What Is A Heat Sink, Working, Why Heat Sink Is Used, Alternatives
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is a heat sink is, working, why heat sink is used, alternatives to the heat_sink, applications of heat_sinks, etc.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- What Is CMOS, Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor, Diagram.
- What Is Modulation, Demodulation, Types, Need For Modulation.
- What Is Electric Drive, Working, Applications, Advantages, Disadvantages.
What Is A Heat Sink
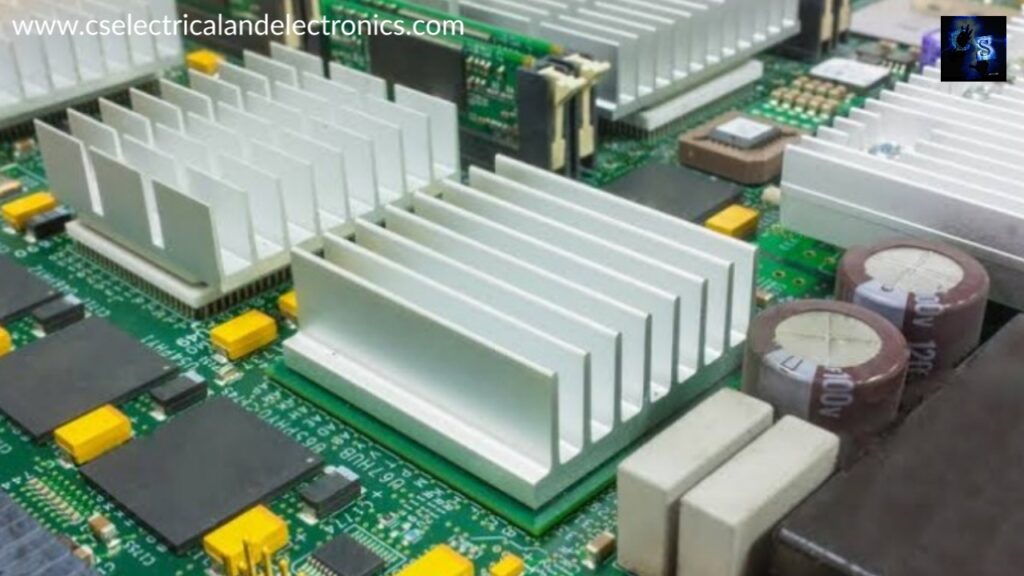
The component that increases the heat flow away from a heated device is known as a heat sink. The heat sink absorbs the heat which is generated by the electronic devices and then it transferred this heat to the surroundings. Now, these surroundings could be the air-water or oil. So, these heat sinks are available in various sizes and shapes, but the purpose of every heat sink is to remove the heat from the components. For example, used in the computer peripherals, then are used in the graphic cards, CPU, and sometimes even the ram modules.
So in high-performance ram modules, they are used as a heat spreader, and not only that they are also used in the LED models. Also used in the electronic components like high power MOSFETs and transistors. The purpose of every heat sink is to remove the heat from the electronic devices so that they can be operated in the eligible temperature range.
Why the electronic devices get heated?

Not all the energy is converted into useful work. For example, if we take the case of an LED then only some fraction of applied power is getting converted into light and the remaining power is getting dissipated in the form of heat. Every electronic device consists of a finite number of resistors and this resistor dissipates the power in the form of heat.
The processors consist of millions and billions of tiny little transistors. In this processor, all the transistors are not in use at once but they still consume some power and this energy or power is getting dissipated in the form of heat. The electronic components have some finite resistance and the power which is getting received across the current resistor is converted into heat and due to this heat, the device temperature increases which not only reduces the lifetime of the device but sometimes it can even damage the device.
That is quite important to maintain the device temperature within the acceptable range and that is the reason the heatsinks are used with electronic devices and particularly those devices which generate a considerable amount of heat.
