What Is A Stepper Motor, Working Principle, Types, Advantages
Hello guys, welcome back to my blog. In this article, I will discuss what is a stepper motor, the working principle of the stepper motor, its types, advantages, and disadvantages of the stepper motor.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics And Chetan Shidling.
Also, read:
- What Is Electrolyzer, Type, Working, Cost Of Electrolyzer
- Types Of Hydrogen Storage That Can Be Used In The Future
- Battery C Rate Online Calculator With Time Calculation
What Is A Stepper Motor
Introduction
- This is the special type of DC motor, that converts input digital Pulses into mechanical shaft rotation.
- It converts a train of Input pulses (square wave pulses ) into a precisely defined increment in the shaft position.
- Every pulse of a square wave moves the shaft of the stepper motor through a fixed angle.
- The movement of the step may be angular or linear. There will be a one-one relation between input pulses And step movement.
- Each and every pulse which is supplied to the motor as input actuates one step movement of the shaft.
- The shaft rotates at some angle. The angle at which the shaft rotates for every pulse is known as the step angle. That will be expressed in degrees. E.g.( 7.5° ). This angle will depend on the number of square wave pulses. This type of system is used to control the position. That’s why this is also called a position control system.
- The average speed of the motor is directly proportional to the rate at which the input pulse is delivered. If the rate is low, then the motor rotates in steps. If the rate of pulses is high, then the motor rotates smoothly like DC motors. This is due to wear and tear i.e. Friction. Due to this property stepper motor can also be used in speed control systems.
- The stepper motors are manufactured with steps of 12,24,72,144,180,200 with an angle of 30, 15, 5, 2.5, 2, 1.8.
- We can operate a stepper motor with or without feedback control.
Working Principle Of Stepper Motor
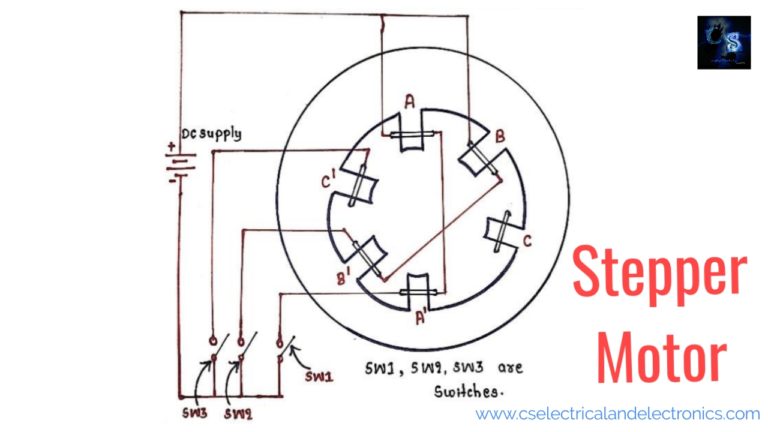
- The stepper motor works on the principle of Electromagnetism. It consists of two main parts i.e., Rotor and Stator.
- For the rotor, we can use a permanent magnet or soft iron and the stator part will be surrounded by electromagnetic stators.
- If we give a voltage at terminals, the rotor tries to align with the stator.
Here I would like to take a stepper motor which consists of 4 pole rotor construction. i.e. rotor is having 4 salient poles without any exciting winding.
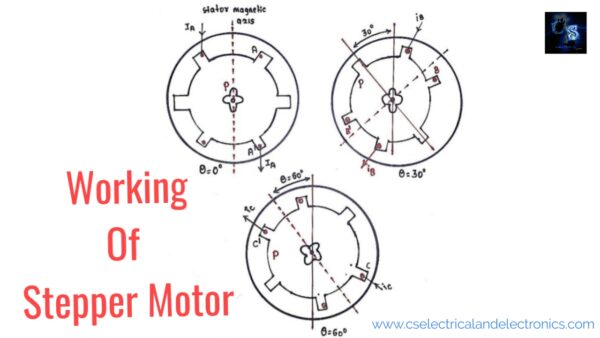
Stages In Stepper Motor
When we excite AA’ phase by keeping the SW1 switch as close, then the stator magnetic axis aligns along the poles formed due to AA’ ( vertical ). Then the rotor tries to adjust itself in a minimum reluctance position i.e. matching its own axis which passes through the two poles exactly with the stator magnetic axis.
