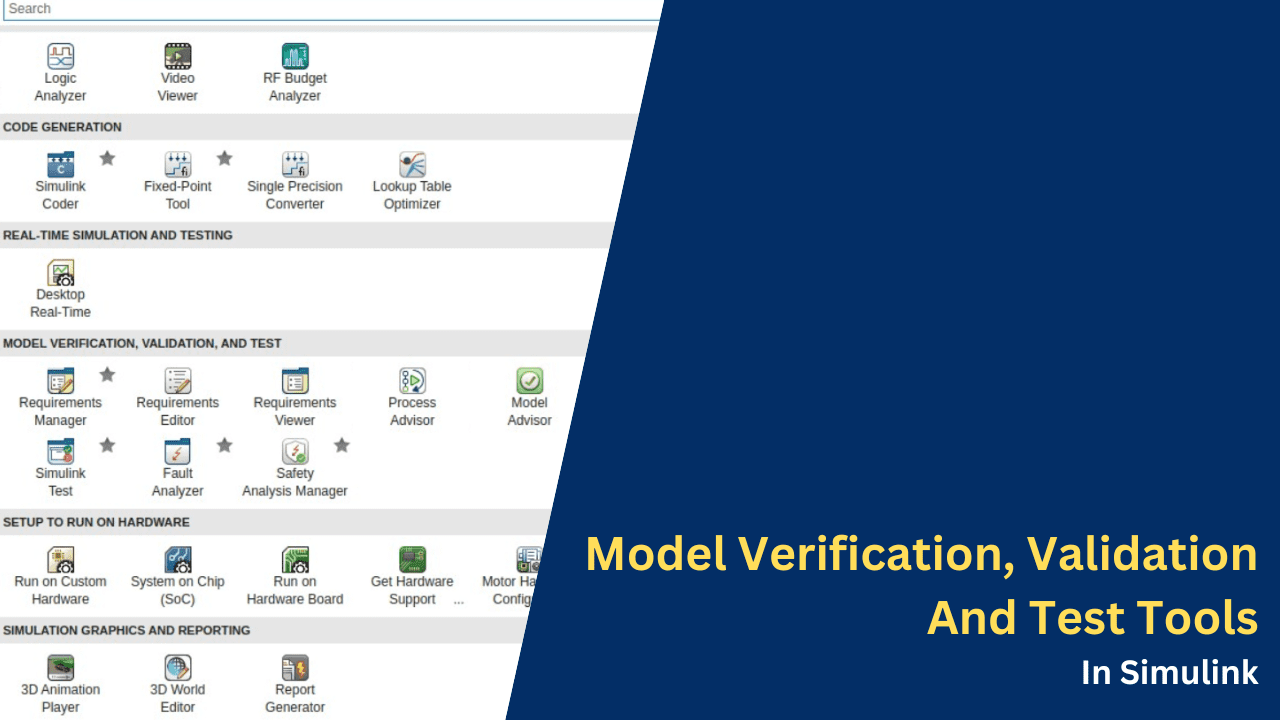
Model Verification, Validation, And Test Tools In Simulink
The tools displayed in the image represent a comprehensive suite of capabilities in MATLAB and Simulink for model-based design, verification, and validation. These tools are essential for ensuring the quality, safety, and efficiency of systems developed in industries like automotive, aerospace, and industrial automation.
They enable engineers to:
- Manage Requirements: Establish traceability between requirements, models, and tests for better compliance and impact analysis.
- Analyze Models: Check for compliance with industry standards, eliminate redundancy, and optimize design.
- Validate Safety and Quality: Ensure robust testing, measure coverage, and verify designs through formal methods.
- Enhance Workflow Automation: Streamline repetitive tasks like test case generation, fault analysis, and metrics reporting.
This ecosystem supports the complete lifecycle of model-based development, from requirement capture to design, testing, and verification, fostering high-quality product delivery.
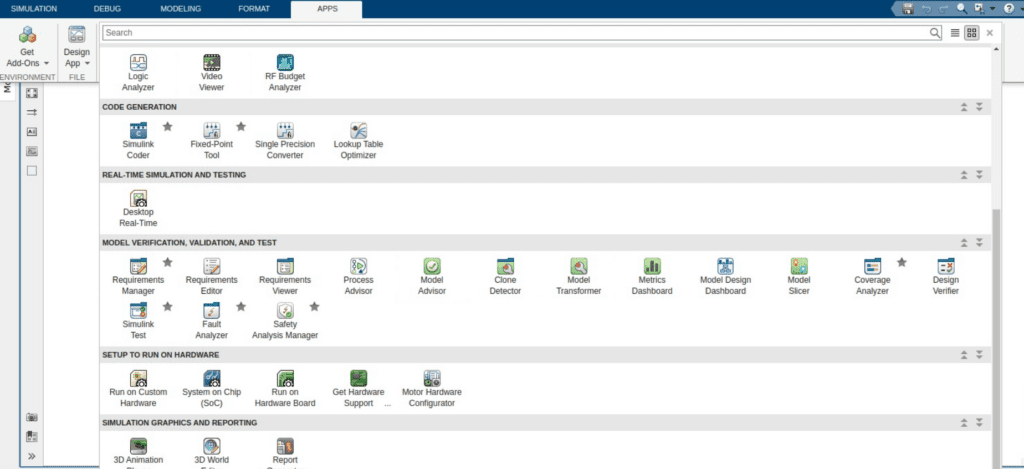
01. Requirements Manager

