What Is ASIL A B C D, Purpose, Applications, Working, Examples
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss what is ASIL A B C D, the purpose of ASIL (Automotive Safety integrity levels) in functional safety ISO 26262, how to determine the ASIL levels, and we will give examples for ASIL A, ASIL B, ASIL C, and ASIL D.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read the following:
- Top 20 Interview Questions On Functional Safety In Automotive
- Top 20 AUTOSAR Interview Questions For AUTOSAR Engineers
- Top 12 Microcontroller Manufacturing Companies In The World
What Is ASIL A B C D
If you are in automobile functional safety there is an increased probability you have attended the word ASIL ratings at some moment in the period. Now, let’s attempt to facilitate what ASIL ratings are and how they have been specified as a part of ISO 26262 functional safety.
Functional safety is evolving into a better mainstream prerequisite as automotive and industrial designs continue to rise in complexity.
An Automotive Safety Integrity Level ( also known as ASIL)-decomposed (or SIL-synthesized) architecture delivers a dedicated and concentrated path to fulfilling the highest levels of diagnostic range and offers end-equipment engineers improved flexibility when designing safety-critical systems with high ASIL or SIL needs.
The record of functional safety in the context of electronic designs is derived from the demand to safely utilize machines that have the possibility to generate injury or property harm. Functional safety standards existed first specified for applications like machinery or flight because of the possible impact that could result from a safety-related defeat.
In such scenarios, a dual or multichannel strategy for functional safety was useful in delivering the highest probability of diagnostic range to help detect or control random hardware losses.
What are ASIL A, B, C, & D, and its purpose
Your typical working flow for functional safety ideas will look something similar to this as pictured above. The item definition describes the system or the array of methods to execute a function that evolves an input for the HA and RA ( known as Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment). HARA is generally completed utilizing the help of quality/system professionals and safety officials by explaining all the possible defeats and risks. Each hazard review then must be categorized based on harshness.
The ISO 26262 standard was initially issued in 2011 to support manage the functional safety of electronics and electrical systems in sequence production road automobiles.
This measure utilizes a risk category approach called Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASILs) that describe the ability of a safety-related function. The four ASILs determined by the measure are ASIL A, ASIL B, ASIL C, and ASIL D, with ASIL A indicating the lowest capability and ASIL D existing the numerous rigid.
Based on the ASIL rating a related safety goal is specified. A hazard item in the ASIL D category is more hazardous and will require more strict safety goals as corresponded to ASIL A. There is a fifth category called QM (known as quality management), which indicates if a risk is not highly adequate it needs a dedicated safety goal.
If a segment is classified as QM and since there are no dedicated safety plans then it is believed that the risks will be mitigated during the regular quality check for the feature functionality.
Examples of ASIL A, B, C, D
ASIL D: Airbag deployment, electric power steering, and antilock braking systems are some of the classic instances of ASIL D-rated applications in the automotive area.
ASIL A: For instance, even if a component is “uncontrollable” and likely to generate “life-threatening or deadly injuries” if it malfunctions, it could still be categorized as ASIL A (low risk) simply because there’s a low chance of openness to the risk. The rear lights on both sides failed.
ASIL B: Instrument cluster (loss of critical data), Radar cruise control (inadvertent braking), brake lights (both side failure.
ASIL C: In engine management like unwanted acceleration.
ASIL A-B: Body and convenience:
- Smart junction boxes
- Instrument clusters
- Heating and cooling
- Steering wheel sensor
- Body control units
- Body gateway
ASIL B-D: Powertrain
- Transmission Control
- Engine control
- Throttle control
- Value control
- Fuel injection control
- Position sensing
- Ignition
ASIL D: Safety and chassis
- Braking/Traction/Stability
- Collision avoidance
- Suspension
- Dynamic braking
- Electronics power steering
ASIL A-QM: Audio and infotainment
- Connectivity – USB, HDMI
- Movie/Game systems
- GPS/Navigation
- Satellite/Digital radio
How ASIL levels are determined?
