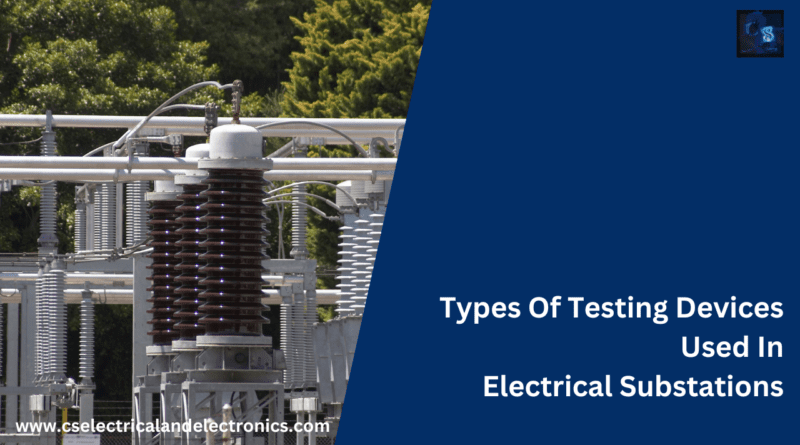
Types Of Testing Devices Used In Electrical Substations
Hello guys, welcome back to our blog. Here in this article, we will discuss the types of testing devices used in electrical substations, why these devices are needed, and the purpose of each device in an electrical substation.
If you have any electrical, electronics, and computer science doubts, then ask questions. You can also catch me on Instagram – CS Electrical & Electronics.
Also, read the following:
- How To Convert A Website Into Android App Using Android Studio
- Top 50+ Different Types Of ECU Used In Heavy Vehicles, Buses
- Best Programming Languages For Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Types Of Testing Devices Used In Electrical Substations
The backbone of the power grid is made up of electrical substations, which serve as crucial nodes for transmitting, converting, and distributing electricity to final users. These vital facilities are in charge of making sure electrical energy is delivered from multiple points of consumption in a secure and effective manner. Substations house a variety of highly advanced electrical devices and systems, thus maintaining and operating them properly is crucial to achieving this. Comprehensive testing and inspection utilizing specialized tools are crucial for ensuring the dependability and safety of substations.
Testing tools serve a crucial role in ensuring the continued flow of power and protecting the infrastructure from potential failures by diagnosing faults, evaluating the effectiveness of protective devices, and monitoring essential electrical characteristics. In this situation, utilizing cutting-edge testing tools and equipment is not just a best practice but also a crucial requirement in the world of electrical substations.
Electrical substations struggle more and more to provide consumers with dependable power as electricity demand rises. To keep the system stable and avoid cascading failures that could cause massive blackouts, substations must operate flawlessly. A thorough testing and maintenance strategy is necessary to guarantee the reliability of these crucial facilities. This strategy calls for the use of state-of-the-art testing equipment created especially for the special needs of electrical substations.
These testing instruments serve as the watchdogs of substation effectiveness and safety, monitoring everything from the insulation integrity of transformers to the analysis of power quality and the performance of protective relays. Power utilities and engineers may proactively address possible faults, optimize system performance, and uphold the highest standards of electrical grid dependability by instituting frequent testing processes and utilizing the capabilities of these instruments.
Typical testing equipment found in electrical substations includes the following:
01. Digital Multimeter (DMM):
An essential tool for electrical substations is the digital multimeter or DMM for short. It is a multifunctional tool that enables specialists to precisely measure a range of electrical properties. The DMM, which can measure voltage, current, resistance, and continuity, is essential for routine inspections and troubleshooting duties.
It is used by technicians to spot potential issues, check for appropriate voltage levels, and guarantee the integrity of electrical connections. In order to maintain the efficient and secure operation of the electrical substations, it is a useful instrument for both fieldwork and laboratory testing because of its small size and user-friendly interface.
02. Insulation Resistance Tester (Megger):
Meggers, also referred to as insulation resistance testers, are essential for evaluating the insulation in electrical equipment at substations. Technicians can identify any degradation or disintegration of insulation that can result in dangerous system flaws or inefficiencies by measuring the insulation resistance. Transformers, cables, motors, and other high-voltage equipment are regularly tested with mergers.
Substations can proactively handle maintenance requirements, avert breakdowns, and improve the overall dependability of the electrical network by identifying potential insulation problems. Regular usage of the Megger is essential to ensuring the equipment’s longevity and safety and reducing the possibility of electrical breakdowns.
