PWM, Definition, Working, Techniques, Advantages, Disadvantages, Uses
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. In this article, we will discuss PWM or Pulse Width Modulation, working, different types of PWM techniques, advantages, disadvantages, and applications or uses.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- What Is Emulator, Debugger, Assembler, Compiler In Embedded Tools
- Difference Between Dual-core And Quad-core Processors
- What Is Infineon Microcontroller, Working, Features, Applications
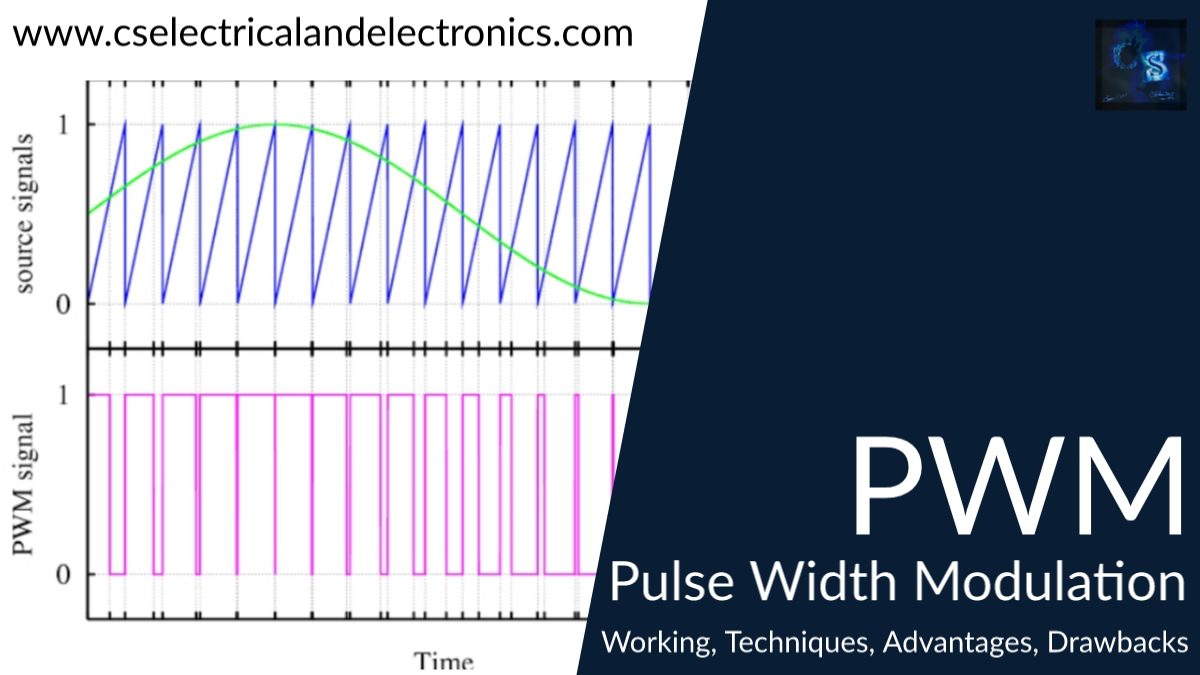
PWM – Pulse Width Modulation
If you are from electrical and electronics background then you have heard about the term PWM which stands for pulse width modulation. You will study PWM in subjects like power electronics, analog electronics, SMPS, etc. Here, in this article, I will discuss what is P_WM, why it is required, and a lot more things I will share.
Nowadays, due to an increase in smart devices the energy to the smart devices must be supplied smoothly without any power losses. P-WM plays a major role in offering smooth energy.
What is PWM?
