Working Principle Of Tubelight, Materials Used, Advantages, Disadvantages
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is fluorescent tubelight, the working principle of tubelight, the materials used in tube light, the advantages of tubelight, and the disadvantages of the tubelight.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics And Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Different Types Of Lithium-Ion Batteries, Working, Applications
- Top 22 MATLAB Simulink Interview Questions And Answers
- Top 12 Longest Transmission Lines In The World In 2022 Must Know
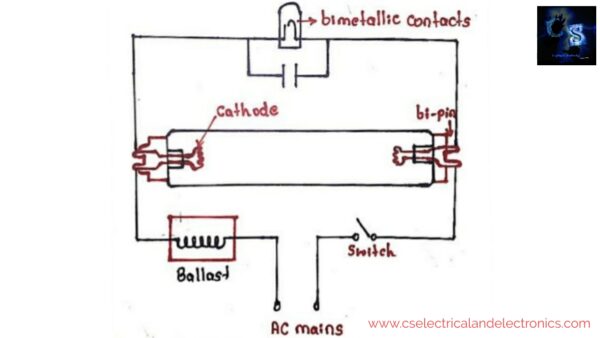
Working Principle Of Tubelight
“ As the name indicates, the tube-shaped fluorescent lamp is called tube light.”
It works on the principle of the low-pressure mercury vapor discharge phenomenon, which converts UV rays into visible rays with the help of phosphor-coated inside the tube.
Materials Used To Build Tube Light
- Filaments coils ( as electrodes )
- Glass tube with a phosphor coating.
- Mercury drop.
- Argon gas ( Inert gas ).
- Electrode shield.
- End cap.
- Glass stem.
The tubelight will not work directly on the power supply. It needs some extra components to work. Those are;
- Ballast: It may be either electromagnetic or electronic ballast.
- Starter: It is a small neon glow up the lamp. It contains a fixed contact, a bimetallic strip, and a small capacitor.
Working Principle Of TubeLight
When we switch on the fuse, the entire voltage comes across the tube light, with the help of ballast, and starter. Initially, no discharge takes place, i.e. the tube light will not glow.
At the full voltage, the glow discharge will be established in the starter. This happens because the gap of electrodes in the neon bulb of the starter is much lesser than that inside the fluorescent lamp.
Due to this full voltage, the gas which will be in the starter gets ionized. Then heats the bimetallic strip, which will be caused to be best to connect to the fixed contact. Now the current starts flowing with the help of the starter. Anyhow the ionization potential of the neon will be a little bit more than argon. But still, due to a small electrode gap, the high voltage gradient will appear in the neon bulb, and glow discharge will be started in the starter at the very first.
Due to the current, the voltage gets reduced and causes a voltage drop across the inductor. And the strip cools and breaks from the fixed contact. At this moment the large L di/dt surge appears across the inductor.
Now the large valued surge will come towards tube light electrodes and they strike the penning mixture. The gas discharge process will be continued and the current will get the path to flow through the tube light gas, because of its low resistance compared to the resistance of the starter.
When mercury discharge takes place, then it produces UV radiation, which excites the phosphor powder coating to radiate visibly light. Then during the operation of the tube light, the starter gets inactive.
Advantages Of Using Tube Light
- Energy-efficient.
- Longer life of tubes.
- Diffused light.
- Heat emission will be less.
Disadvantages Of Using Tube Light
- It contains toxic materials.
- Omnidirectional light.
- Emits UV rays that are harmful to health.
- It consumes more power compared to LEDs bulbs.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading. I think now you are clear with the working principle of tubelight.
Also read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024

