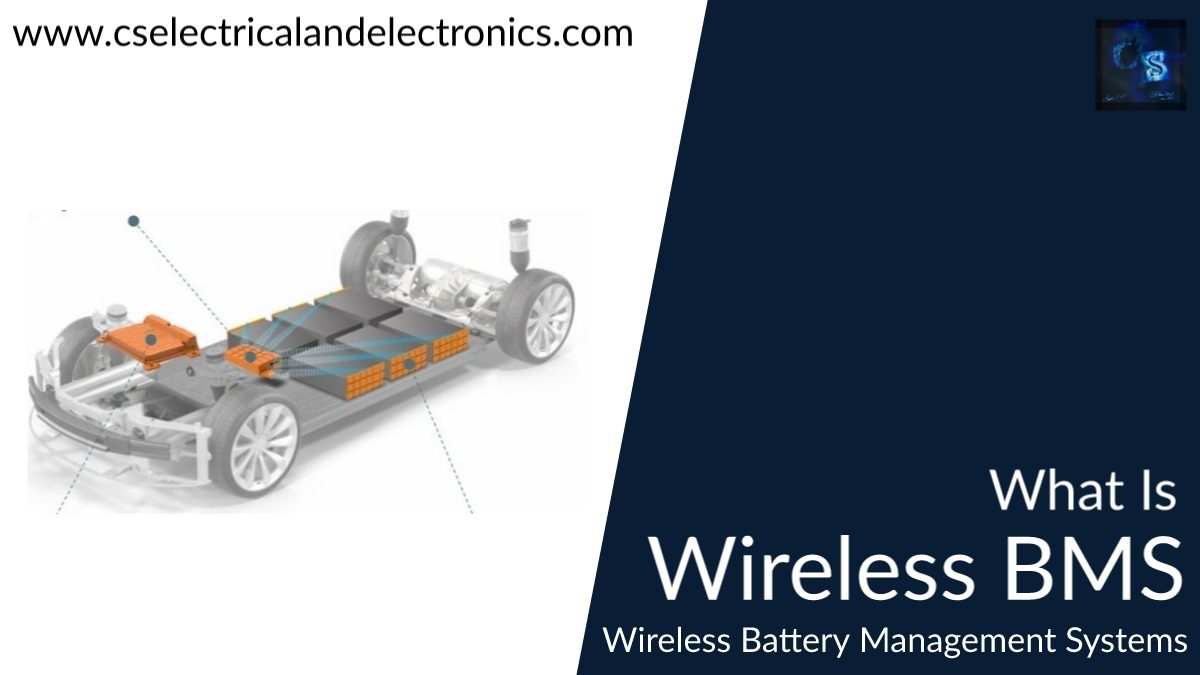
What Is Wireless BMS, Battery Management System, Benefits, Working
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss what wireless BMS is, battery management systems, the benefits of wireless BMS, and working, and we will also share the block diagram of wireless BMS.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- What Is Thermal Management In Electric Vehicle, Purpose, Causes
- Top 12 Latest Technologies In The Power System That Will Change Future
- How To Avoid Thermal Runaway In Electric Vehicles, EV Bikes, EV Car
What Is Wireless BMS
As we all know that the EV is the future of our world, and all fuel combustion engines will be soon replaced by electric vehicles. And it is sure that the number of electric vehicles is going to be increased on large scale. The energy for electric vehicle motors is fed by a lithium-ion battery pack and to monitor & manage the battery pack for efficient usage, a battery management system is needed.
At present, the all-electric vehicle has a wired battery management system, and still, much research is going on wireless battery management systems. In traditional battery management systems (BMS), there is a complicated wire harness between battery cells and battery sensing modules. Individually slave BMS can generally collect sensorial data from 8 to 12 battery cells. In demand to accommodate a considerable number of battery cells, a set of the slave controller is linked to a master BMS, where the gathered data from the battery cells is stored for additional processing.
