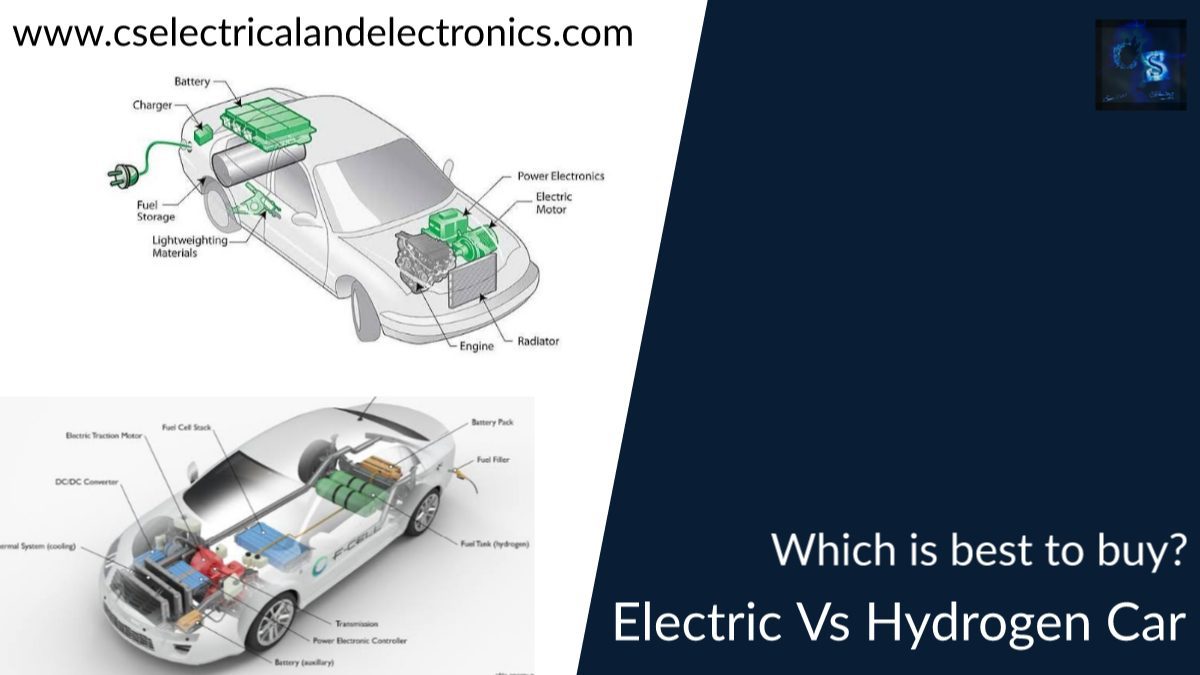
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss electric vehicles Vs hydrogen vehicles, which is best to buy, and we will also share detailed benefits of electric vehicles and hydrogen vehicles.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- Top 15 Technologies in CyberSecurity, Cybersecurity Technology
- What Is VCU (Vehicle Control Unit), Purpose, Working, Drawbacks
- Top 20 Interview Questions On RTOS, Real-Time Operating System
Electric Vehicles Vs Hydrogen Vehicles
Zero-emission vehicles, such as electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), have the potential to lower air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions because they have no exhaust emissions. The two technologies do, however, differ significantly in certain important ways.
The vehicles’ powertrains are one of the key differences. Electric vehicles (EVs) are propelled by electricity stored in batteries that are charged by plugging them into electrical outlets. Contrarily, FCVs are propelled by hydrogen gas that is kept in a fuel tank and transformed into electricity by a procedure known as electrolysis.
The vehicles’ range and refueling times are further different. While FCVs can refuel more quickly than EVs, EVs can often drive farther on a single charge than FCVs can on a single tank of hydrogen. An EV can take many hours to charge completely, but an FCV’s hydrogen tank can be filled in just a few minutes.
The infrastructure required to support these vehicles varies as well. Although both types of stations are becoming more common, there are now far more charging stations for EVs than hydrogen fueling stations for FCVs.
Overall, both EVs and FCVs have the potential to be a part of the transportation of the future, and the decision between them will be based on a number of variables, including individual preferences, driving requirements, and the accessibility of infrastructure for charging or refueling.
Which will be the future? An electric vehicle or a hydrogen vehicle?
Which technology will be used more frequently in the future is hard to forecast. Both hydrogen fuel cell cars (FCVs) and electric vehicles (EVs) have advantages and disadvantages.
There are many EVs on the market, and the technology is mature. They provide a smooth and silent driving experience and are also getting more and more inexpensive. However, they can take a while to charge and might not be suitable for extended drives, particularly in places with a lack of adequate charging infrastructure.
On the other hand, FCVs have a larger driving range and can be refueled more quickly than EVs. They produce just water vapor as a byproduct and are zero-emission automobiles. However, compared to EV charging stations, the infrastructure required to support FCVs, such as hydrogen filling stations, is less accessible. Currently, FCVs cost more than EVs as well.
Both technologies might advance further in the future, and it’s likely that a variety of technologies will be combined to power vehicles in the future. In the end, a multitude of factors, such as consumer preferences, governmental regulations, and the availability of infrastructure, will determine whether a certain technology is adopted.
Benefits of Electric vehicles and Hydrogen vehicles?
Both hydrogen fuel cell cars (FCVs) and electric vehicles (EVs) are seen as being more environmentally friendly than conventional gasoline-powered automobiles. Both kinds of vehicles have the potential to lessen air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which can benefit the environment and the general public’s health. Here are several advantages of EVs and FCVs in particular:
Electric cars:
01. No tailpipe emissions: Since EVs run on electricity rather than gasoline, they don’t emit any tailpipe emissions. This indicates that they do not produce the same amount of greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution as gasoline-powered vehicles.
02. Low running costs: Compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, EVs are typically cheaper to operate. Since electricity is often less expensive than gasoline and electric vehicles have fewer moving components, they require less maintenance and last longer.
03. Operating quietly: EVs are far quieter than gasoline-powered cars, which can help reduce noise pollution.
Vehicles using hydrogen fuel cells
01. No tailpipe emissions: Because FCVs are powered by electricity rather than internal combustion engines, they do not emit any tailpipe emissions. However, FCVs generate energy through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, which only yields water as a byproduct, as opposed to EVs, which do so by using a battery.
02. Fast refueling: FCVs are a practical option for long-distance travel because they can be refueled in a comparable amount of time as it takes to fill a tank with gasoline.
03. High range: FCVs are a wonderful alternative for customers who need a vehicle with a long-range because they can typically travel further on a single tank of fuel than EVs can on a single charge.
It’s important to remember that EVs and FCVs each have particular difficulties and restrictions. For instance, EVs are still more expensive to buy upfront than gasoline-powered cars, despite becoming more affordable. On the other side, FCVs are currently rather uncommon and might be challenging to locate at hydrogen refueling facilities.
This was about “Electric Vehicles Vs Hydrogen Vehicles“. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 100+ Indian Startups & What They Are Building
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 2024 Is About To End, Let’s Recall Electric Vehicles Launched In 2024