Queue In Data Structure And Algorithm Using C, Code, Explanation,
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss queue in data structure and algorithm using c, code of queue in the data structure, types of queue, explanation with diagram, etc.
If you need an article on some other topics then comment us below in the comment box. You can also catch me @ Instagram – Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- Search In Data Structure, Linear, Binary, Explanation, Code, Algorithm.
- Linked List In Data Structure, Explanation, Algorithm, Code, Questions.
- Stack Operation In Data Structure, Definition, Code, Push, Pop, Full.
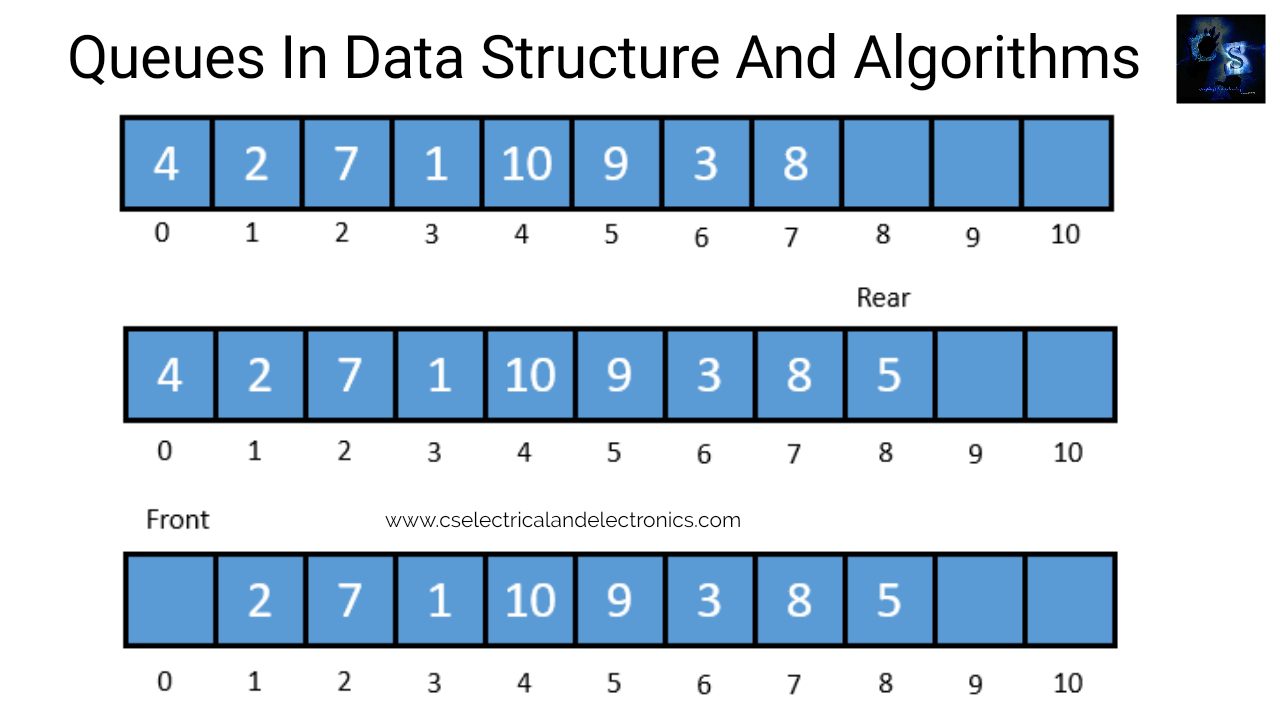
Queue In Data Structure

Assume we require to add another element by value 5, then REAR would be incremented by 1 and that value would be saved at the position pointed by REAR. The queue after addition would be as shown in block 02. Here, FRONT = 0 and REAR = 8. Each time a different element has to be added, we replicate the same procedure. If we need to delete a component from the queue, later the value of FRONT will be incremented. Deletions are made from just this end of the queue. The queue after deletion will be as shown in block 03.
Program to perform queue operation?
In this code, we can add a new element, delete an element, and we can also check whether the queue is full or empty, we can also display all elements.
