Induction Motor Diode Braking Based In MATLAB Simulink
Description
This price is for Indians, if you are from another country then your model price will be different it depends on your country’s currency- Chat with us on WhatsApp.
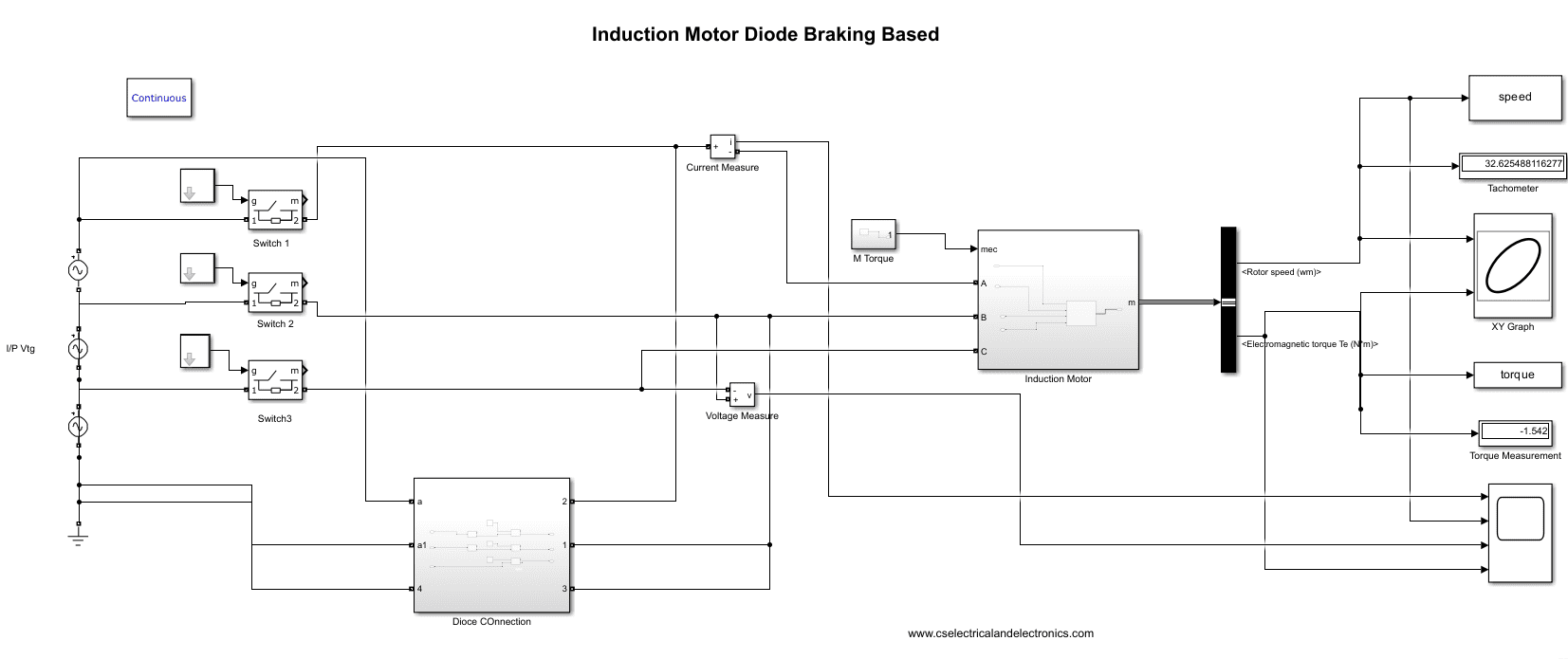
Hello guys, in this zip file, you will find the Matlab Simulink model on Diode-based braking of the Induction motor.