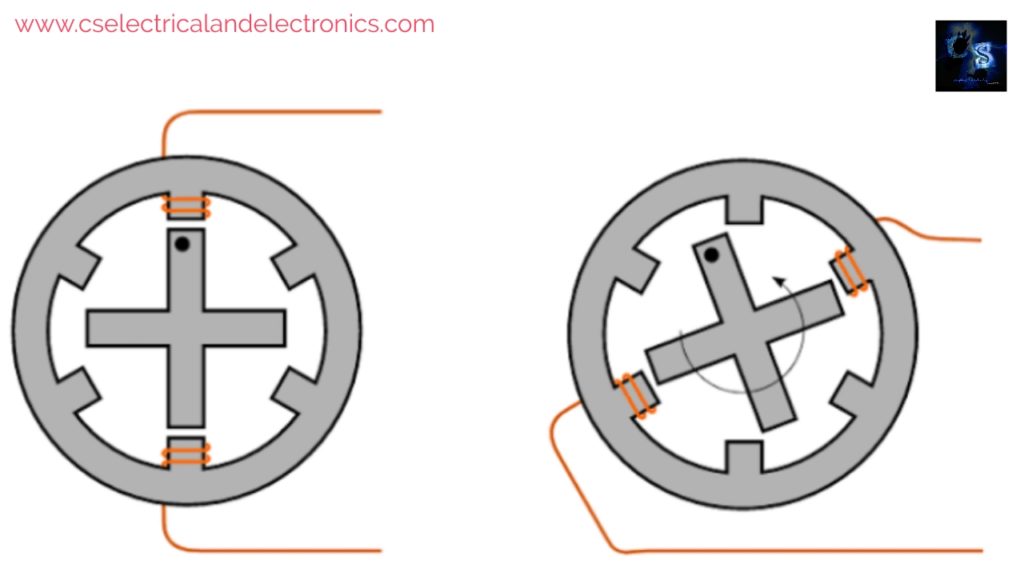
Then next when we excite phase BB’ by keeping the SW2 switch closed and AA’ phase de-energized by keeping the SW1 switch open. Now the stator magnetic axis shifts towards the pole which is formed by BB’. Then again rotor tries to align with minimum reluctance & it will turn by a 30° step angle in an anti-clockwise direction. The axis passing along two diagonally opposite poles of the rotor will match with the stator magnetic axis. Point P will be the new position of minimum reluctance.
Then next when we excite phase CC’ by keeping the SW3 switch closed and AA’ and BB’ phases are de-energized by keeping SW1 & SW2 switches open. Now the stator magnetic axis shifts towards the poles formed due to CC’. Then the rotor tries to align with minimum reluctance & it will turn by a 60° step angle in an anti-clockwise direction.
After exciting the three phases, the motor takes 12 steps to complete one full revolution.
Types Of Stepper Motor
- Variable reluctance stepper motor.
- Permanent magnet stepper motors.
- Hybrid stepper motors.
Comparison between the variable reluctance stepper motor and permanent magnet stepper motor
Variable reluctance motor
- The rotor part is not magnetized.
- The step angle is small.
- It will not be having detent torque.
- Salient rotor.
- A dynamic response will be faster.
- The acceleration rate will be high.
- The torque inertia ratio is low.
Permanent magnet stepper motor
- Having a magnetized rotor part.
- Step angles are of range 30 to 90 degrees.
- It will be having detent torque.
- Cylindrical rotor.
- A dynamic response will be slow.
- The acceleration rate will be slow.
- The torque inertia ratio is high.
Advantages And Applications Of The Stepper Motor
- Used in X-Y plotters.
- It is used in a floppy disk drive.
- In machine tools.
- Used in the process control system.
- Also, used in robotics.
- It is used in printers.
- Used in tape drives and a variety of other industrial applications.
Disadvantages Of Stepper Motor
- It’s having low efficiency.
- Torque drops rapidly with speed.
- Having low output power for size.
- Missing feedback to indicate missed steps.
- Heat experience in high-performance configurations.
- Low accuracy at full load.
I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents
- Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
- Top 100 Automotive Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
- How Renewable Energy Is Transforming Electrical Engineering
- Exploring Electric Vehicles: Technology and Challenges
- The Future of Power Systems: Smart Grids
- What is XCP (Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol)? Introduction, Working, Purpose, Applications
- What Is SIL Testing, Software-In Loop, Working, Purpose
Author Profile
- Chetu
- Interest's ~ Engineering | Entrepreneurship | Politics | History | Travelling | Content Writing | Technology | Cooking
Latest entries
 All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents
All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry
All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose,
All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose, All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers