Why Low Voltage Winding Is Placed On The Core Instead Of HV Winding
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss why low voltage winding Is placed on the core instead of HV winding. Each and everything I will try to explain in a simple way.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- A Definitive Learner’s Guide For Electric Vehicle Technology Enthusiasts
- Top Applications Of Lithium-Ion Batteries / Cells In The Real World
- Top 15 IoT Projects For Electrical Engineers, Electrical Engineering Project
Why Low Voltage Winding Is Placed On Core Instead Of HV Winding
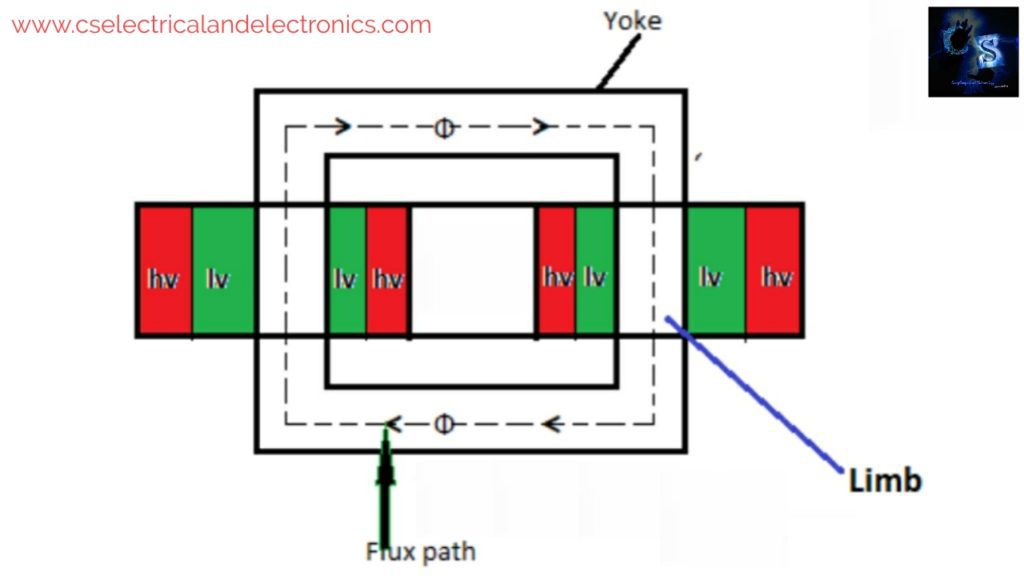
We all know that the transformer is a static device that transfers energy from one part to another part without changing power and frequency. Now, let’s see in the transformer why the low voltage winding is placed on the limb, and why not high voltage winding.
There are two reasons because of those reasons the low voltage winding is placed on the limb, such as:
01. To reduce insulation cost
02. To reduce the size of the transformer
Both the coil of cylindrical type are placed on both the limbs(the vertical portion of the core is called the limb), the low voltage coil is placed near the core whereas the high voltage coil is placed above the low voltage coil to reduce insulation cost and size of the transformer. Now I will explain how it will reduce costs.
Let’s consider two cases:
Case 01: Low voltage winding is placed on the limb
Case 02: High voltage winding is placed on the limb
Case 01: Low voltage winding is placed on the limb and of a transformer of 110KV/33KV.
We will analyze how much insulation is required.
Total insulation required to withstand voltage is = Insulation required to withstand voltage near core + Insulation required to isolate high and low voltage winding.
= 33 KV + (100 – 33)KV
= 33 KV + 77 KV
= 110 KV
Therefore, if the low voltage winding is placed on a limb first, then the insulation required is to withstand 110 kV voltage.
Case 02: High voltage winding near to limb and the transformer is of 110 kV/ 33 kV.
Total insulation required to withstand voltage is = Insulation required to withstand voltage near core + Insulation required to isolate high and low voltage winding.
= 110 KV + (110 – 33) KV
= 110 KV + 77 KV
= 187 KV
Therefore, if high voltage winding is placed on a limb, then the insulation required is to withstand 187 kV voltage.
If the insulation required is more then the size of the transformer also increases. If the insulation required is less then the size of the transformer is also reduced, this is true in case 01. If we use more insulation then the cost will also increase.
Well, guys, that’s why the low voltage winding is placed on the limb and the high voltage winding is placed above the low voltage winding.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Tag: Why Low Voltage Winding Is Placed On Core Instead Of HV Winding
Also, read:
- Types Of Errors Found In MiL, SiL, And HiL Testing
- Top 100 StateFlow Interview Questions With Answers
- Designing An Automotive Test System For ECU Validation
- Top 30 Automotive-Specific ISO Standards Every Automotive Engineer Must Know
- Hazard Identification Techniques In Functional Safety (FuSa) ISO 26262
- Troubleshooting CAN Communication Failures In A Test Environment
- Code Generation In MATLAB Simulink, Things To Be Followed For Efficient Code Generation
- Variable-Step Solvers In MATLAB Simulink: Which One To Select