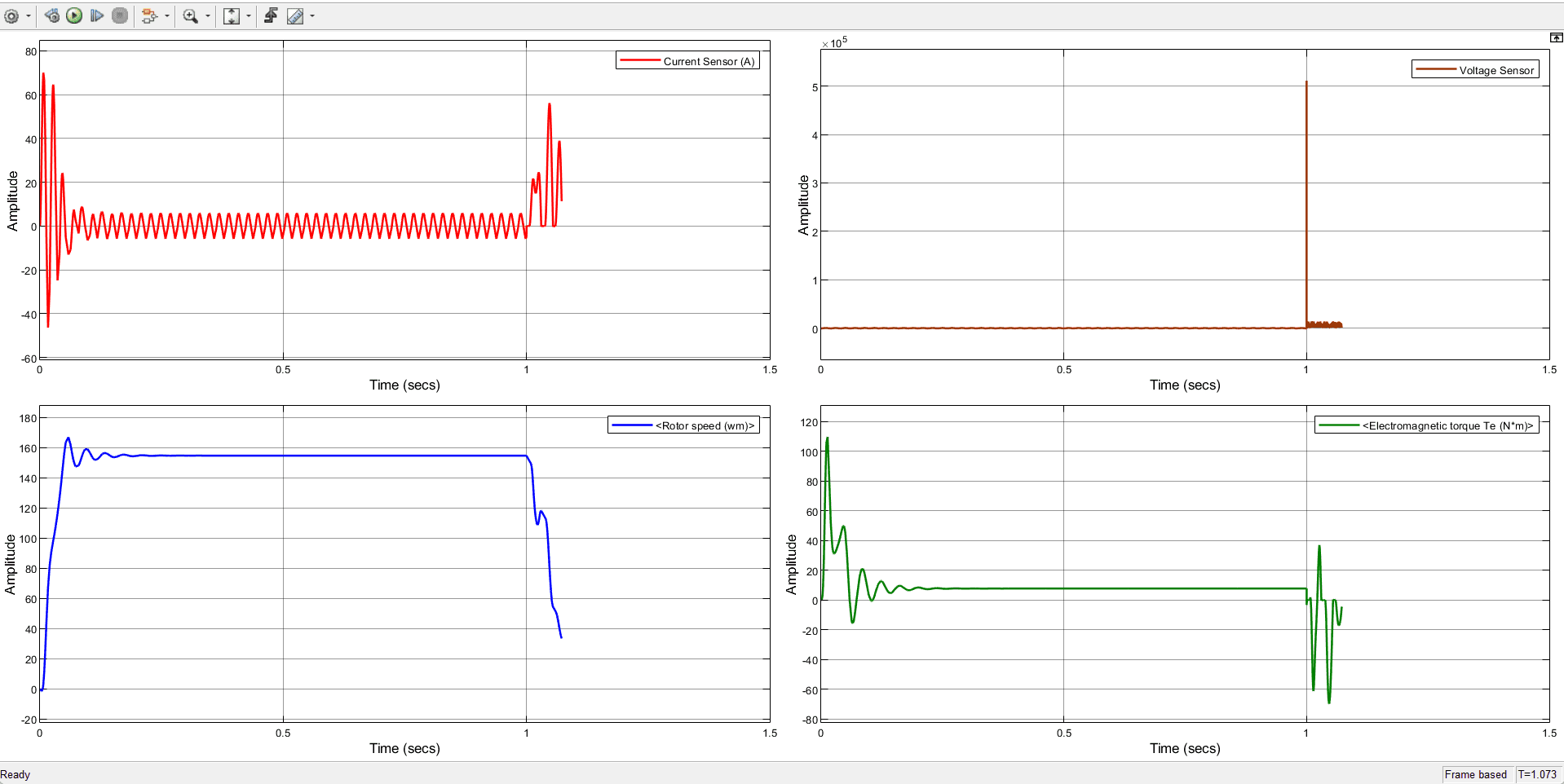
An easy and economical way to stop an induction motor is with a diode. To create a low impedance path for the back EMF produced when the motor is unplugged from the power source, a diode is used and linked in series with the motor’s windings. The magnetic field produced by the back EMF resists the spinning of the motor and causes it to decelerate quickly. This back EMF produces a current that runs between the diode and the motor’s windings.
The braking circuit’s diode must be capable of handling the maximum current and voltage that the motor can produce during braking. Usually, the circuit uses a high-power diode, such as a fast-recovery diode.
Diode braking has the advantages of simplicity and affordability. Small and medium-sized applications where the motor has a low moment of inertia or a low mass can readily apply it. Also, it effectively stops the motor abruptly and stops it from coasting.
Diode braking does have some restrictions, though. The motor’s back EMF, which is often lower than that of other braking techniques like dynamic or regenerative braking, limits the deceleration rate. However, if the braking process is not correctly managed, diode braking might damage the motor or shorten its lifespan by creating heat in the motor’s windings.
Overall, the use of diode brakes to stop induction motors in low-power applications is straightforward and efficient. However, other braking techniques, such as dynamic or regenerative braking, may be more appropriate for high-power applications. The size of the motor, the load characteristics, and the requirements unique to the application all influence the braking method selection.
The ability of diode braking to produce high-voltage transients when the diode is turned off is another drawback. The windings of the motor or other system components may be harmed as a result. The voltage transients can be reduced and the motor can be protected by adding a snubber circuit to the diode braking circuit.
Diode braking shouldn’t be used continuously or for an extended period of time because it can overheat the motor and harm it. It works well for sudden stops or short-term braking.
In applications where the motor has a low moment of inertia or a tiny mass, including fans, pumps, and small machine tools, diode braking is frequently employed. In battery-powered automobiles, where regenerative braking is neither feasible nor practicable, it is also used.
In conclusion, diode braking provides a straightforward and economical technique for stopping induction motors in low-power applications. It works well at abruptly cutting off the motor and keeping it from coasting. The pace of deceleration, heat generation, and voltage transients are its limitations, though. It works best for quick stops or emergencies; for high-power applications, alternative braking techniques should be taken into account.
Disclaimer:
Please note, that this product is owned by us, and if you upload this file on Youtube or Internet after purchasing it. Then you will get a copyright complaint from us.
Thanks & regards,
CS Electrical And Electronics Team
Chat Us On WhatsApp For Support: Click Here