What is XCP (Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol)? Introduction, Working, Purpose, Applications
Hello guys, welcome to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss what is XCP, its introduction and working, and its purpose and applications.
Ask questions if you have any electrical, electronics, or computer science doubts. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read:
- What Is HiL, Hardware In Loop, Working, Tools Used In HiL
- What Is CPC (Common Powertrain Controller) ECU, Working of CPC
- UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services) Tutorials For Automotive Engineers
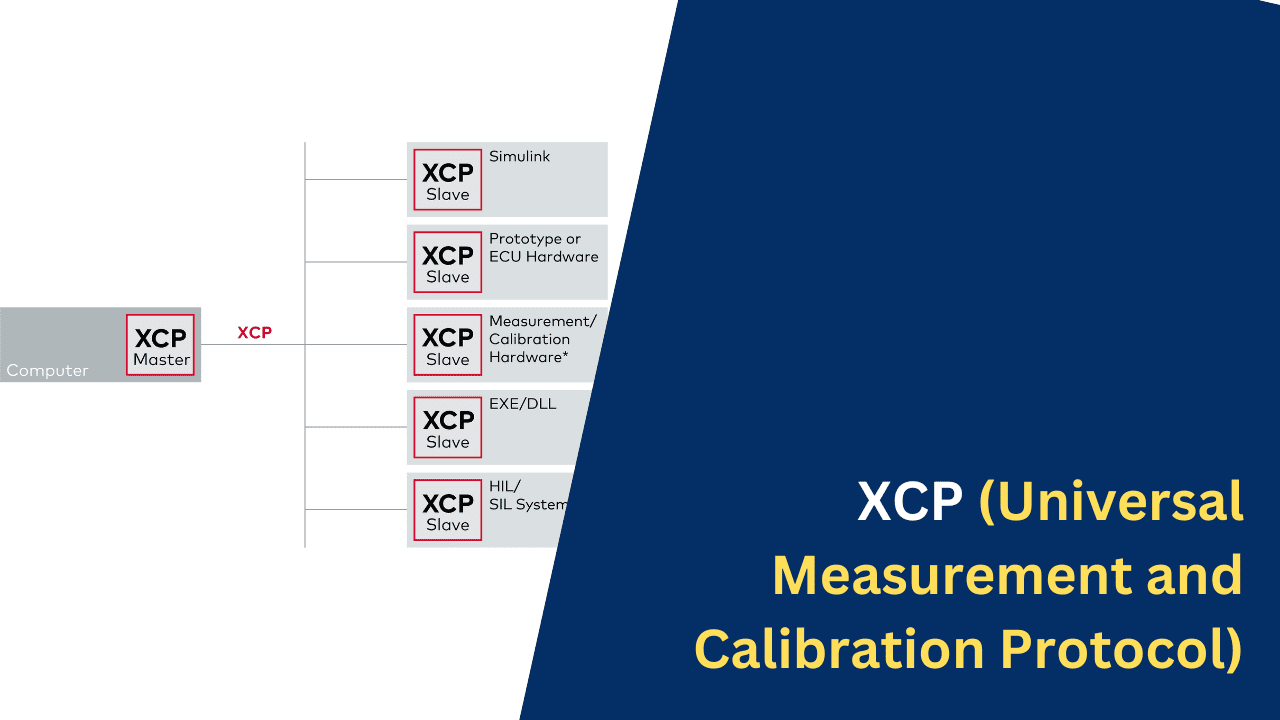
What is XCP (Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol)?
The Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol (XCP) is a standardized communication protocol used in the automotive industry for measuring and calibrating electronic control units (ECUs) in vehicles. ECUs are embedded systems responsible for controlling various functions within a vehicle, such as engine management, transmission control, and other critical systems.
XCP provides a standardized way for external tools, such as calibration and measurement devices, to communicate with and control ECUs during the development, testing, and calibration phases of vehicle development. It is designed to be efficient, allowing for high-speed data exchange between the calibration tool and the ECU.
Key features and aspects of XCP include:
- Measurement and Calibration: XCP facilitates the readout of measurement data from the ECU and the modification of calibration parameters within the ECU.
- High-Speed Communication: XCP is designed to provide high-speed communication between the calibration tool and the ECU. This is crucial for efficient calibration and testing processes.
- Flexibility: XCP is flexible and can be implemented over various communication transport layers, such as CAN (Controller Area Network), FlexRay, and Ethernet.
