Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is linear integrated circuits, why it is used, working, applications of linear integrated circuits, advantages, and disadvantages of linear integrated circuits.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask question. You can also catch me @ Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- What is Cruise Control in a Vehicle, Why is it Required, It’s Working
- Top 15 Applications of Embedded Systems, Embedded System Application
- Highest Paying Jobs For Electronics Engineers, Electronics Engineer Jobs
What is Linear Integrated Circuits
A linear integrated circuit may be found in a wide range of current electrical devices. As the device runs, the circuit may accept, process, and generate a range of various amounts of energy. This sort of circuit, which is characterized by identical input and output signal levels, is commonly used in devices that need amplifiers and oscillators.
These circuits might be analog or digital in nature. Analog integrated circuits are linear integrated circuits. They vary from digital ICs in that they are capable of producing a wide range of output levels. In fact, this circuit should theoretically be able to generate an unlimited number of distinct signal levels. In contrast, a digital integrated circuit can only create a few distinct levels of output.
Because the signal output level of the circuit is a linear function of the signal input level, analog ICs are referred to as linear integrated circuits. This fact is clearly demonstrated by graphing the input and output levels. If the output and input are graphed at the same time, a straight line is produced by connecting the points. In other words, the output of the circuit varies proportionally to the input.
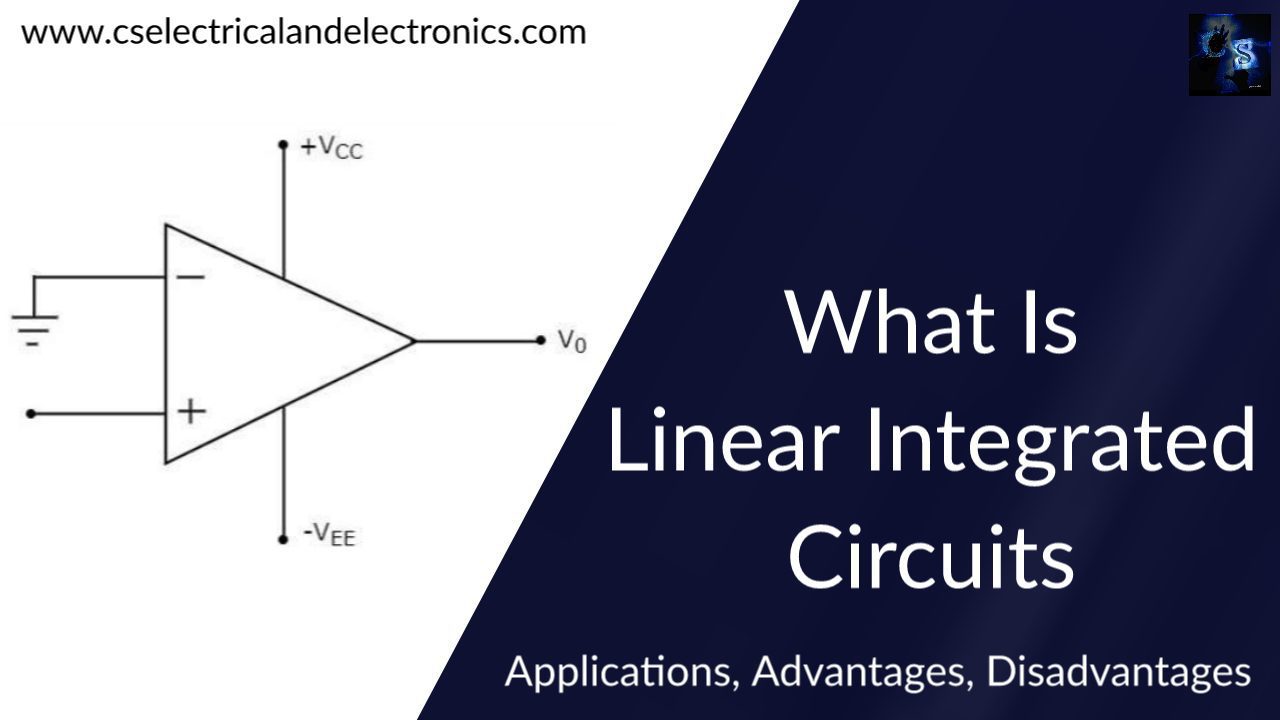
Linear integrated circuits are utilized in tasks like audio-frequency and radio-frequency amplifiers where the signal output has to fluctuate. These circuits are used in devices like audio amplifiers, DC amplifiers, oscillators, and multivibrators. An operational amplifier, or op-amp, is the most common type of linear integrated circuit, and it consists of a traditional analog circuit made up of transistors, resistors, and diodes. An op-amp has two inputs, one of which is inverting and the other of which is non-inverting.