Lithium-Ion batteries need multiple cares if they are predicted to operate reliably over a prolonged period. They cannot be used to the extreme end of their SoC or state of charge. The capacity of lithium-ion cells decreases and splits over time and use, so every cell in a system must be handled to keep it within a restrained SOC. To deliver adequate power for a vehicle, 10’s or 100s of battery cells are needed, configured in a long series generating as much as 1000V or higher. The battery electronics must operate at this very high voltage and reject common-mode voltage effects, while differentially measuring and controlling each cell in these strings. The electronics must be able to transmit data from each cell in a battery stack to a major point for processing.
In addition, working a high-voltage battery stack in a vehicle or other high-power applications sets tough conditions, such as operation with powerful electrical noise and wide working temperatures. The battery management electronics are anticipated to maximize operating range, lifetime, security, and dependability while underestimating the cost, size, and weight. Steady advancements in Linear’s battery cell monitoring ICs have allowed high execution, advanced life, and dependability of battery packs in motorcars today. Wireless BMS vows to further enhance the security and reliability of the entire battery system.
Although the hierarchical Battery Management System architecture is widely acknowledged and utilized, it has some major drawbacks. The wire harness can generate different issues such as material connection failure under a vibratory environment, transmission error under EMI, the complexity of battery pack design, and problems in automated manufacturing.
These issues often result in lower productivity and lower trustworthiness. More significantly, the price of wire harnesses, connectors, protective suits, isolators, and manual work is a substantial portion of the general battery pack cost. For a specific automobile or static application, the number of battery cells varies from a hundred to a few thousand, and the expanded number of battery cells aggravates the issues mentioned above. In this article, we show a new wireless battery management system, or WBMS, which is founded on wireless sensor grid technologies.
The latest BMS architecture totally stops the sensing wire-harness between sensors and the Battery Management System modules. We hope that the WBMS will allow battery packs that are shorter, more delicate, more reliable, more comfortable to automate the manufacturing process, and most notably, low-cost.
Difference between wired BMS and wireless BMS
| Considerations | Wired BMS | Wireless BMS |
| 01. Reliability | • Wiring is trustworthy and completes functional safety measures but can break over time • Circle Architecture features built-in duplicative cables in both directions • Can be more difficult to repair | • No wires to hold • Technique must overwhelm harsh automotive radio-frequency conditions and non-line-of-sight challenges |
| 02. Configuration flexibility and serviceability | • Less flexibility with a bigger overall footprint • More challenging to service, modular once lines are separated | • More undersized footprint allows design flexibility and better flexible arrangement within the vehicle • Easier to service |
| 03. Weight | • Specific reliability standard • Improves overall vehicle volume and complicatedness | • Reduces overall vehicle weight and complicatedness |
| 04. Measurement | • Time-synchronized measures of voltage and current must bear all the path up and down, driving delay between readings • Delayed measurement quality can enhance performance | • Wireless system inherently allows time-synchronized measures • Offers the capability to add more synchronized sensing abilities |
| 05. Secure | • Organized and fully secured system transmission | • Potential to breach badly developed systems that lack safety protocols |
Benefits of wireless BMS
Flourishing and long-term electrification depend on prolonging battery life, so a BMS in electrified equipment is required. So, it’s a fair query to ask, what is the usefulness of adding some wireless stuff to the design?
- Fewer lines and wire reins: Anytime you can reduce wiring harnesses in an automobile or clear them entirely, you’re keeping useful space and lowering total weight. The cables utilized in these methods are also not affordable and are among the weightiest parts in an EV, so eradicating these passes conserving onto the end buyer.
- Modularity: Utilizing a wireless connection stops the requirement for a proprietary line assembly. Everything about a battery system can be completed as more modular, permitting 3rd party retailers to innovate and experience this space.
- More straightforward maintenance: When there are more irregular cables concerned in linking the BMS to the battery cells, the cells, and other electronics are more comfortable to access, sustain, and replace when required. Using a versatile wireless BMS rather than a proprietary wired BMS allows a plug-and-play system to develop and maintain.
- More immediate time to market: Operating with a universal wireless protocol is easier than utilizing a mass of lines and wiring harnesses, which may be redesigned for individual iterations of each model. Proceeding wireless stops this and decreases the time to market.
This was about the “Battery Management System”. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ Electronics Projects For Engineers, Diploma, MTech Students
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students