What Is SF6 Circuit Breaker, Sulphur Hexafluoride, Working, Applications
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is SF6 circuit breaker, working of SF6 circuit breaker or Sulphur hexafluoride, properties of it, advantages, disadvantages, etc.
If you have any doubts related to electrical, electronics, and computer science, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Top 10 Different Power Plants In The World, Hydro, Solar, Wind, Thermal
- Top 15 Transmission And Distribution Companies In The World
- Types Of Cell Balancing Topologies, Active And Passive Cell Balancing
What Is SF6 Circuit Breaker
The arc quenching medium in SF6 circuit breakers is Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas. SF6 is an electronegative gas with a high absorption rate of free electrons. In a high-pressure SF6 gas flow, the breaker’s contacts are opened, and an arc is formed between them. The gas quickly captures the conducting free electrons in the arc, forming relatively stationary negative ions. The arc’s loss of conducting electrons soon accumulates enough insulating strength to extinguish it. For high power and high voltage service, SF6 circuit breakers have shown to be particularly effective.
Construction of SF6 Circuit Breakers
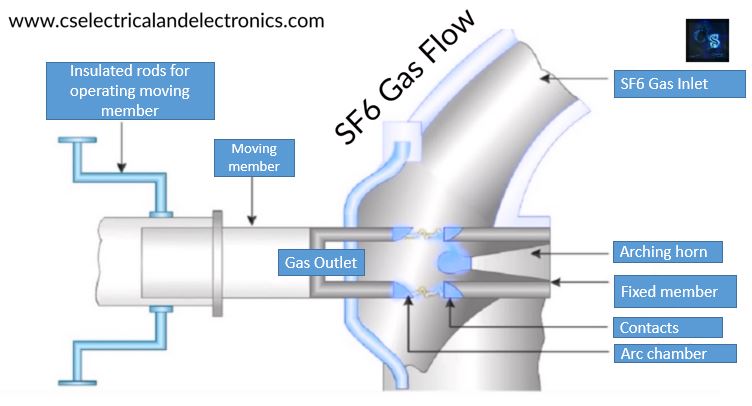
The interrupter unit and the gas system are the two major components of SF6 circuit breakers. The interrupter unit is made up of movable and stationary contacts, as well as a collection of current-carrying components and an arcing probe. It’s linked to the SF6 gas storage tank. Slide vents in the movable contacts allow high-pressure gas to enter the main tank of this machine.
Closed-circuit gas system – SF6 circuit breakers use a closed circuit gas system. Because SF6 gas is expensive, it is recycled after each operation. Low and high pressure chambers, as well as low-pressure alarm and warning switches, are included in this device. This system sounds a warning when the gas pressure is very low, the dielectric strength of the gases diminishes, and the arc quenching capability of the breakers is threatened.
Working Principle of SF6 Circuit Breaker
The contacts of the SF6 circuit breaker remain surrounded by SF6 gas at a pressure of around 2•8 kg/cm2 while the circuit breaker is closed. When the breaker is activated, the moving contacts are separated and an arc is formed between them. The opening of a valve that permits SF6 gas to flow from the reservoir to the arc interruption chamber at a pressure of 14 kg/cm2 is timed to coincide with the movement of the moving contact.
The free electrons in the arc route are quickly absorbed by the high-pressure SF6 flow, resulting in stationary negative ions that are inefficient as charge carriers. As a result, the dielectric strength of the medium between the contacts rapidly increases, causing the arc to be extinguished. After the breaker action, a series of springs seal the valve (i.e., after arc extinction).
Properties of Sulphur hexafluoride Circuit Breaker
The insulating and arc-quenching characteristics of Sulphur hexafluoride are excellent. These characteristics include,
- It’s a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and inflammable gas.
- The density of SF6 gas is five times that of air, making it exceptionally stable and inert.
- It has a higher thermal conductivity than air, which helps to cool current carrying devices more effectively.
- Because SF6 gas is very electronegative, it is easy to remove free electrons from discharge by forming negative ions.
Advantage of SF6 circuit breaker
- The major advantages of SF6 circuit breakers are their outstanding insulating, arc extinguishing, and many other features.
- The gas is chemically stable and non-flammable. There is no risk of fire or explosion since their breakdown products are non-explosive.
- Because of SF6’s strong dielectric strength, electric clearance is greatly decreased.
- Variations in air conditions do not affect its performance.
- It provides noiseless operation and eliminates overvoltage issues by extinguishing the arc at natural current zero.
- Because no carbon particles are generated during arcing, there is no change in dielectric strength.
- It needs minimal maintenance and does not require the use of a pricey compressed air system.
- SF6 is capable of removing short-line faults, switching, opening unloaded transmission lines, and acting as a transformer reactor, among other things.
Disadvantages of SF6 Circuit Breakers
- To some extent, SF6 gas suffocates. When there is a leak in the breaker tank, the SF6 gas is heavier than air and settles in the surrounding area, causing the operating staff to suffocate.
- Moisture in the SF6 breaker tank is extremely destructive to the breaker and causes several failures.
- Internal parts must be cleaned during routine maintenance in a clean, dry atmosphere.
- The particular facility is required for gas transportation and quality control.
To conclude, an SF6 circuit breaker is made up of interrupter units that can handle currents up to 60 kA and voltages between 50 and 80 kV. Several units are linked in series depending on the system voltage. SF6 circuit breakers were designed for voltages ranging from 115 to 800 kV, power ratings ranging from 10 to 20 MVA, with interrupting times of fewer than three cycles.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students