The heat sinks operation is based on the Fourier law of heat that means whenever the temperature gradient exists in the body then hit transfers from the high-temperature section to the low-temperature section and this heat can transfer in three different ways. They are
- Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat energy by direct contact
- Convection: Convection is the movement of heat by actual motion of matter and
- Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of energy with the help of electromagnetic waves
Types of the heat sink
- Clip-on type heat sink with TO-18 transistor enclosure.
- TO-220
- TO-204AA (TO-03)
- Sheet-metal heat sink with TO-220 transistor
- Aluminium extrusion hear sink with TO-3 transistor
Working of the heat sink
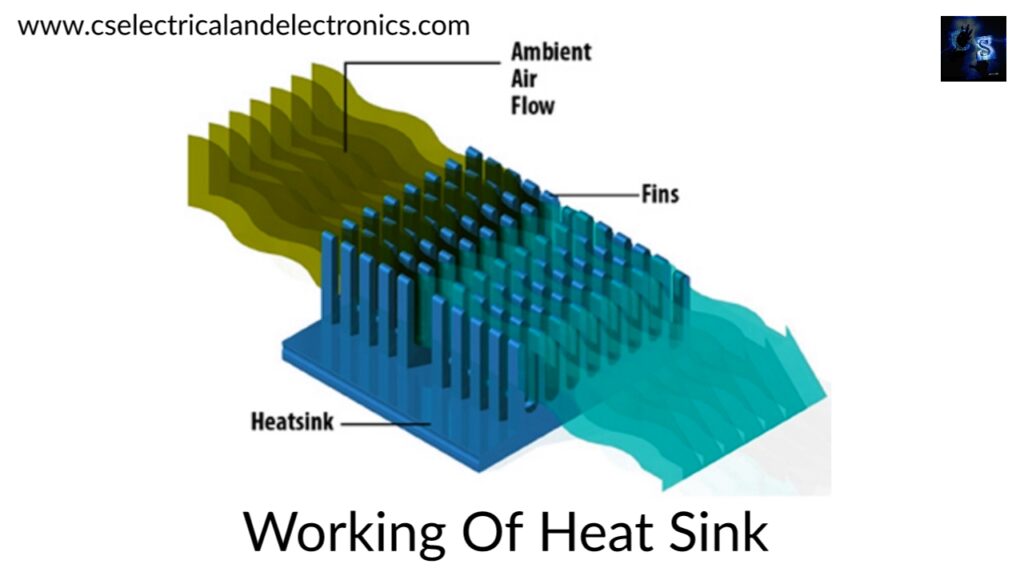
No matter what kind of heat sink is used, the purpose is to lower the case temperature because this will lower the internal or junction temperature of the transistor.
The heatsink is connected to the device and this device transfers the heat to the heat sink via conduction. Now to maximize this heat transfer the device and the heat sink should be in the proper contact, then also at the microscopic level if you see some air gap still remains between the two services and due to this air gap the heat transfer between the two surfaces will get affected.
By using the heatsink compound the air gap can be minimized and the heat transfer between the device and the heat sink can be maximized. From the heatsink, the heat is transferred to the surrounding through the convection method and a minor amount of heat is also transferred using the radiation method. The heat sink is designed in such a way that the surface area which is in the contact with the cooling medium can be maximized. The contact area of the heatsink should be at least 10 to 20 times more than the surface area of the device.
The performance of this heatsink to transfer the heat depends on multiple parameters like the area of the heatsink, the fin density, and the fin spacing, material, and airflow.
Alternatives to the heat sink
It is an improvement to the known cooling technologies by 30%. By using PINBLOC which consists of pure aluminum material with thermal conductivity of 220W/MK. It is an alternative heat sink technique for modern microprocessors and power electronics and is designed for applications with a high power density and space-saving, small fittings.
The cooling is more efficient, the less is the thermal difference between the device and the heatsink. The speed or thermal flow of a PINBLOC heat sink is faster, more homogeneous, and complex.
Applications of the heat sink
- Heat sinks are used in AC / DC converters.
- Active heat sinks are used in IC cooling systems.
- Passive heat sinks are used in LED.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students