- Standardization: XCP is an open standard that is maintained by ASAM (Association for Standardization of Automation and Measuring Systems), an organization that develops and maintains standards for the automotive industry.
- Compatibility: XCP is widely adopted in the automotive industry, and many ECUs and calibration tools support the protocol. This ensures interoperability between different tools and ECUs from various manufacturers.
Introduction to XCP
- Purpose:
- XCP is primarily designed for the measurement and calibration of ECUs in vehicles.
- It facilitates the exchange of data between calibration tools and ECUs during development, testing, and calibration phases of automotive projects.
- Communication Speed:
- This speed is crucial for efficient calibration processes, as it enables quick adjustments to parameters and measurements.
- XCP is known for its high-speed communication capabilities, allowing rapid exchange of data between the calibration tool and the ECU.
- Flexibility:
- XCP is designed to be flexible and adaptable to various communication transport layers.
- It can be implemented over different networks, such as CAN (Controller Area Network), FlexRay, and Ethernet, making it versatile for use in different vehicle architectures.
- Data Measurement and Calibration:
- XCP supports the readout of measurement data from the ECU, allowing engineers to monitor various parameters in real-time.
- It also enables the modification of calibration parameters within the ECU, allowing for adjustments to optimize the performance of the vehicle.
- Standardization:
- XCP is an open standard maintained by ASAM (Association for Standardization of Automation and Measuring Systems), ensuring consistency and compatibility across different tools and ECUs.
- This standardization encourages interoperability and simplifies the integration of XCP into various automotive development environments.
- Widespread Adoption:
- XCP has gained widespread acceptance within the automotive industry, and many ECUs and calibration tools support the protocol.
- Its adoption by various manufacturers and suppliers promotes a common interface for communication, making it easier for developers to work with different systems.
Working of XCP
The Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol (XCP) operates as a standardized communication protocol between external tools, such as calibration and measurement devices, and electronic control units (ECUs) in vehicles. The working of XCP involves a set of commands and responses that allow for the exchange of measurement data and the calibration of parameters within the ECUs. Here is a simplified overview of how XCP works:
Initialization and Connection Establishment: The working of XCP begins with the initialization phase, where a connection is established between the calibration tool and the electronic control unit (ECU). During this phase, the calibration tool and the ECU negotiate communication parameters such as the communication transport layer (e.g., CAN, FlexRay, Ethernet) and other relevant settings. This ensures that both the calibration tool and the ECU are synchronized and ready for data exchange.
Data Acquisition and Measurement: Once the connection is established, the calibration tool can request real-time measurement data from the ECU. This data may include information about various parameters such as sensor readings, engine performance metrics, and other critical data relevant to the vehicle’s operation. XCP supports high-speed data transfer, allowing for efficient and rapid acquisition of real-time data.
Calibration Parameter Adjustment: XCP facilitates the modification of calibration parameters within the ECU. Calibration parameters are settings that influence the behavior of the vehicle’s electronic systems. The calibration tool can send commands to the ECU to adjust these parameters, enabling engineers to fine-tune and optimize the performance of the vehicle. This aspect of XCP is crucial for achieving optimal fuel efficiency, emissions control, and overall vehicle performance.
Command and Response Interaction: XCP communication involves a structured set of commands and responses. The calibration tool sends specific commands to the ECU, and the ECU responds accordingly. These commands are part of the XCP protocol and are standardized, ensuring a consistent and reliable communication interface. This command-response interaction allows for precise control and monitoring during the calibration and measurement processes.
Termination and Session Conclusion: Once the necessary measurement and calibration tasks are completed, the communication session between the calibration tool and the ECU can be terminated. This may occur when the calibration process is finished or when there is a need to switch to a different ECU or task. The termination phase ensures that resources are appropriately released, and the communication channel is closed, marking the conclusion of the XCP session.
Purpose of XCP
The purpose of the Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol (XCP) lies in providing a standardized and efficient means of communication between external tools and electronic control units (ECUs) in the automotive industry. XCP is specifically designed to address the challenges associated with measuring and calibrating the intricate electronic systems within vehicles. Its foremost purpose is to facilitate the exchange of data between calibration tools and ECUs during the various stages of vehicle development, testing, and calibration.