001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050 051 052 053 054 055 056 057 058 059 060 061 062 063 064 065 066 067 068 069 070 071 072 073 074 075 076 077 078 079 080 081 082 083 084 085 086 087 088 089 090 091 092 093 094 095 096 097 098 099 100 101 102 103 104 | #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>struct queue{ int size; int f; int r; int * arr;};int isEmpty(struct queue *q){ if(q->r==q->f){ return 1; } return 0;}int isFull(struct queue *q){ if(q->r==q->size-1){ return 1; } return 0;}void enqueue(struct queue *q, int val){ if(isFull(q)){ printf("This Queue is full\n"); } else{ q->r++; q->arr[q->r]=val; }}int dequeue(struct queue *q){ int a = -1; if(isEmpty(q)){ printf("This Queue is Empty\n"); } else{ q->f++; a = q->arr[q->f]; } return a;}int main(){ int O, val; struct queue q; q.size = 100; q.f = q.r = -1; q.arr = (int*)malloc(q.size*sizeof(int)); printf("1: For Enqueue\n"); printf("2: For Dequeue\n"); printf("3: To check empty\n"); printf("4: To check full\n"); printf("5: Display\n"); printf("6: To exit\n"); while(q.r != q.size-1){ printf("Enter the operation you want to perform\n"); scanf("%d", &O); switch(O) { case 1: printf("Enter the element you want to store\n"); scanf("%d",&val); enqueue(&q, val); printf("Element is %d\n",q.arr[q.r]); break; case 2: printf("Dequeueing element %d\n", dequeue(&q)); break; case 3: if(isEmpty(&q)){ printf("Queue is Empty\n"); } else printf("Not Empty\n"); break; case 4: if(isFull(&q)){ printf("Queue is Full\n"); } else printf("Not full\n"); break; case 5: printf("Display All Values Stored\n"); while(q.f!=q.r) { q.f++; printf("Element are %d\n",q.arr[q.f]); } break; default: exit(0); } } return 0;} |
Output:
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | 1: For Enqueue2: For Dequeue3: To check empty4: To check full5: Display6: To exitEnter the operation you want to perform1Enter the element you want to store22Element is 22Enter the operation you want to perform1Enter the element you want to store44Element is 44Enter the operation you want to perform1Enter the element you want to store66Element is 66Enter the operation you want to perform4Not fullEnter the operation you want to perform3Not EmptyEnter the operation you want to perform2Dequeueing element 22Enter the operation you want to perform5Display All Values StoredElement are 44Element are 66Enter the operation you want to perform |
Types of queues
- Circular Queue
- Deque
- Priority Queue
- Multiple Queue
Applications Of Queue
01. Queues are generally used as waiting lists for a single shared device like a printer, disk, CPU.
02. Queues are utilized to transfer data asynchronously (data not necessarily received at the same rate as sent) between two processes (IO buffers), e.g., pipes, file IO, sockets.
03. Queues are employed as buffers on MP3 players and portable CD players, iPod playlist.
04. Queues are used in Playlist for the jukebox to add songs to the end, play from the front of the list.
05. Queues are used in the operating system for handling interrupts. When programming a real-time system that can be interrupted, for example, by a mouse click, it is necessary to process the interrupts immediately, before proceeding with the current job. If the interrupts have to be handled in the order of arrival, then a FIFO queue is the appropriate data structure.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 100+ C Programming Projects With Source Code, Coding Projects Ideas
- 1000+ Interview Questions On Java, Java Interview Questions, Freshers
- App Developers, Skills, Job Profiles, Scope, Companies, Salary
- Applications Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Renewable Energy
- Applications Of Artificial Intelligence, AI Applications, What Is AI
- Applications Of Data Structures And Algorithms In The Real World
- Array Operations In Data Structure And Algorithms Using C Programming
- Artificial Intelligence Scope, Companies, Salary, Roles, Jobs
- AWS Lambda, Working, Cost, Advantages, Disadvantages
- AWS Technical Interview Questions, Top 200+ AWS Questions
- Battery Management Systems Using Artificial Intelligence
- Best Engineering Branch For Future
- Best Programming Languages For Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- Big Data, Evolution Of Big Data, Benefits Of Big Data, Opportunities
- Bit Operation In C Programming With Example & Applications
- Blockchain Projects For Computer Science Engineers
- Blockchain Technology, History, Working, Applications, Advantages
- Brain Computer Interfaces Technology, Beyond AI, ML, IoT, Blockchain
- C Language Interview Questions On Programs With Output
- C Program On Arrays With Output For Placement Exams