What Is VCU (Vehicle Control Unit), Purpose, Working, Drawbacks
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss what is VCU or vehicle control unit, its purpose of VCU, its working, categories of VCU, advantages, and limitations.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- What Is TPT (Total Processing Time) In MATLAB Simulink, Purpose
- Troubleshooting Electronic Circuit? Top 10 Steps For Engineers
- What Is Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS), Applications
What Is VCU (Vehicle Control Unit)
The vehicle control unit (VCU) is one of the major components of an electric vehicle. It is the major controlling part for the whole vehicle, including the drive train, power control, user inputs, and user outputs.
It is the brain of the automotive that is equipped with modern features. Each system has a separate VCU, like engine control, ABS control, steering, accelerator VCU, etc. It takes value from all the sensors, decides what to do, and gives the instruction to be carried out.
Purpose of a vehicle control unit
The purpose of VCU is to regulate the timing of ignition, regulate the air-to-fuel mixture, regulate variable valve timing and idle speed, and reduce vehicular pollution. The vehicle controller, the most crucial component of a pure electric vehicle control system, is in charge of overall control, coordination, and monitoring of the running state of the vehicle.
It is also responsible for the operation of the pilot signal and the signal from the sensor via the control strategy inherent to the vehicle controller to the electronic control unit, energy management, fault diagnosis, and the running state control and monitoring of the vehicle, among other functions, and through the LCD.
Working of VCU (vehicle control unit)
VCU serves as the command and control center. Its primary functions are to analyze transducers’ data and provide orders to executors or actuators to complete each action. VCU transmits different control instructions to sub-systems controllers, sending orders to a lower system to govern the whole vehicle based on information about the driver’s activity, vehicle movement, and general battery state.
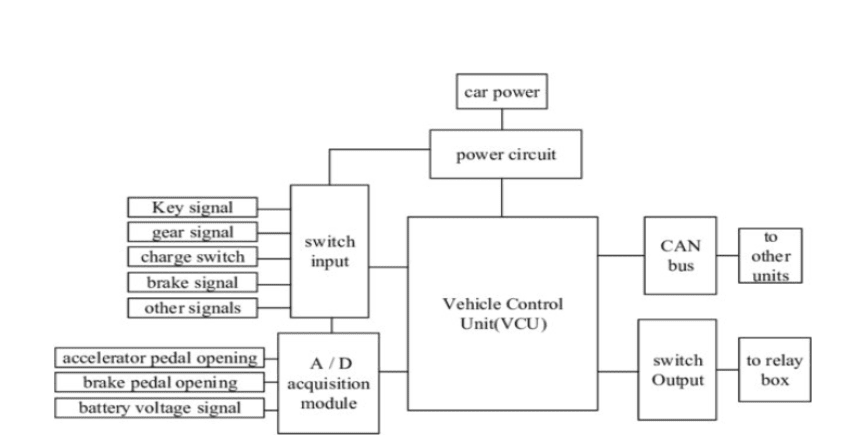
The Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) is the hub of communication between the various electric vehicle subsystems and coordinates their functioning. The main components include a power supply, I/O circuitry, analog inputs, and a CAN communication module. In a modern vehicle, the basic control principle of engine operation is still based on combustion; the only difference is that VCU now controls the process.
The VCU controls the opening and closing of the input/output valves by taking input from the accelerator of the vehicle’s pedal. The VCU is also responsible for calculating the amount of fuel and spark injection. The VCU results in accurate synchronization, rendering more power and efficiency and highly functional engines to the vehicles. VCU-controlled vehicles can deliver higher efficiency as compared to mechanical automobiles. The VCU in automotive is subdivided into three categories.
Powertrain control module
In many instances, almost every engine function (and gearbox) is managed by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), an electronic control center. It regulates the ignition, fuel supply, valve timing (in VVT engines), emissions, turbo boost pressure (in turbocharged engines), idle speed (in non-turbocharged engines), throttle position (in turbocharged engines), and cruising speeds. The seven symptoms of bad PCM,
- Check engine light is on
- The car won’t start or starts roughly
- Sudden loss of gas mileage
- Failed your emission test
- Engine stutters or stalls
- Erratic or random shifting
- Receiving a PCM-related error code
Body control unit
The electronic modules in today’s automobiles have allowed for an explosion in both the variety and sophistication of available functions. This is mostly attributable to the fact that people in the automobile business worldwide are becoming more concerned with providing their customers with a secure and pleasant ride.
When communicating with other ECUs in the car, the Body Control Module relies on the vehicle’s bus system (CAN, LIN, etc.). By transmitting and receiving signals via the nerves, this module may be compared to the brain, which controls many bodily functions (vehicle BUS). When communicating with other ECUs, a BCM unit (an ECU) serves as a hub or gateway. Because of this, less stringent requirements for cabled plug-in connections between ECUs in the car are needed.
Chassis control module
The chassis control module will maintain the integrity of your vehicle’s key safety systems. It collects information from different suspension, steering, and braking sensors. The module then provides control signals to the ABS or other systems to maintain the vehicle’s stability and safety in all situations.
Having a VCU for each system’s operations helps simplify and organize the whole thing. However, there may also be a few potential drawbacks to consider. Let’s look at them both!
Advantages of VCU or vehicle control unit
- The Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) coordinates the function of the various vehicle subsystems to meet performance goals such as optimizing fuel efficiency and minimizing exhaust emissions.
- The VCU serves as the central processing unit of the hybrid electric vehicle system.
- Their capabilities will directly impact the dependability and performance of HEVs.
- It acts as the control center for the overall electric vehicle.
- The centralized nature of the architecture makes it simple to pinpoint the location of the problem.
- A lower total number of ECUs results in a shorter time-to-market and lower overall design cost.
Limitations of VCU
- Since several Sensors must be wired directly to the vehicle control unit, this results in a tangled web of cables and connectors.
- Having a single VCU usually requires a larger board, which might take up a significant amount of space.
- Since problems with the primary VCU might have severe consequences, it is essential to have a redundant system as a backup. This results in additional expenses once again.
This was about “What Is VCU (Vehicle Control Unit)“. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 500+ Embedded System Projects For Engineer, Diploma, MTech, PhD
- 500+ Projects For Diploma Electrical, Electronics Student, Diploma Project
- 8051 Microcontroller Timers, TCON Register, TMOD Register
- Advancements In 3D Printing Technology And It’s Future
- Advancements In Power Electronics For Energy Efficiency
Author Profile
- Chetu
- Interest's ~ Engineering | Entrepreneurship | Politics | History | Travelling | Content Writing | Technology | Cooking
Latest entries
 All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry
All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose,
All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose, All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers All PostsMarch 22, 2024Driver Monitoring Systems In Vehicles, Working, Driver Sleepy Alert
All PostsMarch 22, 2024Driver Monitoring Systems In Vehicles, Working, Driver Sleepy Alert