03. Power Quality Analyzer:
The Power Quality Analyzer is the tool created to achieve this goal. Maintaining excellent power quality is crucial for the modern electrical system. Technicians can use this device to track and examine a variety of power metrics, such as voltage, current, frequency, harmonics, and power factor. Substations can identify and address problems such as voltage fluctuations, harmonic distortions, and low power factor, which can cause equipment failure or inefficient use of power, by evaluating the quality of the electricity.
Engineers can optimize the electrical network’s performance, enhance efficiency, and minimize energy waste with the comprehensive data offered by the Power Quality Analyzer, which will ultimately lead to cost savings and a more sustainable power grid.
04. Circuit Breaker Analyzer:
In electrical substations, circuit breakers play a crucial role as safety equipment by guarding against overloads and failures. The Circuit Breaker Analyzer is used to make sure they are operating properly. The timing, insulation integrity, and contact performance of the circuit breakers can all be evaluated by technicians using this equipment.
By carrying out these tests on a regular basis, substations can ensure that the circuit breakers react to fault circumstances quickly and accurately, reducing the risk of equipment damage and boosting the dependability of the overall power network. Additionally, the Circuit Breaker Analyzer helps substations anticipate maintenance requirements, enabling them to make repairs or replacements in a timely manner, minimizing downtime, and guaranteeing a reliable and secure electrical infrastructure.
05. Transformer Turns Ratio (TTR) Tester:
Transformers are a key component of electrical substations, and effective power distribution depends on them functioning properly. An essential piece of equipment for precisely measuring the turns ratio of power and distribution transformers is the transformer turns ratio (TTR) tester. The primary to the secondary turns ratio of the transformer can be checked by technicians to check for any winding problems that might be affecting the transformer’s performance.
In order to prevent potentially catastrophic failures and ensure the longevity of the transformers, substations can take remedial action, such as repairs or replacements, as soon as these issues are identified. A crucial component of transformer maintenance that promotes a reliable and resilient electrical system is the use of the TTR Tester.
06. Digital Clamp Meter:
A flexible and practical tool for non-intrusive current measurements at electrical substations is the digital clamp meter. The clamp meter can easily “clamp” around a conductor to measure the current flowing through it, unlike conventional multimeters, which need to break the circuit to measure current. Due to this characteristic, it is incredibly useful for real-time current monitoring and fault diagnosis without affecting the power supply or putting workers in danger.
The clamp meter is particularly helpful for measuring AC and DC currents in cables, conductors, and equipment in substations. This enables personnel to spot aberrant current levels and solve electrical problems efficiently. It is a crucial instrument for routine maintenance and fault diagnosis in electrical substations due to its portability and simplicity of use.
07. Protective Relay Test Set:
In substations, protective relays act as the first line of defense against electrical problems and potential dangers. The Protective Relay Test Set is utilized for testing and calibration in order to guarantee its dependability. Using this tool, professionals can create numerous failure scenarios and check whether the protective relays react adequately to them.
Substations may make sure that their protective schemes are effective, enabling quick and accurate fault clearance, minimizing equipment damage, and improving overall grid stability by checking the accuracy and reaction times of the relays. In order to preserve the substation’s security and safeguard it from electrical faults and system disturbances, regular testing with the Protective Relay Test Set is essential.
08. Primary Injection Test Set:
Specialized equipment called the Primary Injection Test Set is used in electrical substations to test the primary side of current transformers (CTs). Technicians can test the CT’s efficiency and accuracy in converting primary current to secondary current by producing large currents on the primary side. For the electrical system to be properly protected and metered, accurate CT performance is essential.
With the help of the Primary Injection Test Set, substations can spot any CT failures or performance deviations from the norm and take corrective action, including calibration or replacement. Substations can maintain dependable protection and measurement capabilities and improve the overall effectiveness and safety of the electrical network by assuring the accuracy of CTs.
09. Secondary Injection Test Set:
An essential tool for evaluating the effectiveness of protective relays in electrical substations is the Secondary Injection Test Set. The technicians can check to see if the protective relays respond effectively and start the necessary protection measures by using this device to simulate fault situations on the secondary side of the relays.
Protective relays must operate correctly in order to identify and isolate problems quickly, prevent equipment damage, and guarantee a steady electrical grid. In order to maintain a high degree of safety and operational integrity, substations can use the Secondary Injection Test Set to test the precision and dependability of their protective relay systems.