- Helps manage requirements and ensures traceability between requirements, models, and test cases.
- Enables linking of design elements to requirements for easy tracking.
- Supports compliance with industry standards like ISO 26262.
- Facilitates impact analysis for requirement changes.
- Integrates seamlessly with tools like Simulink and Simulink Test.
02. Requirements Editor

- Provides a user-friendly interface to create and edit requirements.
- Organizes requirements hierarchically for better management.
- Allows real-time linking to models and test cases.
- Offers compatibility with external requirement tools like IBM DOORS.
- Ensures consistency and clarity in requirement definitions.
03. Requirements Viewer

- Offers a read-only interface for reviewing requirements.
- Ideal for team members or stakeholders without editing access.
- Displays requirement links to models and test results.
- Helps in collaborative workflows by providing transparency.
- Ensures everyone stays updated on the latest requirement changes.
04. Process Advisor

- Guides users through predefined workflows for standard compliance.
- Automates verification tasks for efficiency.
- Supports modeling standards like MAAB guidelines.
- Identifies non-compliance issues in design models.
- Helps improve process consistency and quality assurance.
05. Model Advisor

- Analyzes Simulink models for compliance with standards and guidelines.
- Detects model errors, inefficiencies, and improvement opportunities.
- Offers recommendations for improving model quality.
- Supports custom checks to meet specific project needs.
- Increases reliability and maintainability of the models.
06. Clone Detector

- Identifies duplicate blocks or subsystems within Simulink models.
- Helps eliminate redundancy to optimize models.
- Supports modularization and reuse of components.
- Reduces complexity and enhances maintainability.
- Saves time in debugging and updating models.
07. Model Transformer

- Automates modifications to Simulink models for specific tasks.
- Supports refactoring, optimizing, or customizing models.
- Reduces manual effort in model updates.
- Ensures consistency across complex design changes.
- Speeds up workflows by applying predefined transformations.
08. Metrics Dashboard

- Provides insights into model complexity and maintainability.
- Tracks design quality metrics for project management.
- Highlights areas needing improvement with visual representations.
- Ensures compliance with project standards and goals.
- Enables informed decision-making with quantitative data.
09. Model Design Dashboard

- Offers a high-level view of the model architecture and design.
- Highlights critical design issues early in the development cycle.
- Supports collaborative reviews with clear visuals and data.
- Provides actionable insights to enhance model quality.
- Assists in aligning design goals with project requirements.
10. Model Slicer

- Isolates specific execution paths in the model for analysis.
- Helps debug issues by focusing on relevant sections of the model.
- Highlights dependencies between different model elements.
- Simplifies understanding of large and complex models.
- Useful for impact analysis and design verification.
11. Simulink Test

- Enables creation, management, and automation of test cases.
- Supports simulation-based testing for real-time validation.
- Integrates with coverage analysis for complete test validation.
- Provides detailed reports and logs for traceability.
- Ensures robust and reliable testing of Simulink models.
12. Fault Analyzer

- Identifies and analyzes faults in safety-critical models.
- Simulates failure scenarios for robust system design.
- Helps improve fault tolerance and recovery mechanisms.
- Supports industries like automotive and aerospace for safety compliance.
- Enhances reliability and performance of the final product.
13. Safety Analysis Manager

- Assists in compliance with safety standards like ISO 26262.
- Analyzes safety-critical paths and identifies risks.
- Helps document and track safety requirements and their validation.
- Automates tasks to reduce manual errors in safety analysis.
- Facilitates certification processes for safety-critical systems.
14. Coverage Analyzer

- Measures model coverage during simulations to ensure testing completeness.
- Highlights untested model components for corrective action.
- Supports branch, decision, and condition coverage metrics.
- Helps optimize test cases to achieve maximum coverage.
- Ensures high-quality and reliable system performance.
15. Design Verifier

- Automates property proving and test generation using formal methods.
- Verifies that the model design meets functional requirements.
- Detects design errors and inconsistencies early in the process.
- Provides counterexamples to assist in debugging.
- Supports functional safety standards and compliance efforts.
In today’s fast-paced world, ensuring the quality, safety, and reliability of systems is more important than ever. Tools like Requirements Manager, Model Advisor, Simulink Test, and Design Verifier empower engineers to seamlessly design, test, and validate models with precision. From managing requirements to performing safety analysis, these tools make complex workflows simple and efficient.
Whether you’re working on automotive, aerospace, or industrial systems, these tools are your ultimate partners in achieving compliance, improving performance, and driving innovation. They help you analyze models, streamline processes, and ensure complete coverage for robust testing.
Step into the future of engineering with these game-changing solutions that bring accuracy, automation, and efficiency to your development process. Let’s build the next generation of smarter, safer systems together!
This was about “Model Verification, Validation, And Test Tools In Simulink“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- “Mother of All Deals”: How The EU–India Free Trade Agreement Can Reshape India’s Economic Future
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 7 Ways EV Batteries Stay Safe From Thermal Runaway