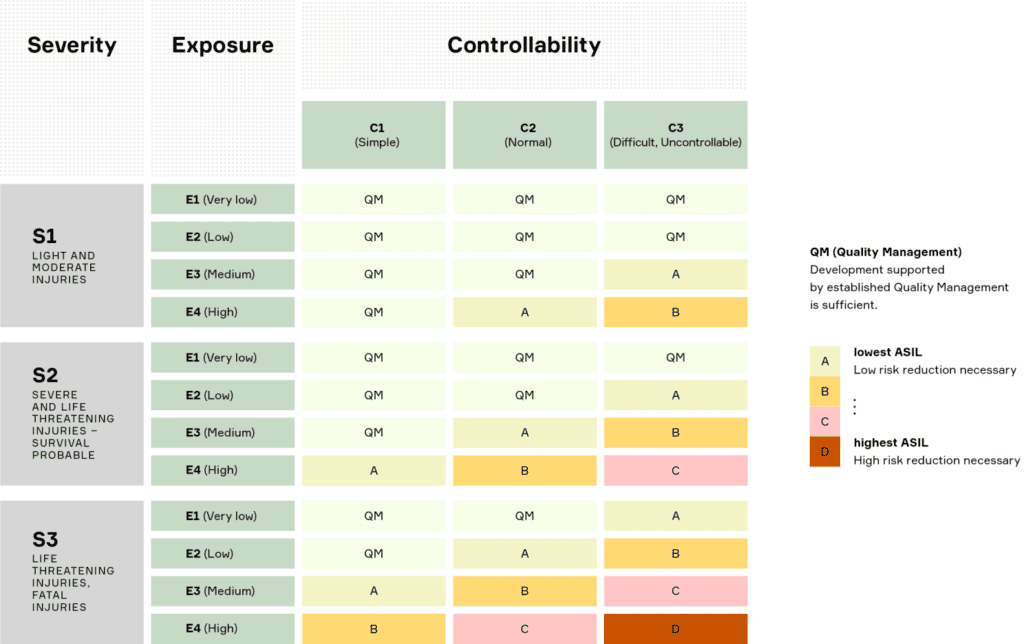
A mixture of 3 factors defines the ASIL need.
- Severity – how bad are the safety outcomes should a risk take place?
- Exposure – the possibility of happening for the given hazard and
- Controllability – how possible is the driver able to prevent the hazard scenario?
ASIL = Severity x (Exposure x Controllability)
ISO 26262 delivers us with the table to choose the ASIL rating founded on the above 3 factors. As you can notice the risk with the highest harshness rating is S3, with exposure rating E4, and with the most challenging controllability, C3 gives us the most elevated likely ASIL rating ASIL D.
There are different techniques by which professionals can come up with the S, E, and C categories but the more engineering method is by utilizing a fault tree examination/analysis or FTA. Fault tree analysis is utilized for deciding what are the reasons for a particular event.
Once you have recognized each root reason for an event a corresponding S, E, and C rating can be estimated utilizing a probability technique.
After the S, E, and C rating is determined the following above table can be utilized to choose the ASIL rating.
ASIL levels are always A, B, C, or D?
You may question can a complete feature/software/hardware can be categorized with one ASIL rating. Well guys, not necessarily. Since ASIL ratings are involved with reference to a special risk, safety officials must go down several layers to choose which interfaces result in the respective safety risk.
To provide an instance let’s take the Cruise control method. In a cruise control design, there is a software component that defines the control force input to the machine and then there is an actuator controller which certainly involves the control of the throttle which will direct to acceleration.
In this point, if the risk is acceleration above a particular threshold then the signal from the software element for the control force will organize as QM and the input to the actuators will be categorized as ASIL C.
A steering lock is a bolt pushed into the steering queue when the steering wheel is fully twisted or when the vehicle is locked. The primary goal of a steering lock is to stop unauthorized functions and operates as an antitheft device.
The functional safety purpose of a steering lock is that it shall not employ unintentionally while the vehicle is being driven. The results of the steering lock engaging unintentionally could be destructive; thus, this function is rated ASIL D.
This was about “What Is ASIL A B C D“. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read the following:
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting
- 500+ Embedded System Projects For Engineer, Diploma, MTech, PhD
- 500+ Projects For Diploma Electrical, Electronics Student, Diploma Project
- 8051 Microcontroller Timers, TCON Register, TMOD Register
- A Complete Guide To FlexRay Automotive Protocol