10. Oscilloscope:
An electronic device called an oscilloscope is used in electrical substations to view and examine electrical waveforms. Its graphical display makes it a great tool for diagnosing transient occurrences, analyzing waveforms, and finding anomalies or distortions in the electrical system since it enables professionals to look at the voltage and current signals in real-time.
Oscilloscopes are very helpful for analyzing irregular signal behaviors and intermittent errors that are difficult to detect with conventional multimeters. The oscilloscope helps technicians understand the electrical behavior of equipment and enhances system performance and stability by giving thorough waveform data.
11. Thermal Imaging Camera:
A potent instrument for identifying and examining temperature differences in electrical equipment inside substations is the thermal imaging camera. The camera can provide visual images that depict temperature distributions by catching infrared radiation. With this capacity, professionals can see hotspots or unusual heat patterns in electrical components that could be signs of problems or breakdowns.
Early identification of these abnormalities enables substations to proactively resolve possible issues, minimizing equipment damage and unanticipated outages. When evaluating high-voltage equipment, such as transformers and switchgear, where overheating may be a sign of underlying issues, the thermal imaging camera is extremely useful.
12. Dielectric Strength Tester:
Providing electrical insulation and ensuring the equipment operates effectively, insulating oils and other dielectric fluids are essential parts of some electrical equipment. To ascertain the dielectric strength or insulating qualities of these fluids, a specialized instrument called the Dielectric Strength Tester is used. The tester determines the voltage at which the fluid degrades and conducts electricity by subjecting it to high-voltage electrical stress. This breakdown voltage is a crucial indicator of the dielectric fluid’s condition.
The insulating fluid can get contaminated or degrade over time, which can diminish insulation effectiveness and increase the risk of equipment failure. Regular testing with the Dielectric Strength Tester helps identify these issues. The overall dependability and safety of the electrical equipment inside the substation depend on maintaining the dielectric strength of insulating fluids.
13. Voltage Detector/Pen:
The Voltage Detector or Voltage Pen is a crucial piece of equipment to protect the safety of workers working in and around live electrical systems since safety is of the utmost importance in electrical substations. A non-contact gadget called a voltage detector can be used to check for voltage without coming into touch with live conductors. The voltage pen emits visual or auditory alarms to indicate the presence of voltage when it is brought close to an energized conductor.
This aids technicians in spotting potentially dangerous circumstances and preventing unintentional contact with live electrical components. Voltage detectors are particularly useful when performing maintenance work and troubleshooting since they give an extra degree of security and reduce the possibility of electric shock or other harm.
In conclusion, these testing instruments are essential for making sure electrical substations are secure, dependable, and performing at their best. Each instrument has a distinct function in preserving the integrity of the power grid, from measuring fundamental electrical properties to identifying potential defects and anomalies. The efficient operation of electrical substations and protection of the electrical system from potential risks and downtime is made possible by the regular use of these tools in conjunction with correct maintenance procedures.
This was about “Types Of Testing Devices Used In Electrical Substations“. I hope this article may help you all a lot. Thank you for reading.
Also, read:
- 10 Tips To Maintain Battery For Long Life, Battery Maintainance
- 10 Tips To Save Electricity Bills, Save Money By Saving Electricity
- 100 (AI) Artificial Intelligence Applications In The Automotive Industry
- 100 + Electrical Engineering Projects For Students, Engineers
- 1000+ Control System Quiz, Top MCQ On Control System
- 1000+ Electrical Machines Quiz, Top MCQs On Electrical Machines
- 1000+ MATLAB Simulink Projects For MTech, Engineering Students
- 50 Tips To Save Electricity At Home, Shop, Industry, Office
Author Profile
- Chetu
- Interest's ~ Engineering | Entrepreneurship | Politics | History | Travelling | Content Writing | Technology | Cooking
Latest entries
 All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents
All PostsApril 29, 2024Top 11 Free Courses On Battery For Engineers With Documents All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry
All PostsApril 19, 2024What Is Vector CANoe Tool, Why It Is Used In The Automotive Industry All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose,
All PostsApril 13, 2024What Is TCM, Transmission Control Module, Working, Purpose, All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers
All PostsApril 12, 2024Top 100 HiL hardware in loop Interview Questions With Answers For Engineers