When a signal is applied to the inverting input, the output produces a signal with the opposite phase. When a signal is applied to the circuit’s non-inverting input, the output has the same phase as the input. The inverting input and the output are connected by variable resistance, which regulates the signal’s amplification.
Advantages of Linear Integrated Circuits:
- The physical size of an integrated circuit is much smaller than that of a discrete circuit.
- When compared to full discrete circuits, an IC is relatively light.
- It is more dependable.
- Because of their tiny size, they require less energy.
- In the event of failure, it is simple to replace but difficult to repair.
- Its operating speed has been enhanced due to the lack of parasitic and capacitance effects.
Disadvantages of Linear Integrated Circuits:
- It is impossible to make coils or indicators.
- It can only handle a certain amount of power.
- It is not feasible to assemble high-grade P-N-P.
- Low-temperature coefficients are difficult to produce.
- The maximum power dissipation is 10 watts.
- Low-noise and high-voltage functioning are difficult to come by.
Applications of Linear Integrated Circuits:
01. Operational Amplifiers: The Operational Amplifier is the most popular and widely used linear IC. It is a very efficient and resourceful gadget, despite its internal complexity and many terminals. It is a key building component in analog circuits and has a wide range of applications in the electronic industry.
Signal conditioning, analog computing, analog instrumentation, unique transfer functions, and special systems design are just a few of the applications. Operational amplifiers circuits may be utilized to execute mathematical operations like subtraction, addition, integration, averaging, and differentiation by using the right feedback components.
02. Power amplifiers are used to boost the power of an input signal’s magnitude. It takes a weak signal and reproduces a louder signal at the output to drive output devices such as loudspeakers, headphones, and other devices by using an external power source.
03. Small-signal amplifiers, sometimes known as voltage amplifiers, are devices that transform low input voltage levels from sensors or audio signals into a significantly higher output value.
04. Microwave amplifiers: Traveling wave tube amplifiers are utilized for high power amplification at low microwave frequencies. They have the ability to magnify a wide range of frequencies. They’re utilized in microwave applications in the military and aerospace that operate in harsh environments.
05. RF and IF amplifiers: A radio frequency power amplifier is an electrical amplifier that transforms a low-power radio frequency signal into a higher power signal (RF). It’s utilized in microwave cavity resonators and transmitting antennas. Radar, which uses transmitting-receiving antennas, is used in weather sensing.
To sum up, The workings, applications, and benefits, and disadvantages of linear IC are covered above in this article. If the voltage and current of an analog IC are in a linear relationship, the IC is said to be linear. Linear ICs include the 8-pin Dual In-line Package (DIP)op-amp IC 741.
I hope this article ” What is Linear Integrated Circuits ” may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading ” What is Linear Integrated Circuits “.
Also, read:
- 10 Free ADAS Projects With Source Code And Documentation – Learn & Build Today
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 100+ Indian Startups & What They Are Building
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2026 Hackathons That Can Change Your Tech Career Forever
- 50 Advanced Level Interview Questions On CAPL Scripting