XCP serves as a vital tool in the calibration process, enabling engineers to adjust and fine-tune the parameters within ECUs. This calibration is essential for optimizing the performance of critical vehicle systems, including engine management, transmission control, and emission control. The standardized communication protocol ensures consistency across different tools and ECUs, allowing for interoperability and compatibility in an industry with diverse hardware and software components.
Another purpose of XCP is its high-speed communication capabilities. The protocol supports rapid data transfer between the calibration tool and the ECU, facilitating real-time measurement and quick adjustments to calibration parameters. This speed is crucial for efficient development processes, allowing engineers to make timely modifications and gather essential data for analysis.
Moreover, XCP’s flexibility across various communication transport layers, such as CAN, FlexRay, and Ethernet, enhances its utility in different vehicle architectures. The protocol’s open standardization, maintained by the Association for Standardization of Automation and Measuring Systems (ASAM), ensures that XCP implementations are widely adopted and consistently applied across the automotive industry.
- XCP enables the exchange of measurement data between calibration tools and ECUs in real time. This allows engineers and developers to monitor various parameters and performance metrics within the vehicle.
- Support for Various ECUs:
- XCP is widely supported in the automotive industry, making it compatible with a broad range of ECUs from different suppliers. This widespread adoption allows developers to use common tools and protocols across various vehicle platforms.
- Facilitation of Development Processes:
- By providing a standardized communication protocol, XCP simplifies the development processes related to calibration and measurement tasks. This leads to more efficient workflows and a streamlined development cycle for automotive engineers.
Applications
XCP (Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol) is widely utilized in the automotive industry for a variety of applications related to the development, testing, and calibration of electronic control units (ECUs) in vehicles. Some key applications of XCP include:
- ECU Calibration:
- XCP is primarily designed for calibrating electronic control units. It allows engineers to adjust and fine-tune parameters within the ECU to optimize the performance of various vehicle systems, such as engine control, transmission, and emission control.
- Real-time Measurement and Data Logging:
- XCP enables real-time measurement and data logging from ECUs. This functionality is crucial for monitoring and analyzing parameters like sensor readings, engine performance metrics, and other relevant data during vehicle development and testing.
- Powertrain Optimization:
- XCP is commonly applied in the calibration and optimization of powertrain systems, including engine management. It allows for adjustments to parameters related to fuel injection, ignition timing, and other factors to enhance fuel efficiency, performance, and emissions.
- Functional Testing:
- XCP supports functional testing of ECUs, allowing engineers to interact with the ECU and assess its response to various inputs and scenarios. This is essential for verifying that the ECU functions correctly under different operating conditions.
- Embedded System Development:
- XCP facilitates the development of embedded systems within vehicles by providing a standardized communication protocol. As vehicles incorporate increasingly sophisticated electronic systems, XCP helps ensure efficient communication between calibration tools and ECUs.
- Prototype Validation:
- During the prototyping phase, XCP is utilized to validate the functionality and performance of ECUs. Engineers can make real-time adjustments to calibration parameters based on testing results, contributing to the refinement of vehicle systems.
- Manufacturing and Production Testing:
- XCP may be applied in manufacturing environments for production testing of ECUs. This helps ensure that the ECUs meet specified performance criteria before they are integrated into vehicles during the production process.
- Diagnostics and Debugging:
- XCP assists in diagnosing issues and debugging electronic systems in vehicles. Engineers can use the protocol to interact with ECUs, retrieve diagnostic information, and make adjustments to identify and address problems.
- Flexibility Across Communication Networks:
- XCP’s flexibility to operate over various communication transport layers, such as CAN, FlexRay, and Ethernet, makes it suitable for different vehicle architectures and communication networks.
- Integration with Simulation Environments:
- XCP is often integrated into simulation environments, allowing engineers to perform virtual testing and calibration before physical prototypes are available. This accelerates the development process and reduces the need for extensive physical testing.
In summary, XCP is a standardized protocol that plays a crucial role in the calibration and measurement of ECUs in the automotive industry, providing a common interface for communication between external tools and electronic control units.
This was about “What is XCP (Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol)?“. Thank you for reading.
Also, read.
- 1000+ Automotive Interview Questions With Answers
- RTOS In The Automotive Industry: The Brains Behind Real-Time Vehicle Control
- High Performance Computers in Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs): Architecture, Challenges, and Future Trends
- Automotive HPC Wars: The Race To Power Software-Defined Vehicles
- Why The Automotive Industry Is Down: No Automotive Jobs and When Will It Become Normal Again?