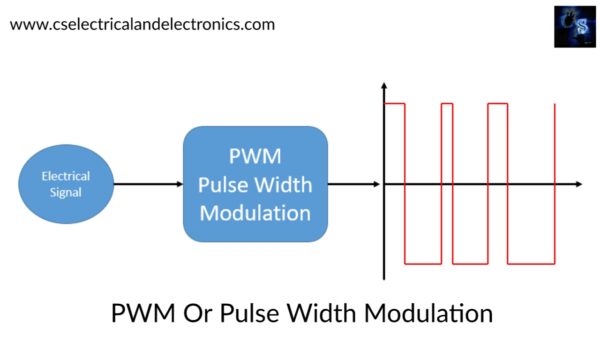
The PWM or Pulse Width Modulation is a technic of minimizing the average power delivered by an electrical supply, by properly chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of supply or voltage fed to the load (motor, light, device) is controlled by turning on and off the switch between supply and load. Here the switching On and Off is done at a fast rate.
Pulse width modulation is a great technic for controlling the amount of energy supplied to a load without dissipating the energy.
Working of PWM
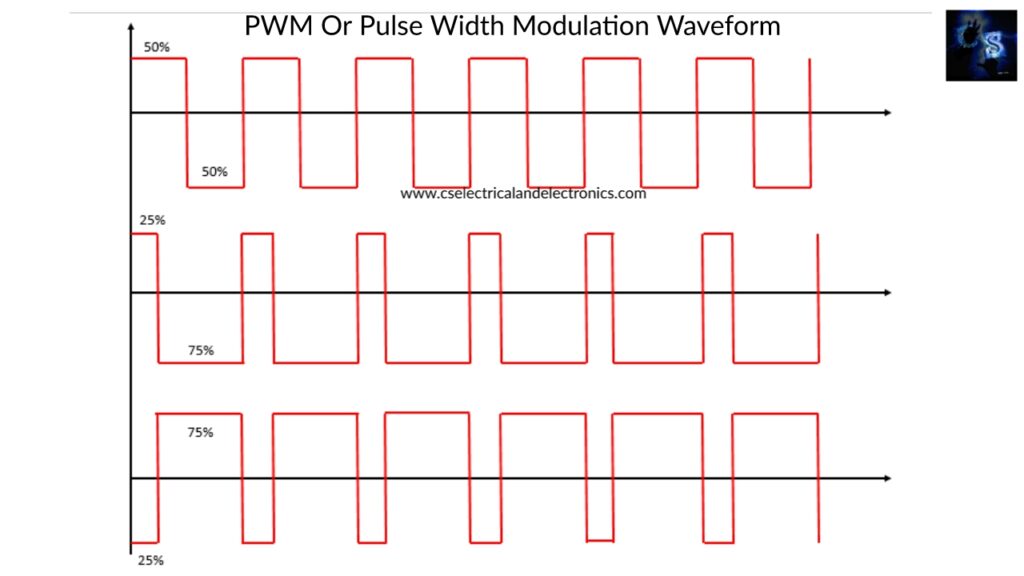
PWM works by continuously switching on and off the device at a fast rate in terms of KHz. The switching takes place 1000’s times per second, when the switch is on the energy is supplied to load and when the switch is off the energy is not supplied. By pulse width modulation we can chop the magnitude based on our requirement by changing the duty ratio. If the duty ratio is 50% then the on-time and off time will be the same. Below this image shows the output waveform for different duty ratios.
Advantages Of PWM Or Pulse Width Modulation
- Cheap to make.
- Low power consumption.
- Can utilize very high frequency (50 – 100 kHz).
- PWM techniques enable greater efficiency of DC motors.
- This method improves speed control and reduces power loss.
- Internal motor resistance can be easily overcome.
- The pulse reaches full supply voltage which in turn produces more torque.
- High power handling capability.
- Efficiency up to 90%.
- Low noise
Disadvantages Of PWM Or Pulse Width Modulation
- Increase the complexity of the circuit.
- Radiofrequency interference.
- Voltage spikes – TO reduce the use of snubber circuits.
- Electromagnetic noise
Applications Of PWM Or Pulse Width Modulation
The P_WM is used in:
- Telecommunication for encoding purposes.
- Voltage regulation
- Power delivery
- Amplification
- In ADC
- It is used to control the speed of motors.
This was about “PWM – Pulse Width Modulation“. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students